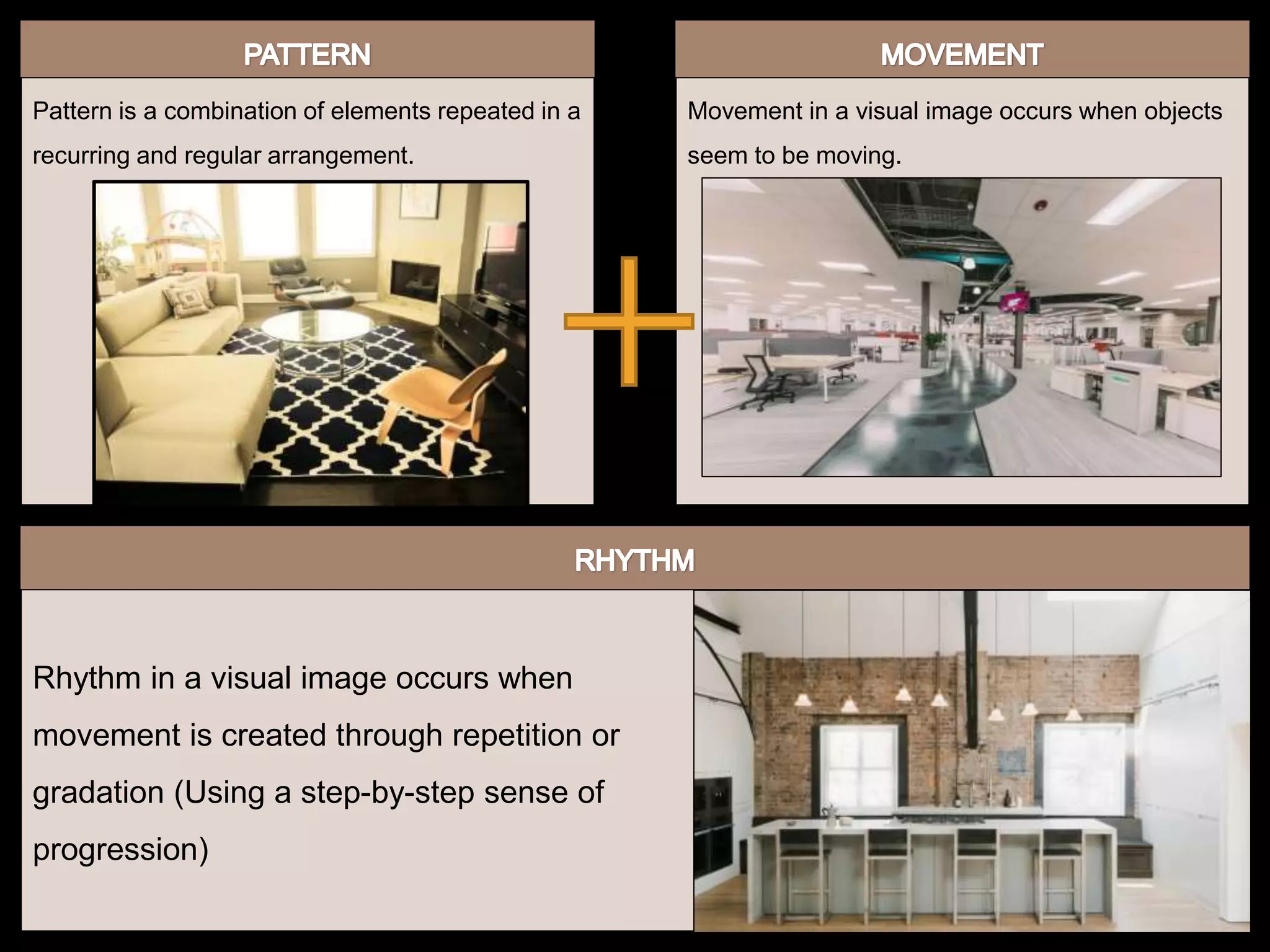
The document discusses various principles of design including:
1) Balance - symmetrical, asymmetrical, radial, and crystallographic balance which involve distributing visual weight evenly.
2) Contrast and dominance/emphasis/focus - arranging light vs dark, rough vs smooth, large vs small elements to create visual interest or draw attention to certain areas.
3) Unity and variety - achieving a balanced design through elements that belong together but are also interestingly different.