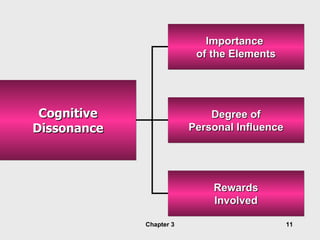
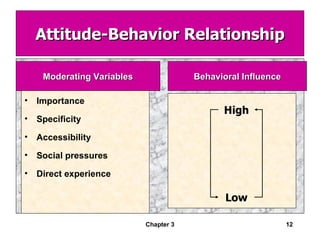
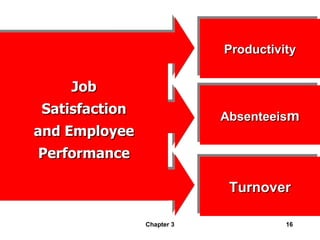
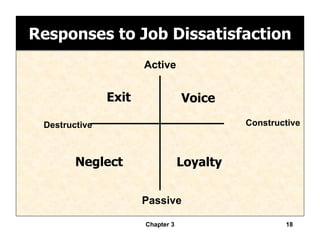
This document discusses values, attitudes, and job satisfaction. It defines values and attitudes, and describes how values influence attitudes. It also explores the relationship between attitudes, job satisfaction, and employee performance, finding that job satisfaction can affect individual productivity, organizational productivity, absenteeism, turnover, and organizational citizenship behavior. Finally, it discusses measuring job satisfaction and potential employee responses to job dissatisfaction.