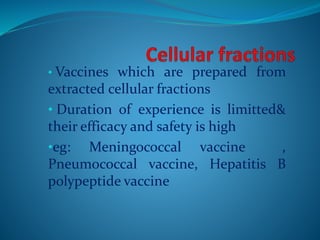
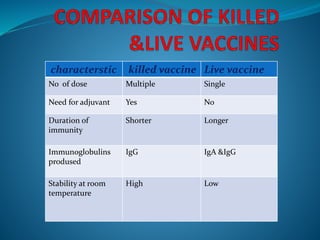
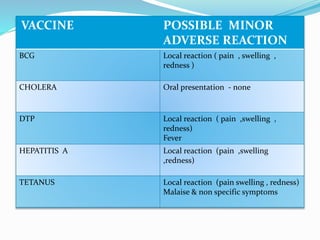
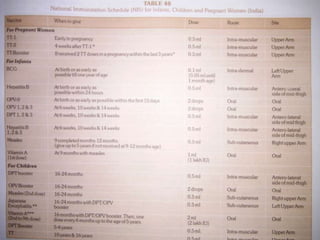
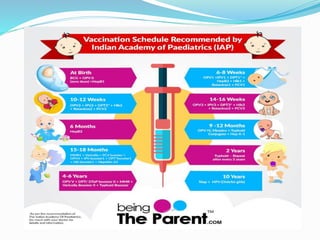
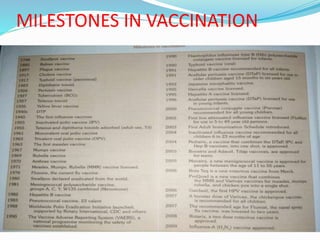
Vaccination involves administering antigenic material to stimulate the immune system and develop immunity against pathogens. There are several types of vaccines including live attenuated, inactivated, toxoids, and cellular fractions. Common minor adverse reactions include pain, swelling, and fever at the injection site. National immunization schedules provide recommended vaccine doses starting at age 6 weeks. Vaccines help prevent disease and reduce vaccine-related reactions through producing protective immunity.