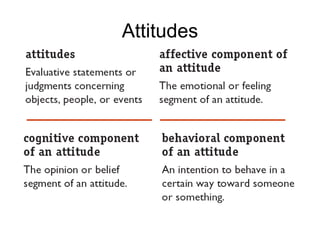
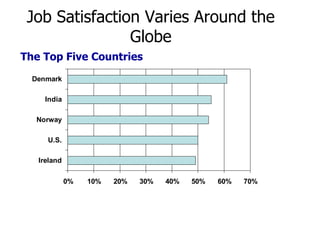
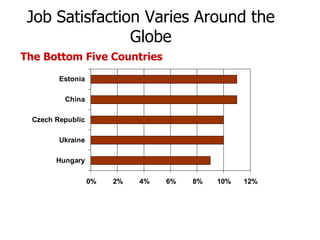
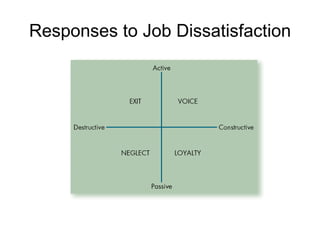
The document discusses how attitudes, specifically job satisfaction, impact job performance and satisfaction. It defines job satisfaction as an emotional response to one's job and discusses how it varies globally and is influenced by factors like need fulfillment, values, and equity. Higher job satisfaction is linked to less absenteeism and turnover as well as better performance, while lower satisfaction can lead to behaviors like tardiness. The document also examines organizational commitment, job involvement, and responses to job dissatisfaction.