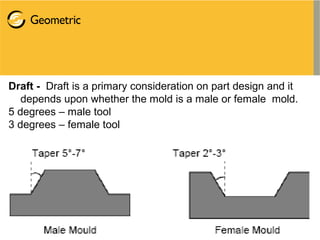
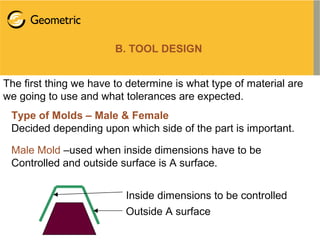
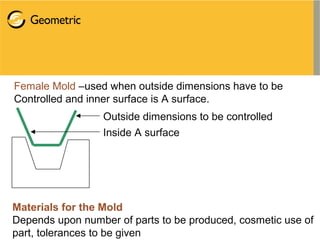
Vacuum forming is a thermoforming process that uses vacuum pressure to mold a plastic sheet over a mold. The process involves heating a plastic sheet until soft, draping it over a mold, applying vacuum pressure to suck the sheet onto the mold, then cooling and ejecting the molded part. Key aspects of vacuum forming include part and tool design, material selection, and processing techniques like heating, vacuum application, and cooling. Common applications are food containers, baths, vehicle interiors, and more.