This document provides descriptions of various ECG patterns and cardiac conditions:
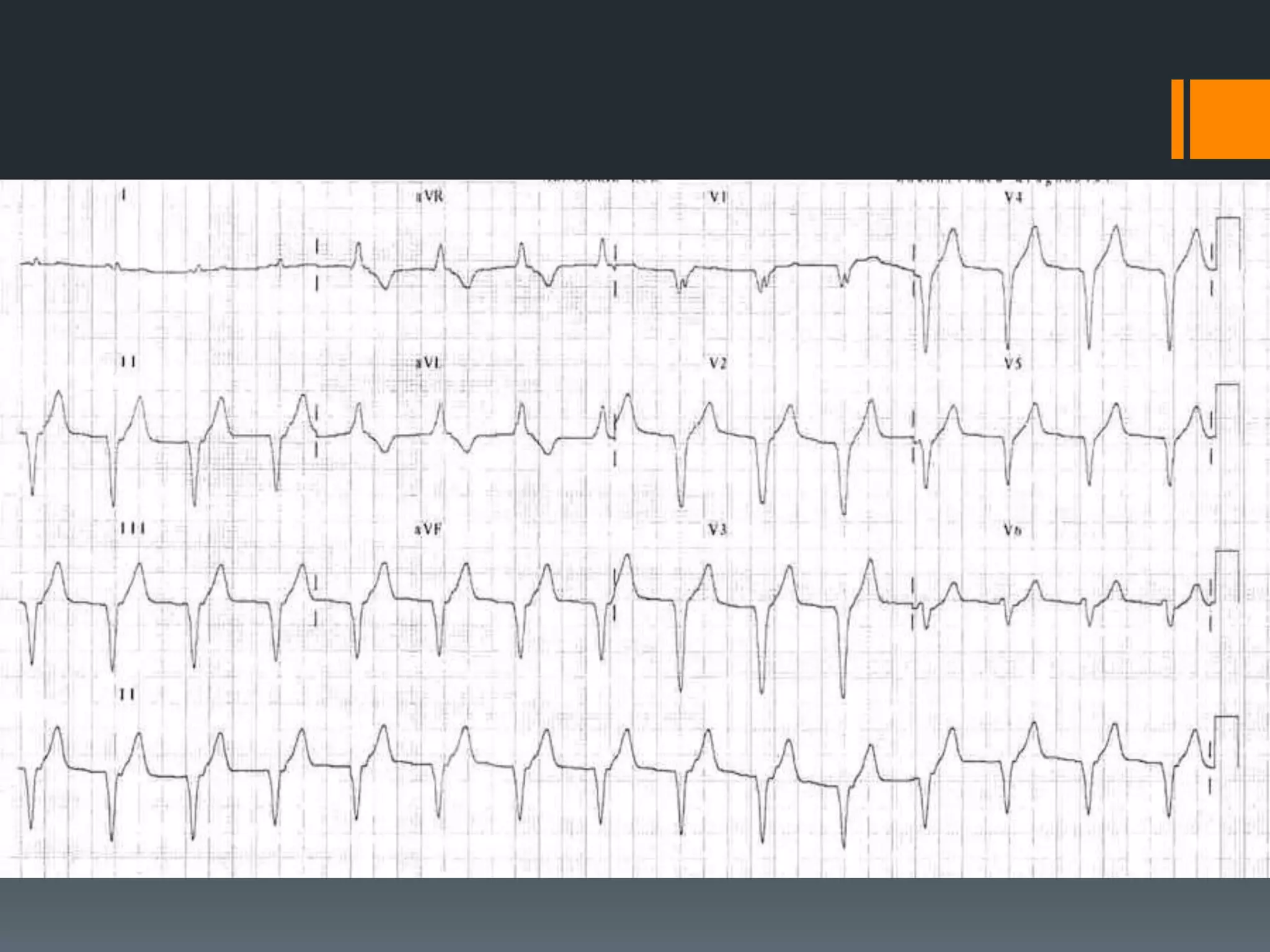
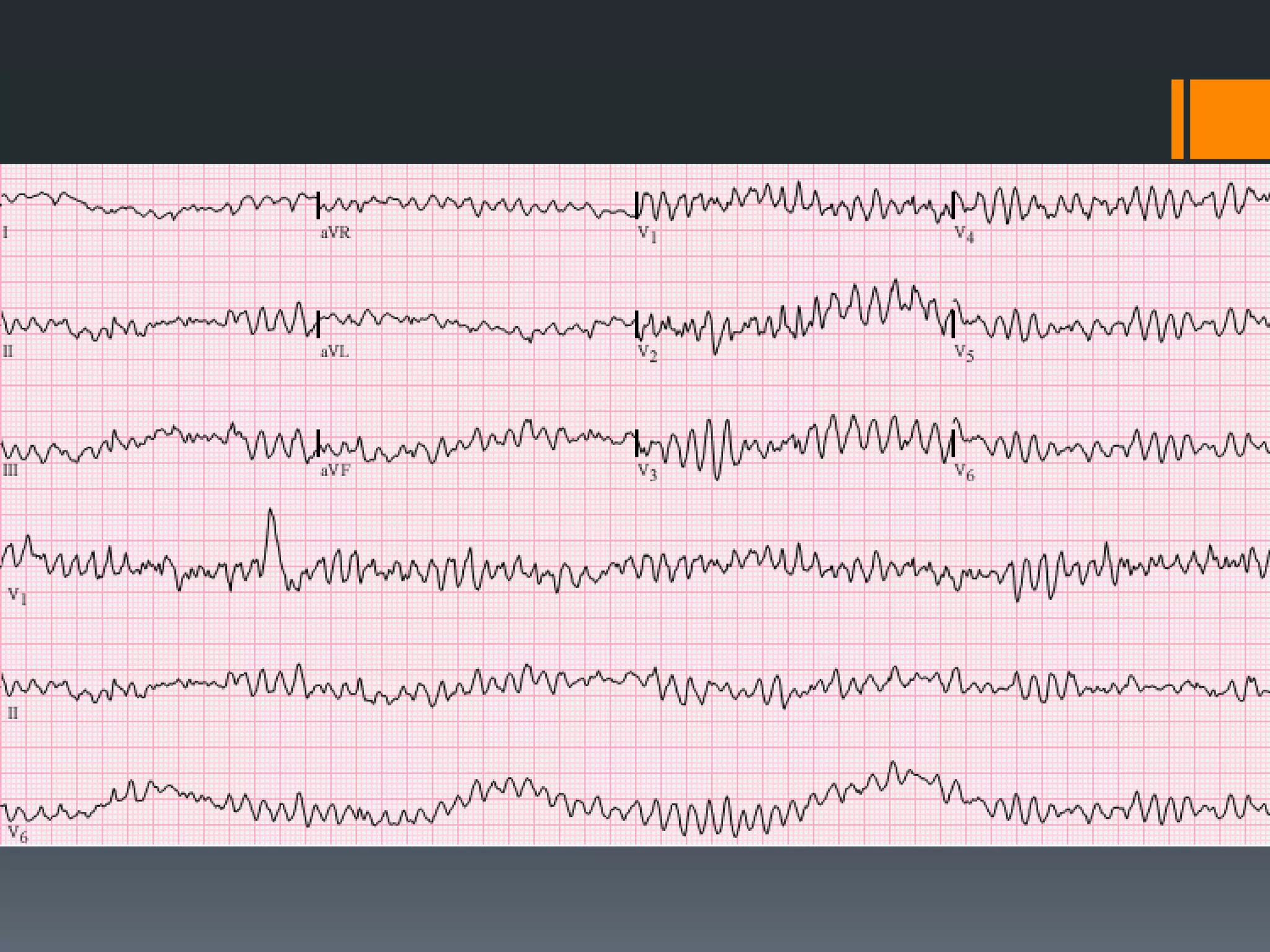
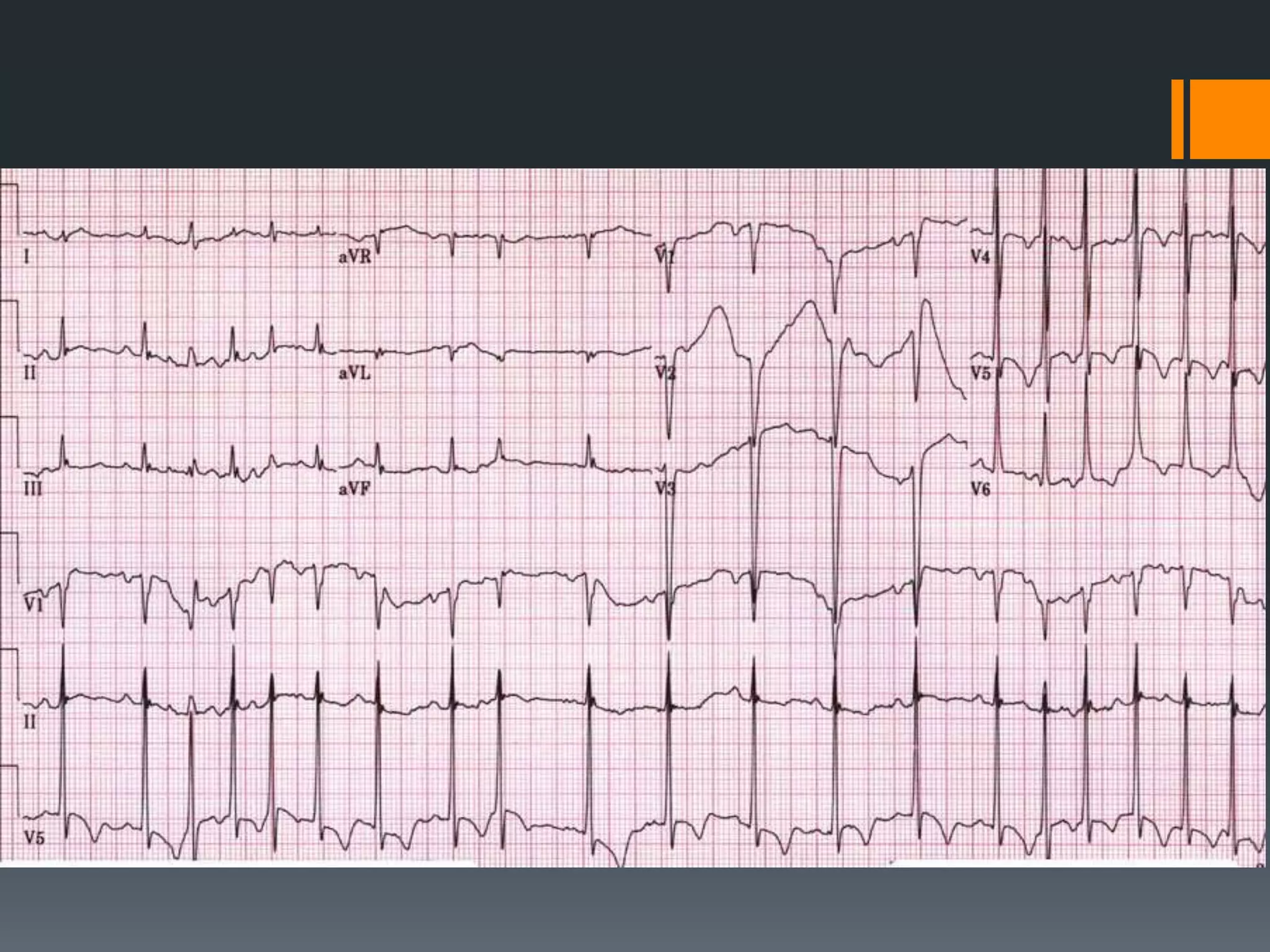
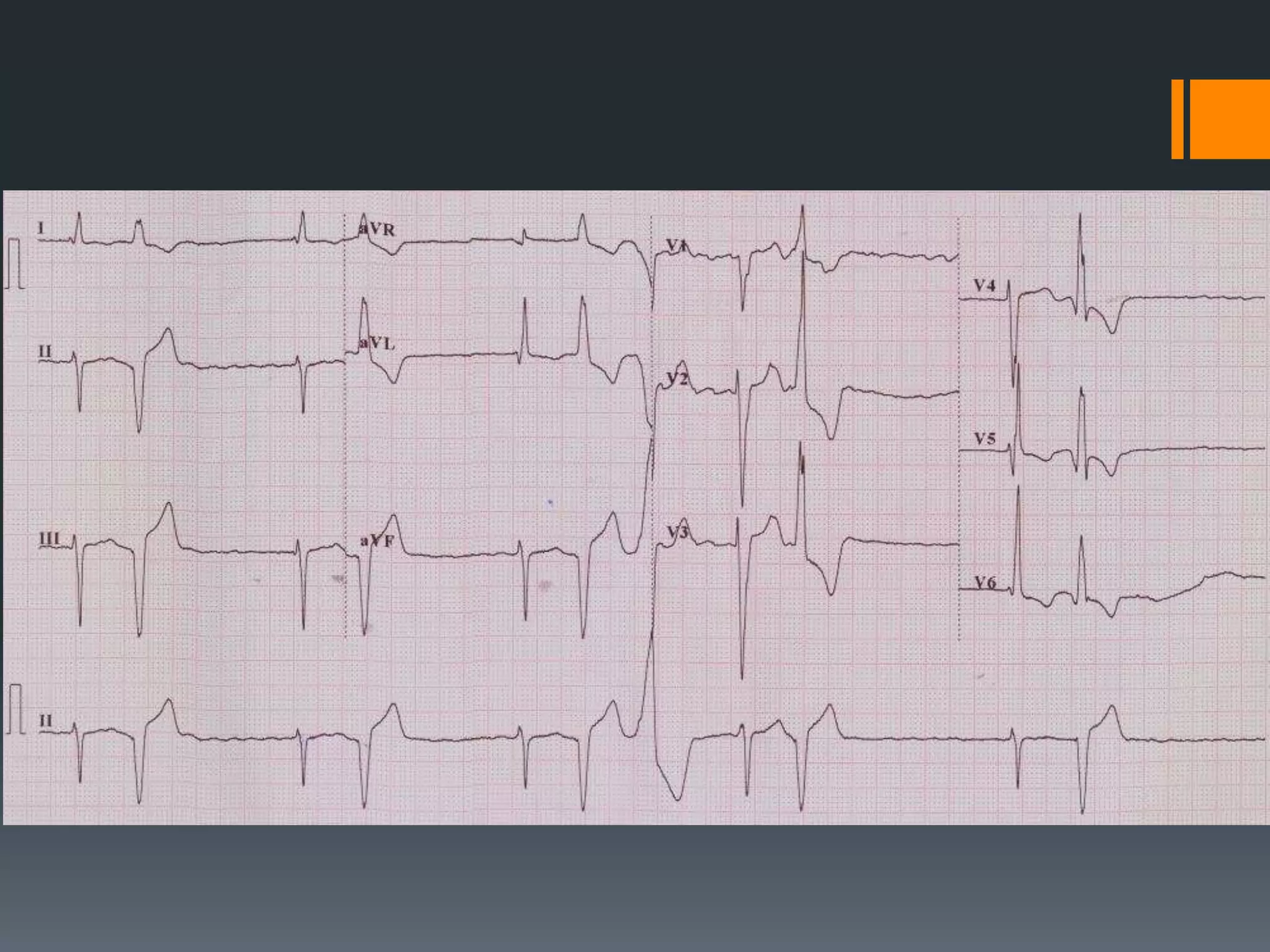
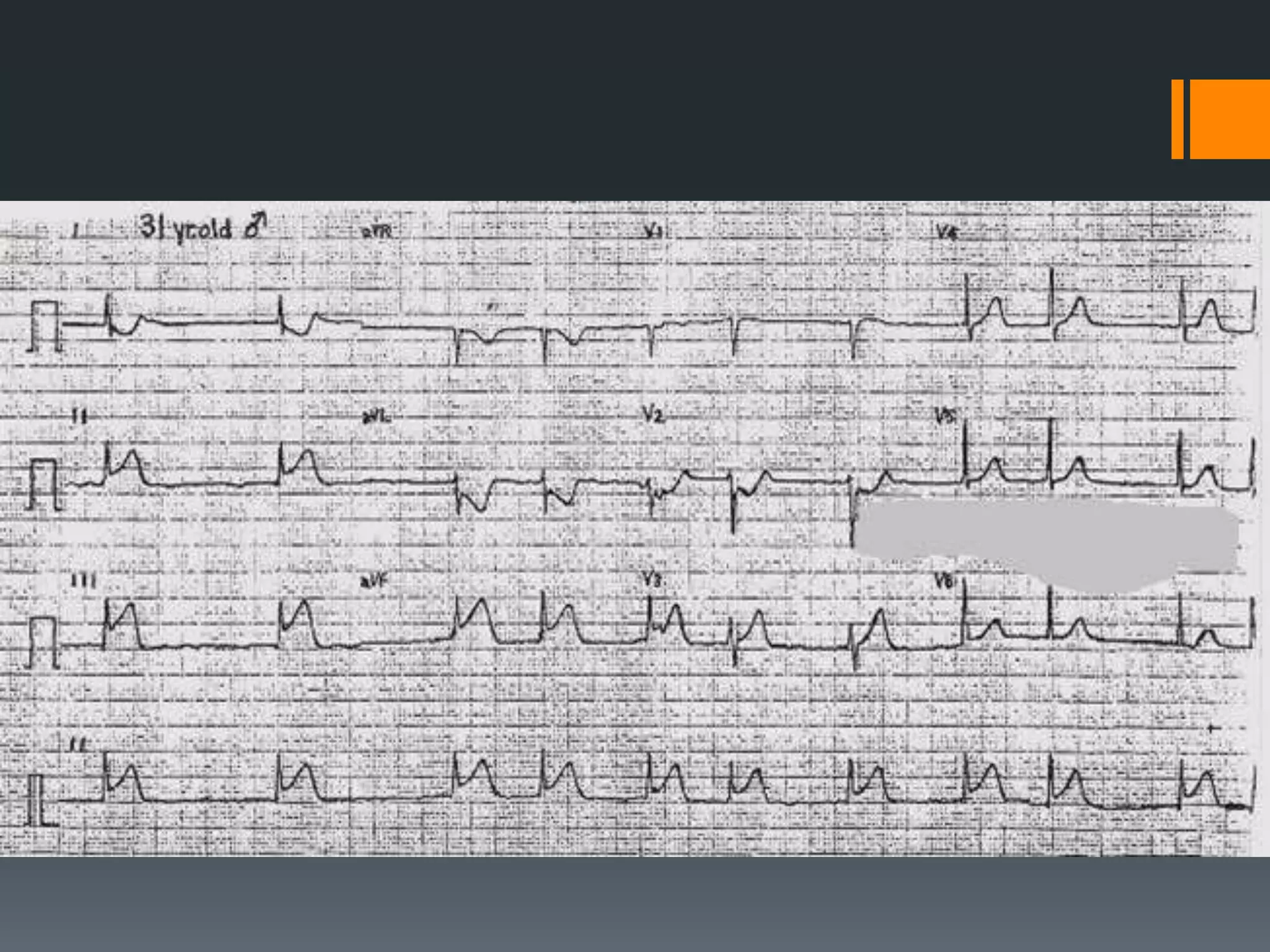
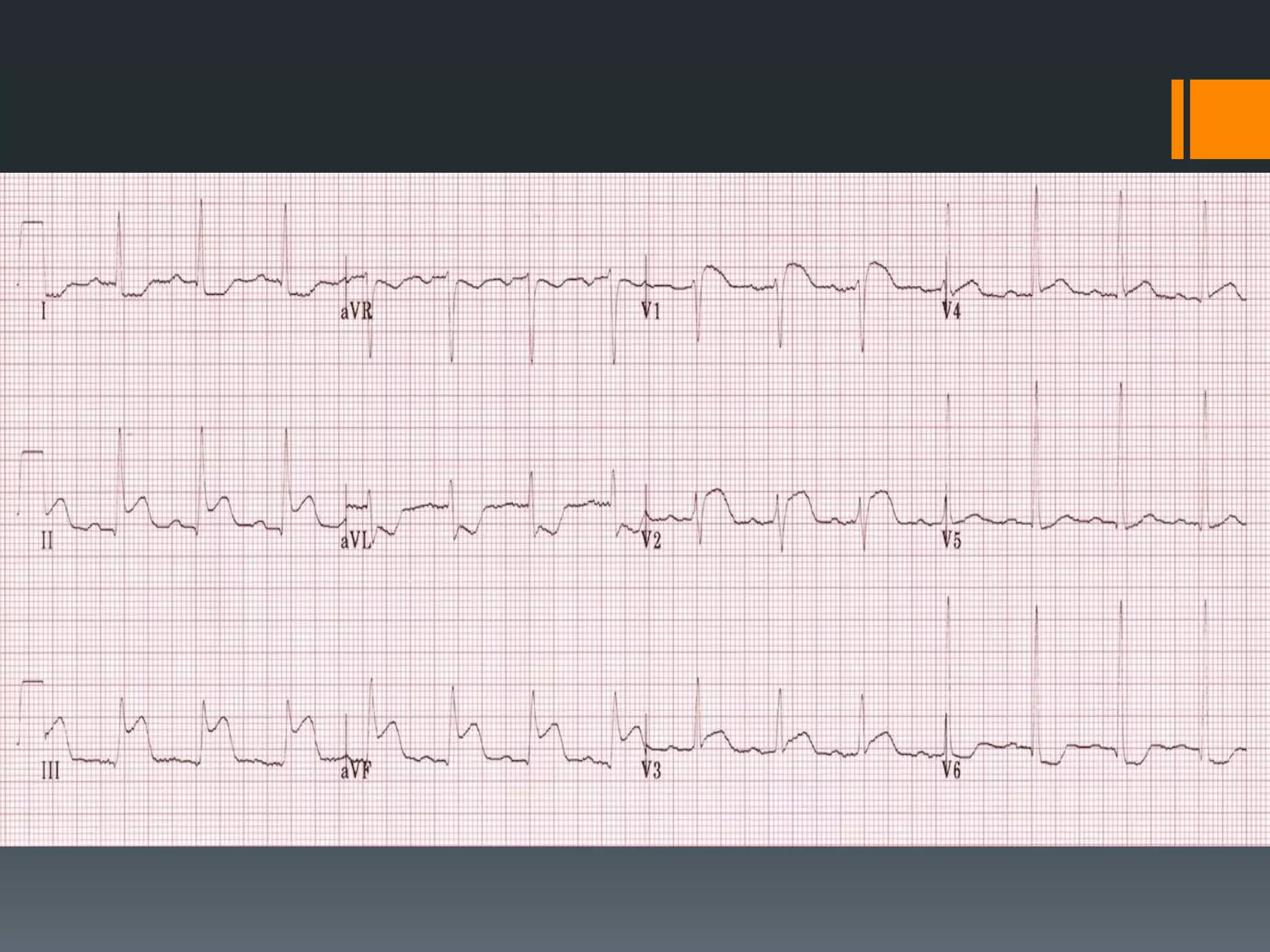
- It describes limb lead reversal showing a sine wave pattern typical of hyperkalemia. Calcium gluconate and other treatments are recommended.
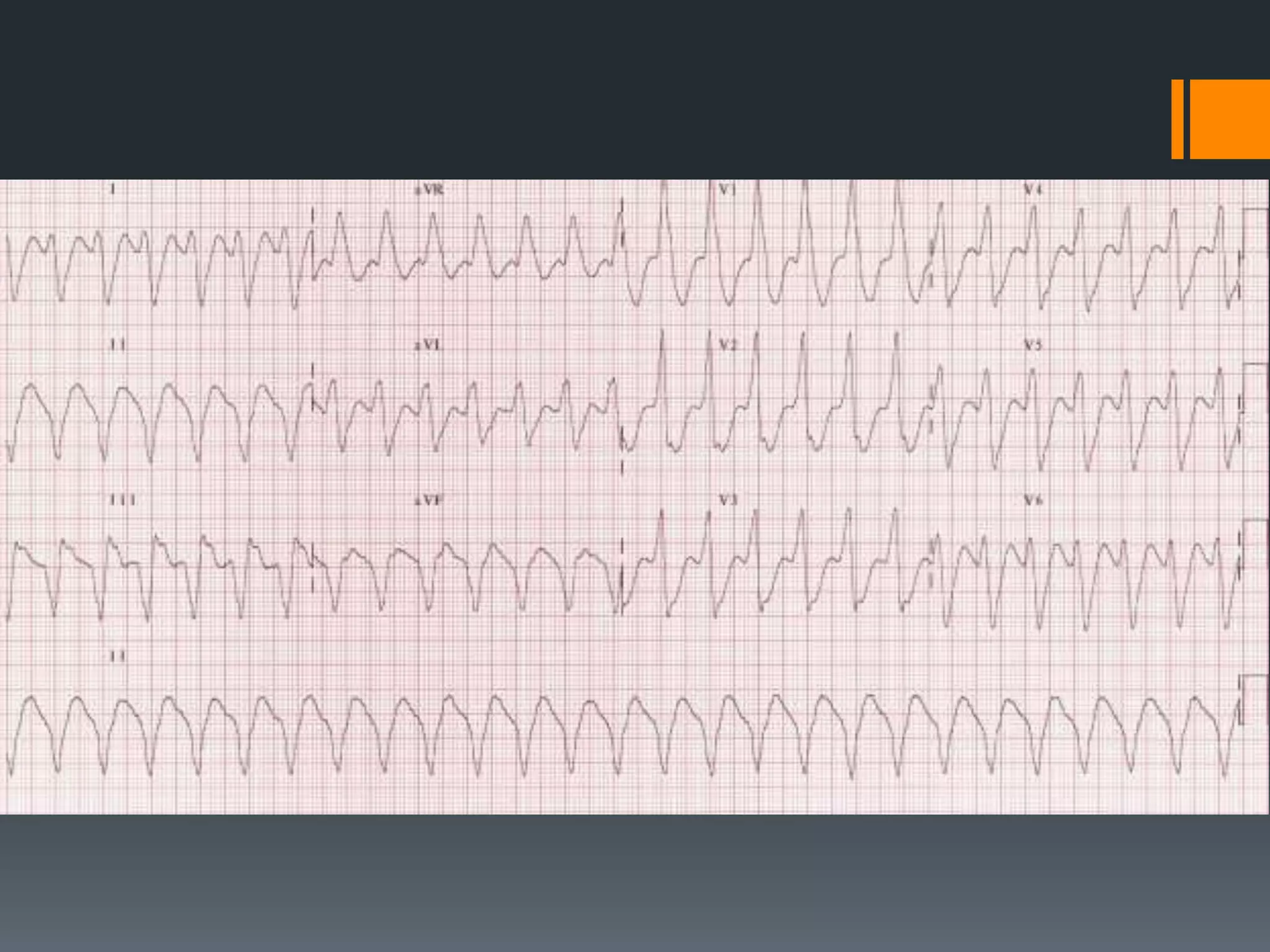
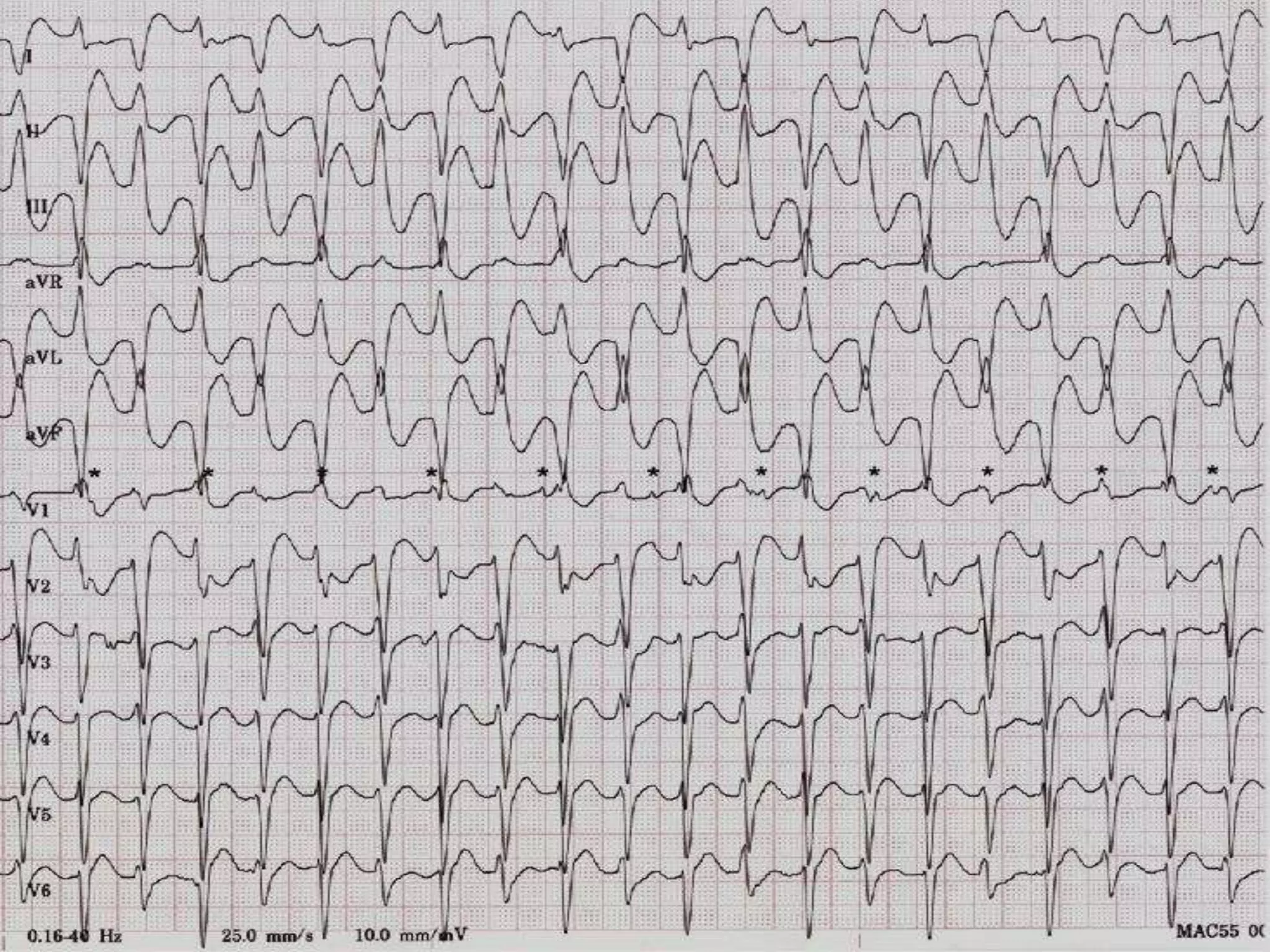
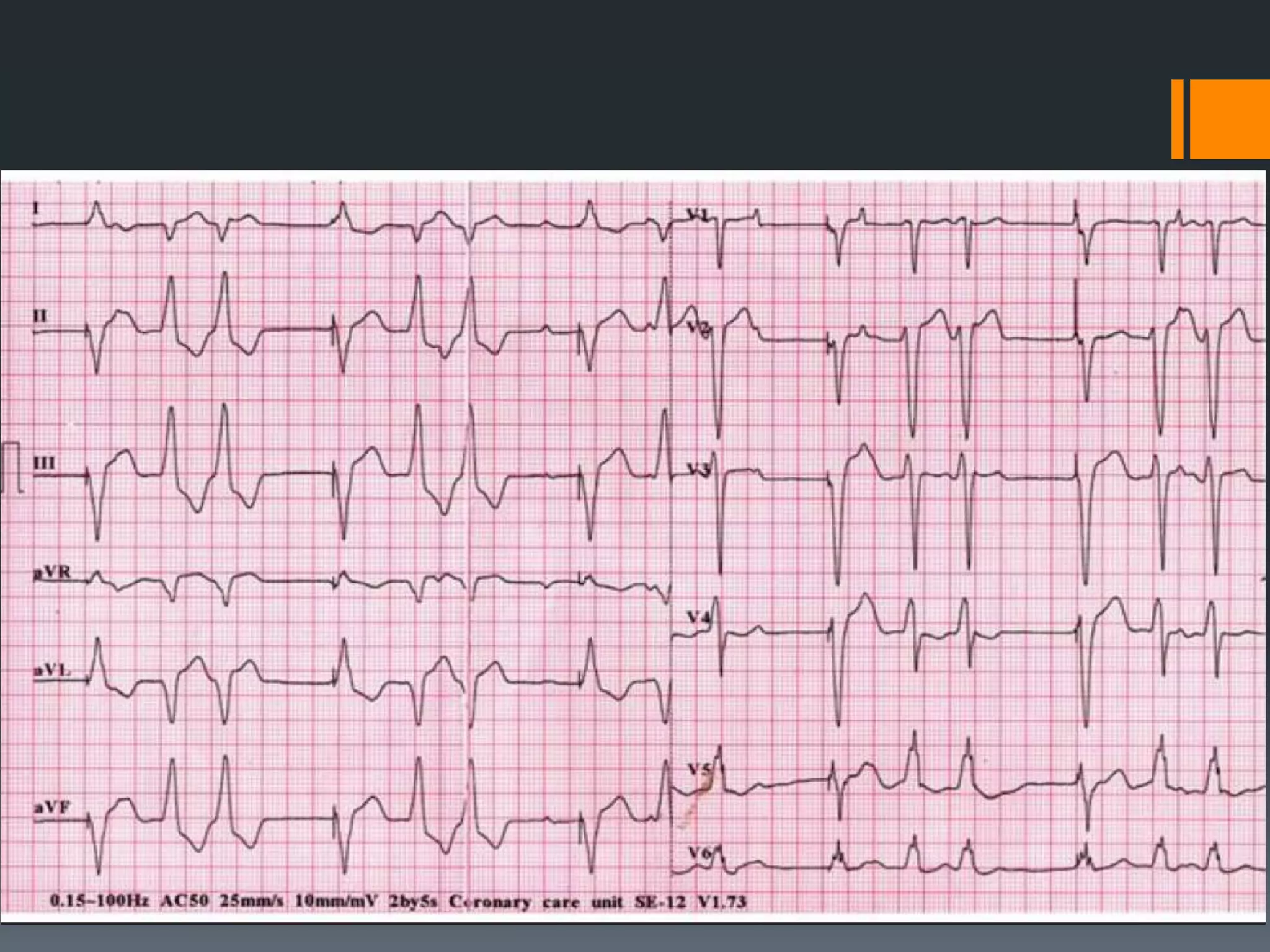
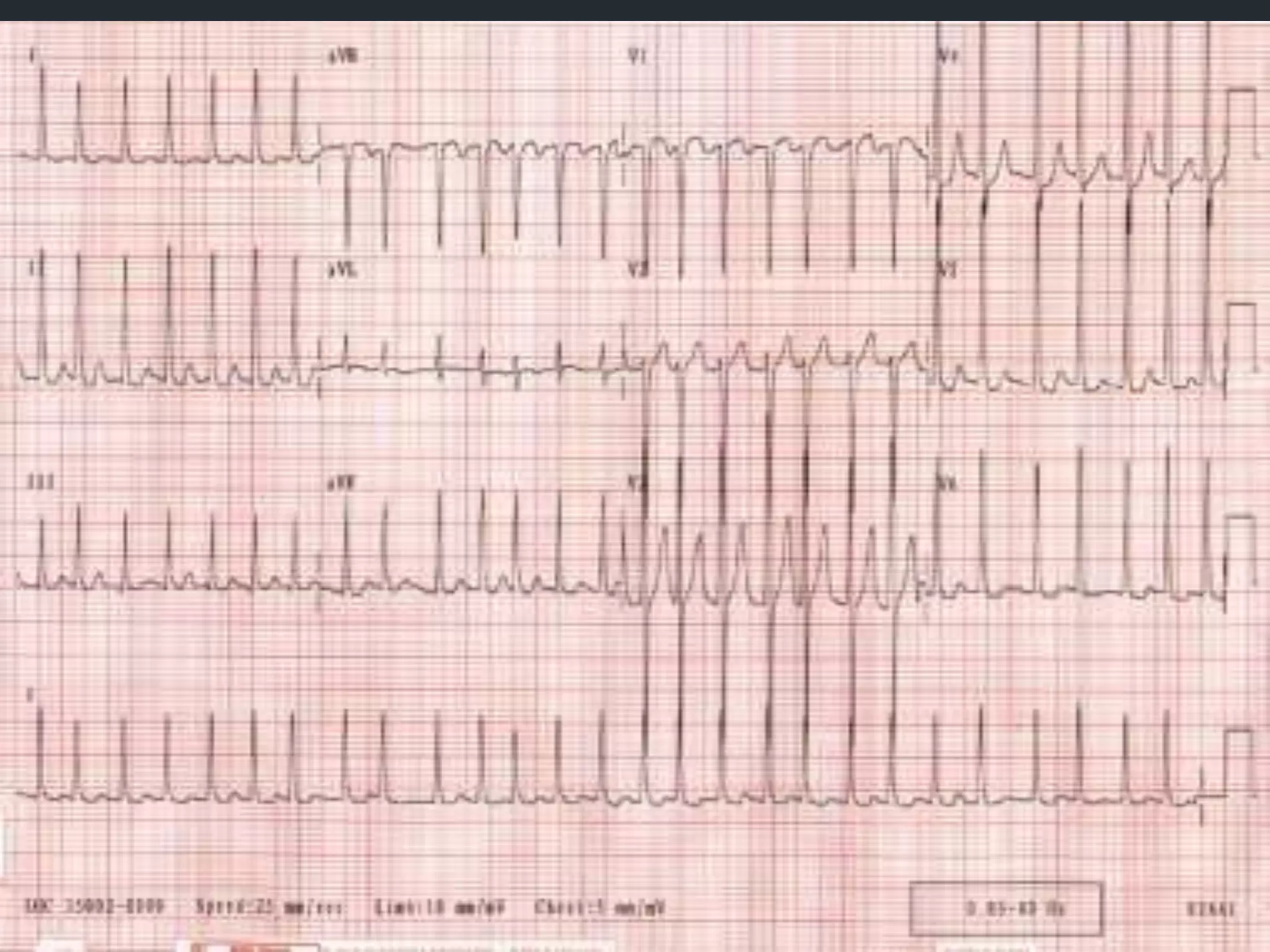
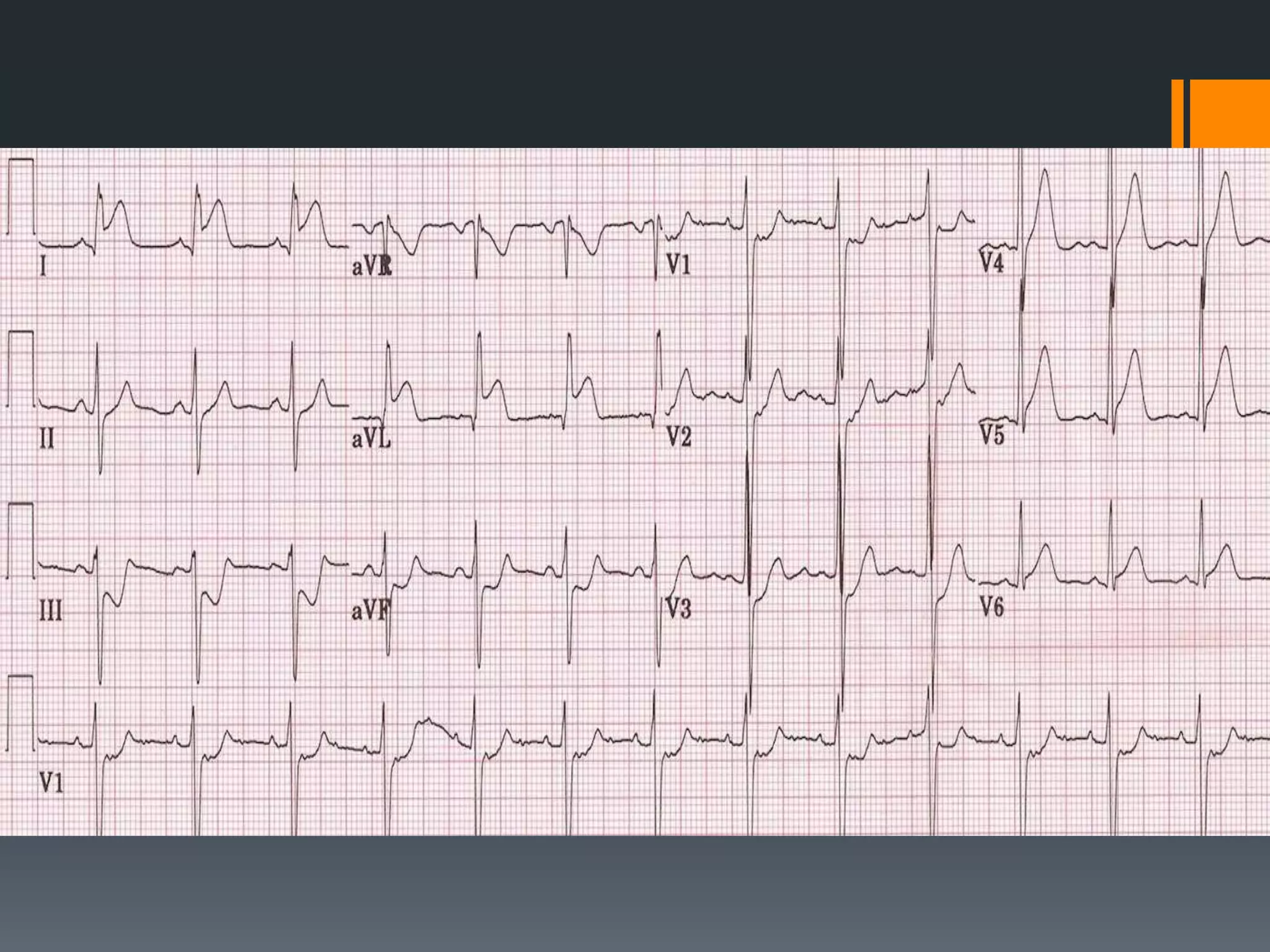
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm is defined as having a rate between 50-100 bpm and being a type of slow ventricular tachycardia that does not typically require treatment.
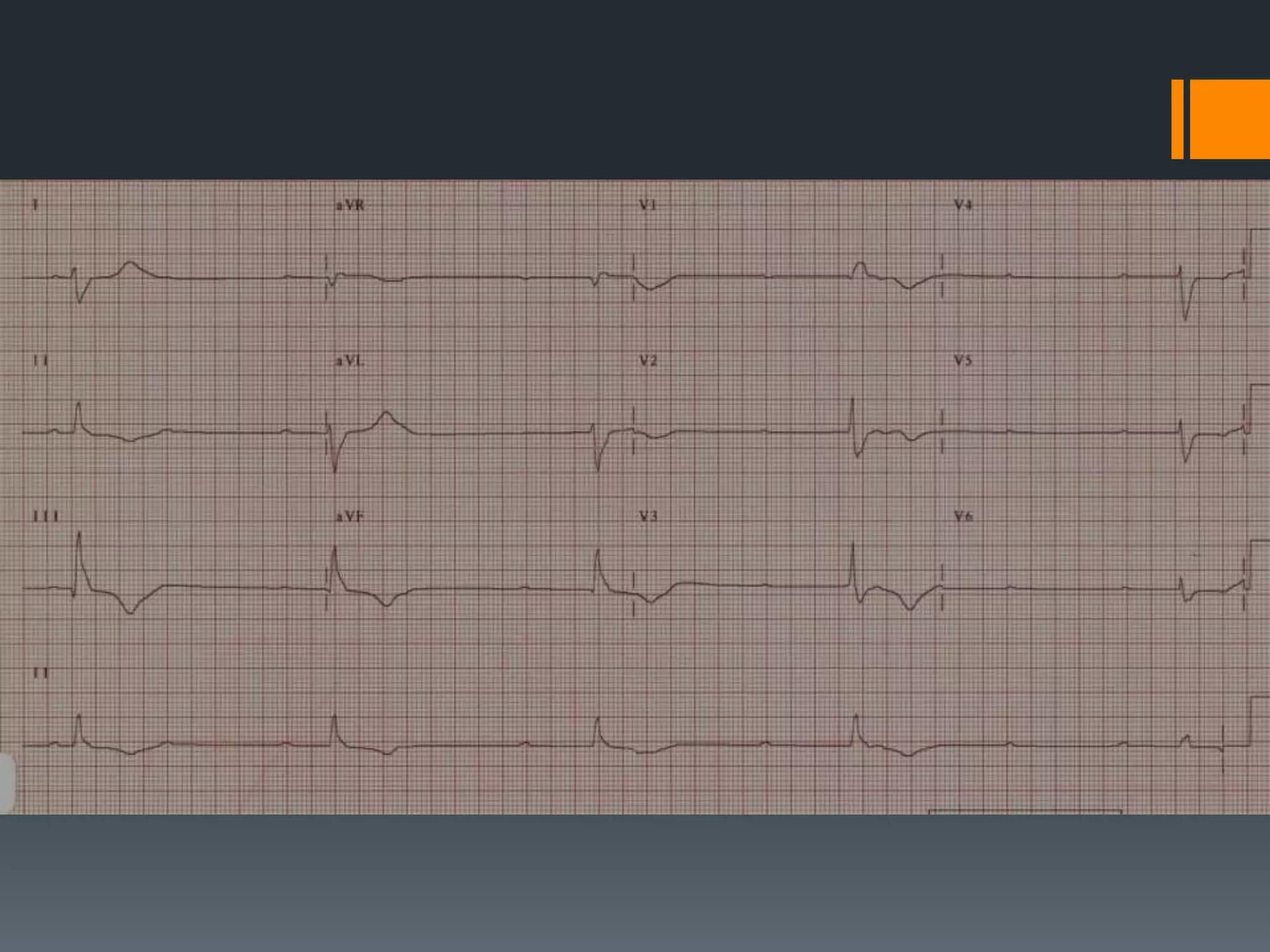
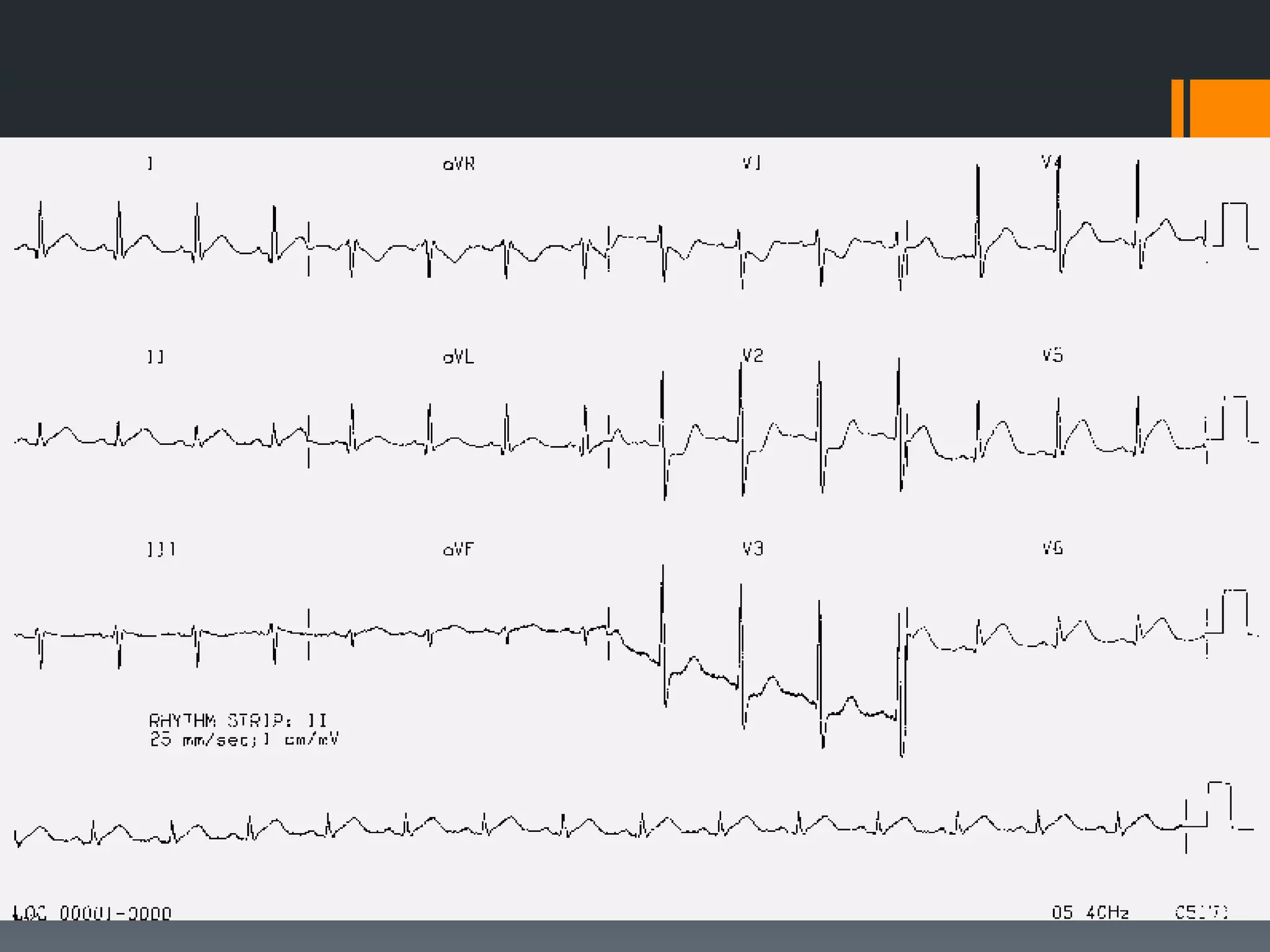
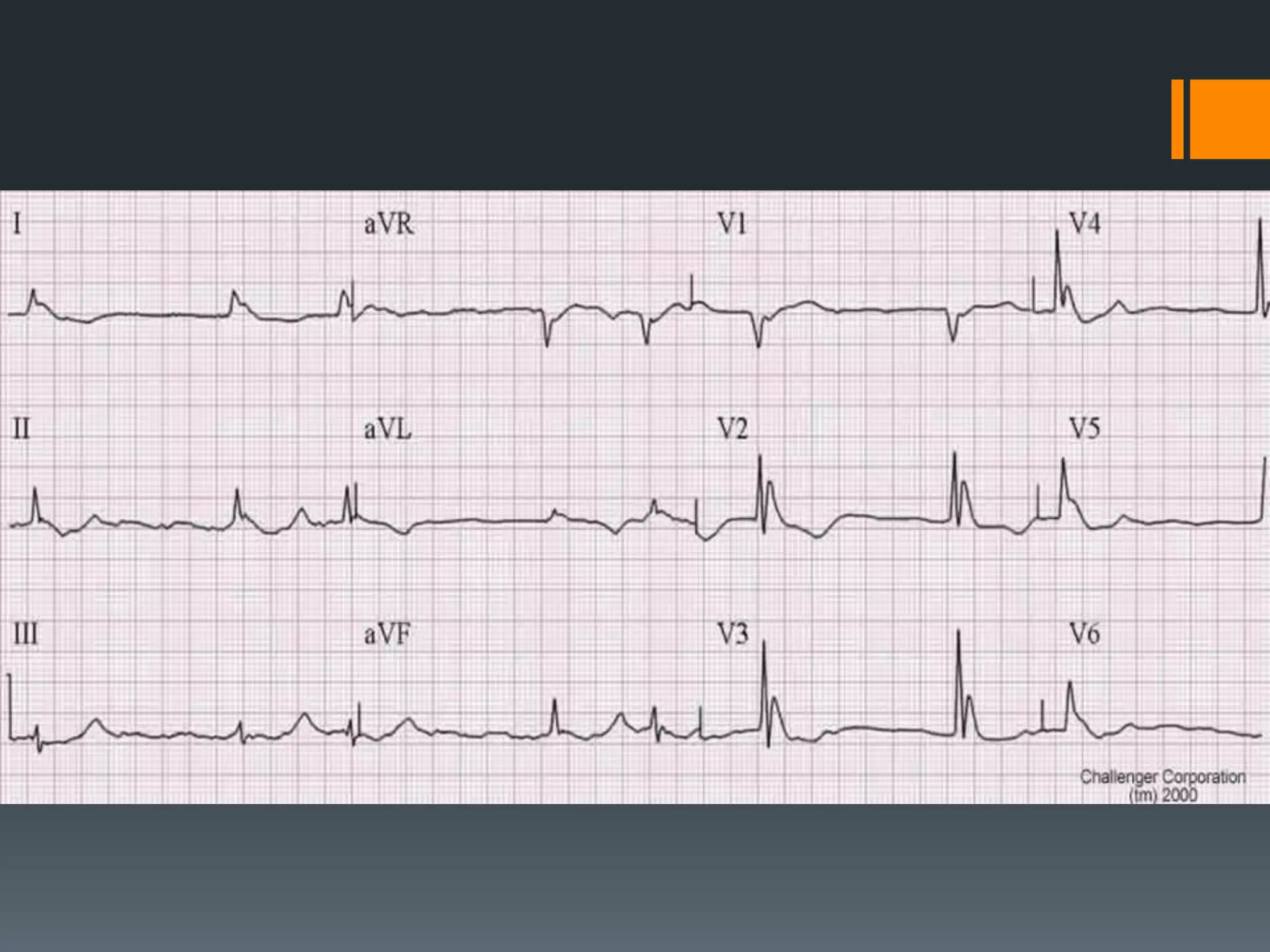
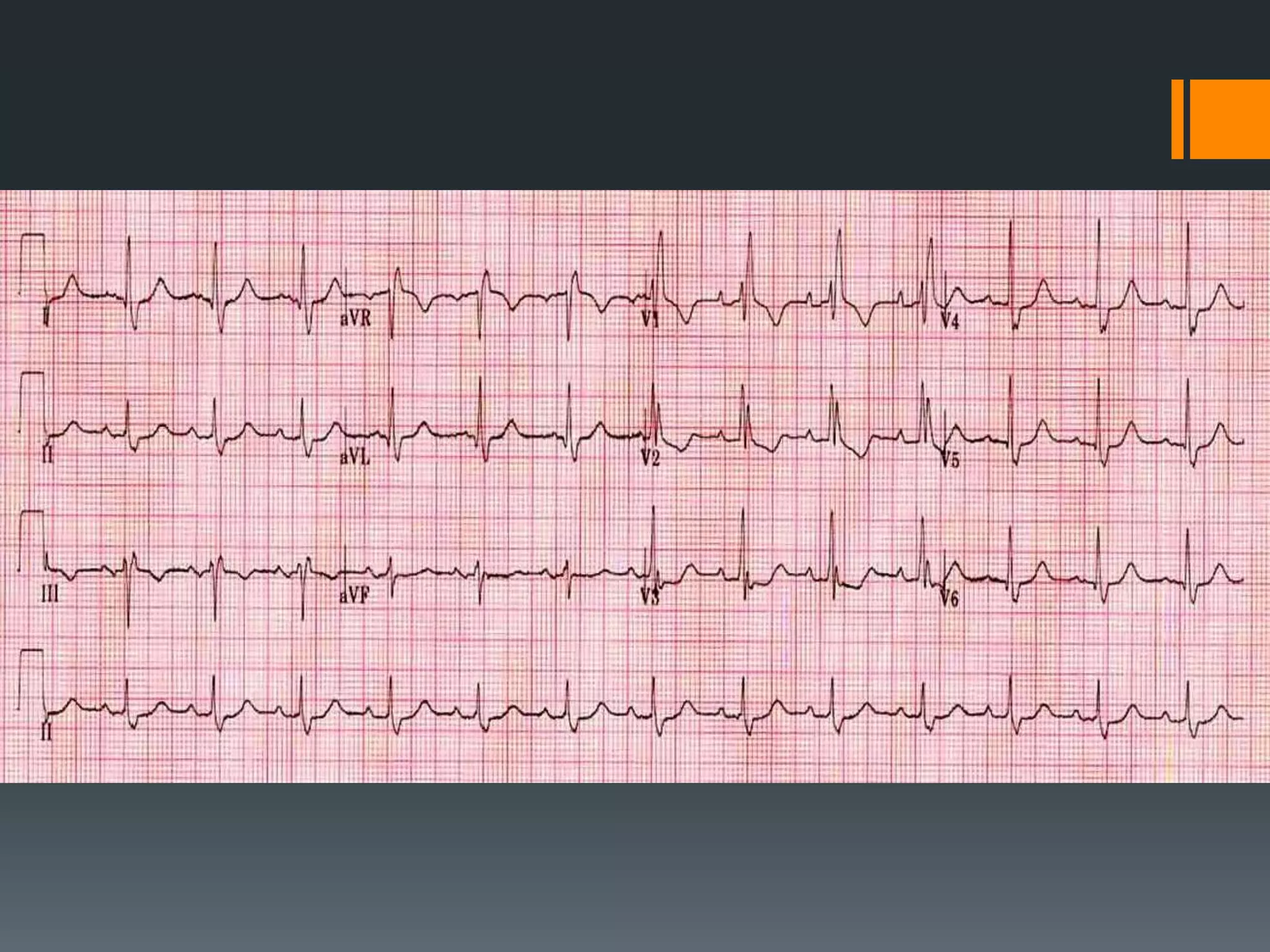
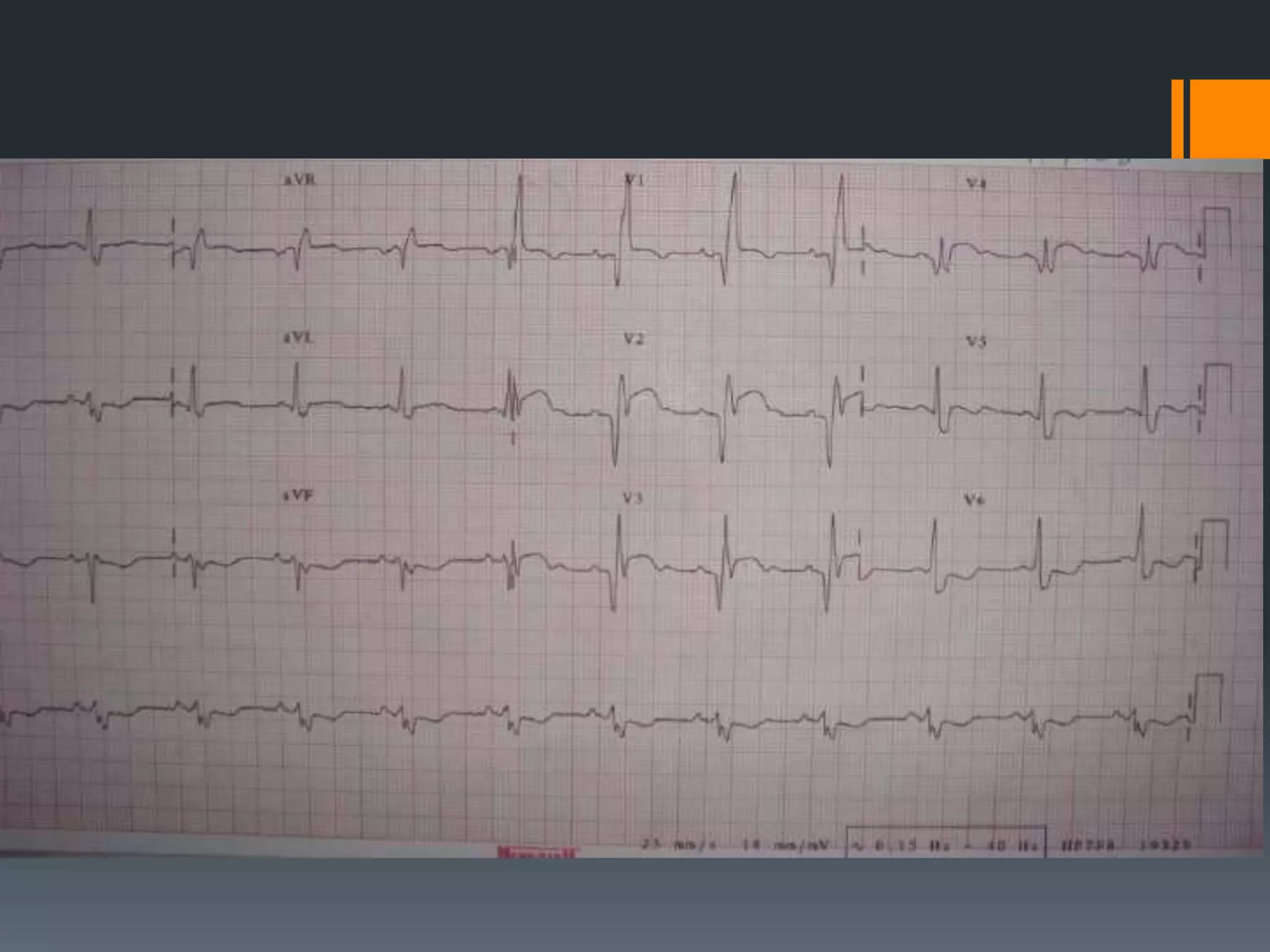
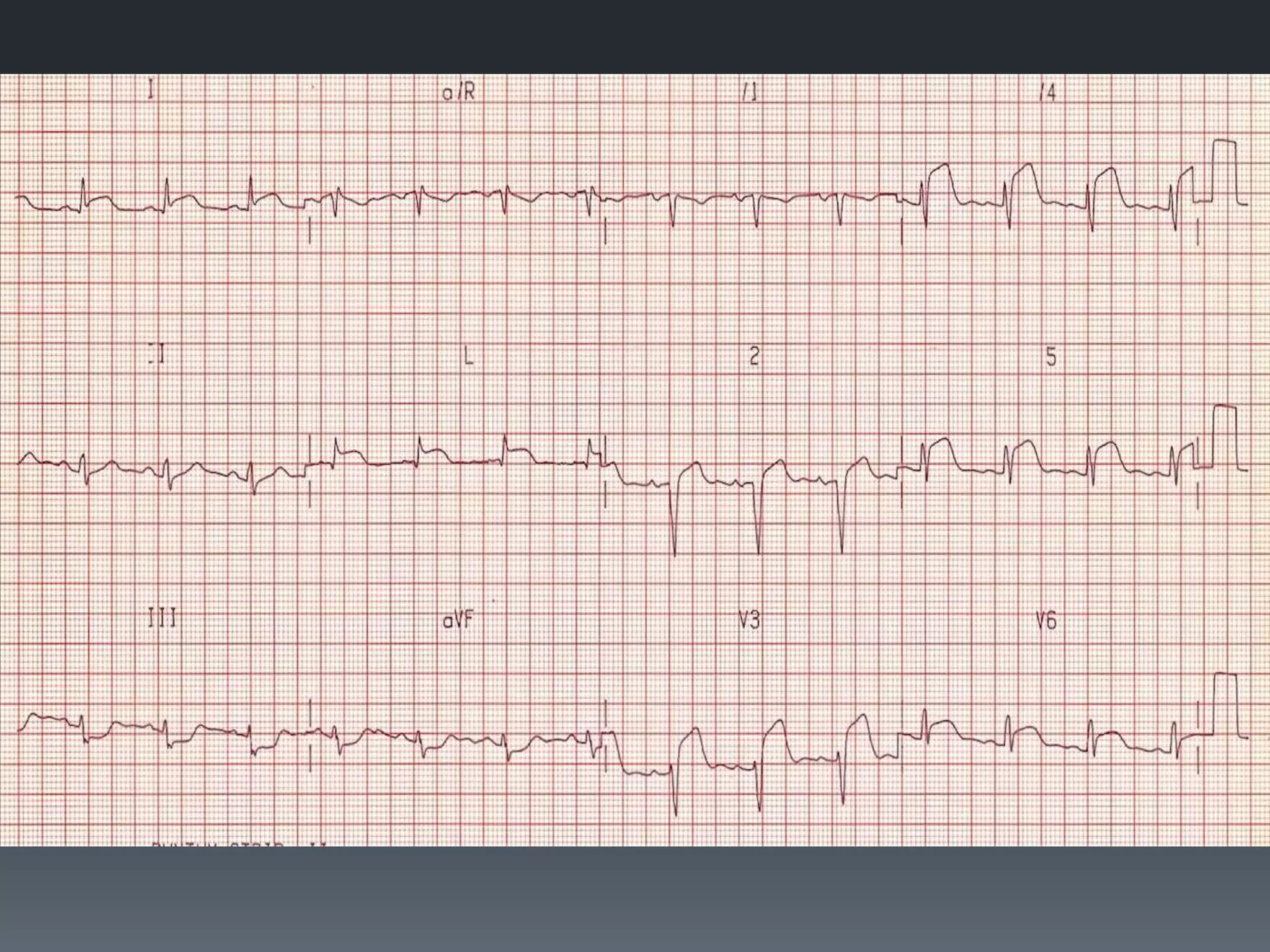
- Atrial flutter with a 4:1 conduction is described as typical or atypical, with atypical often occurring after surgeries. Atrial flutter can be cardioverted with the least amount of energy.
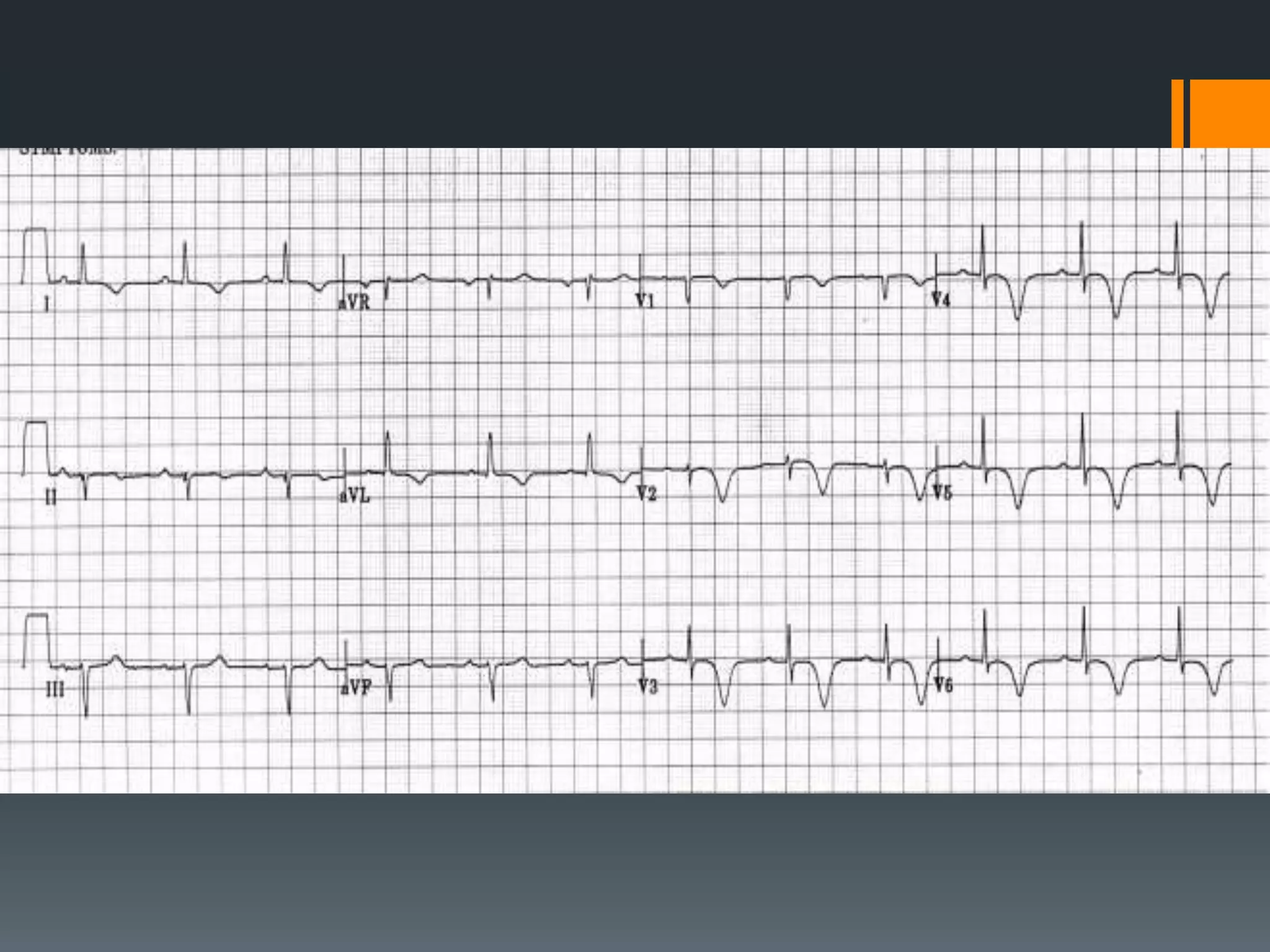
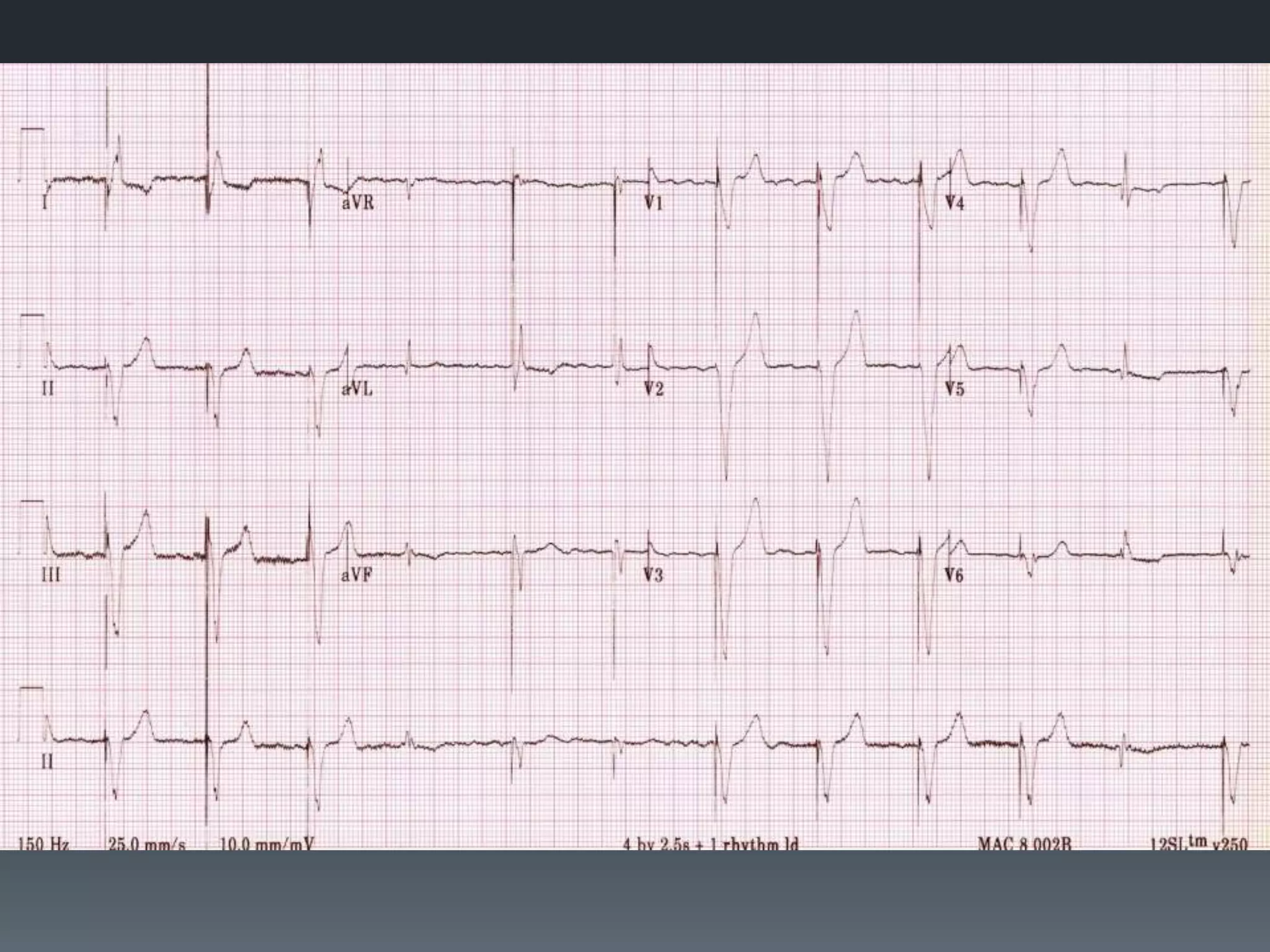
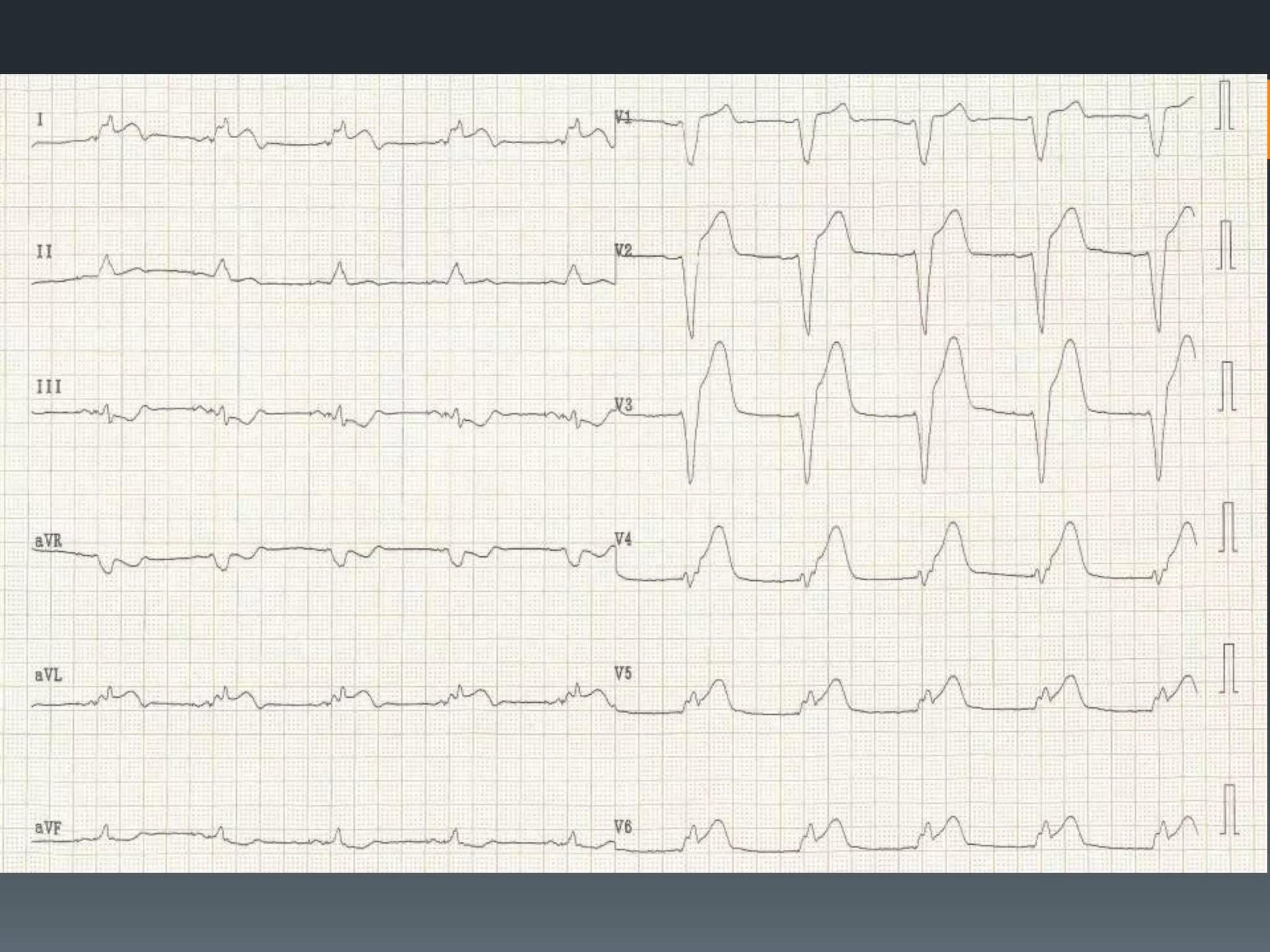
- Several other conditions are briefly defined such as complete heart block, dextro