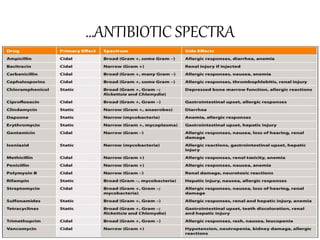
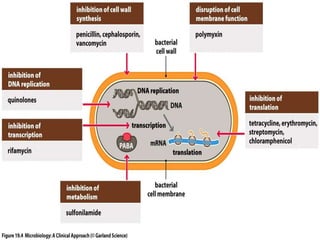
Antibiotics are drugs that kill or inhibit bacteria and were first discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. They can be classified as broad-spectrum or narrow-spectrum and work by targeting specific bacterial structures or functions, although bacteria have developed resistance mechanisms. The development of new antibiotics is a costly and time-consuming process, requiring rigorous testing for safety and effectiveness.