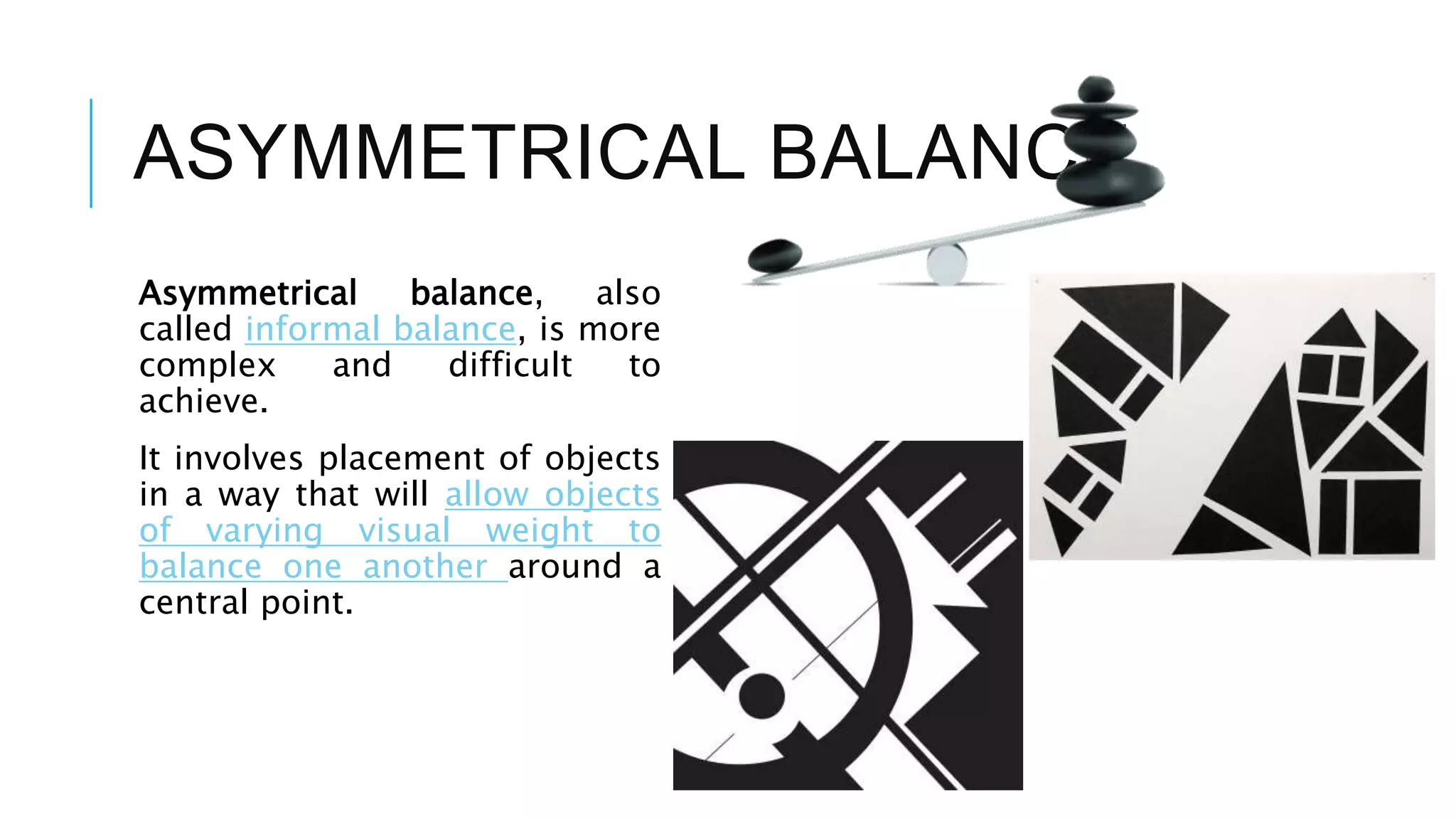
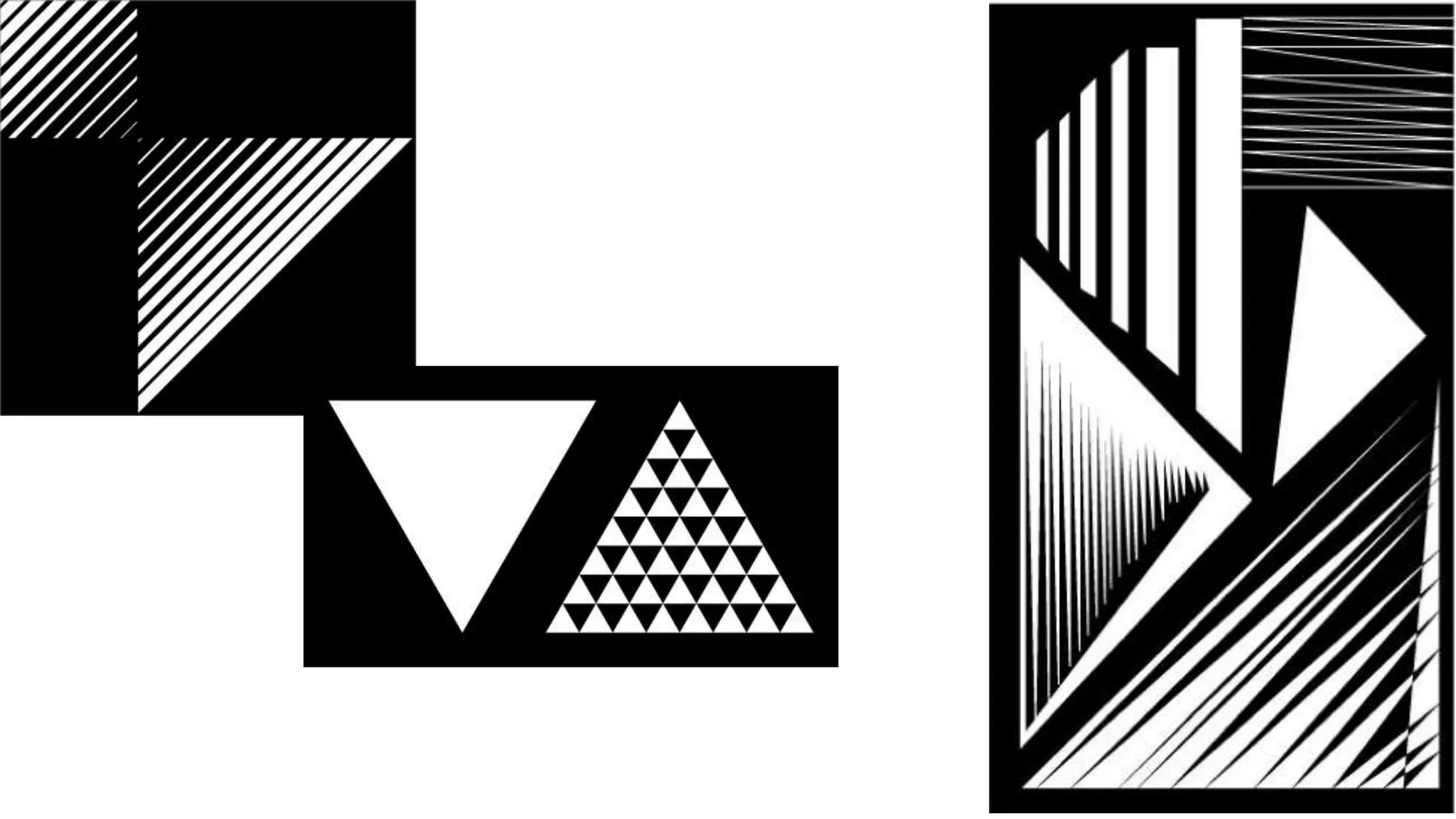
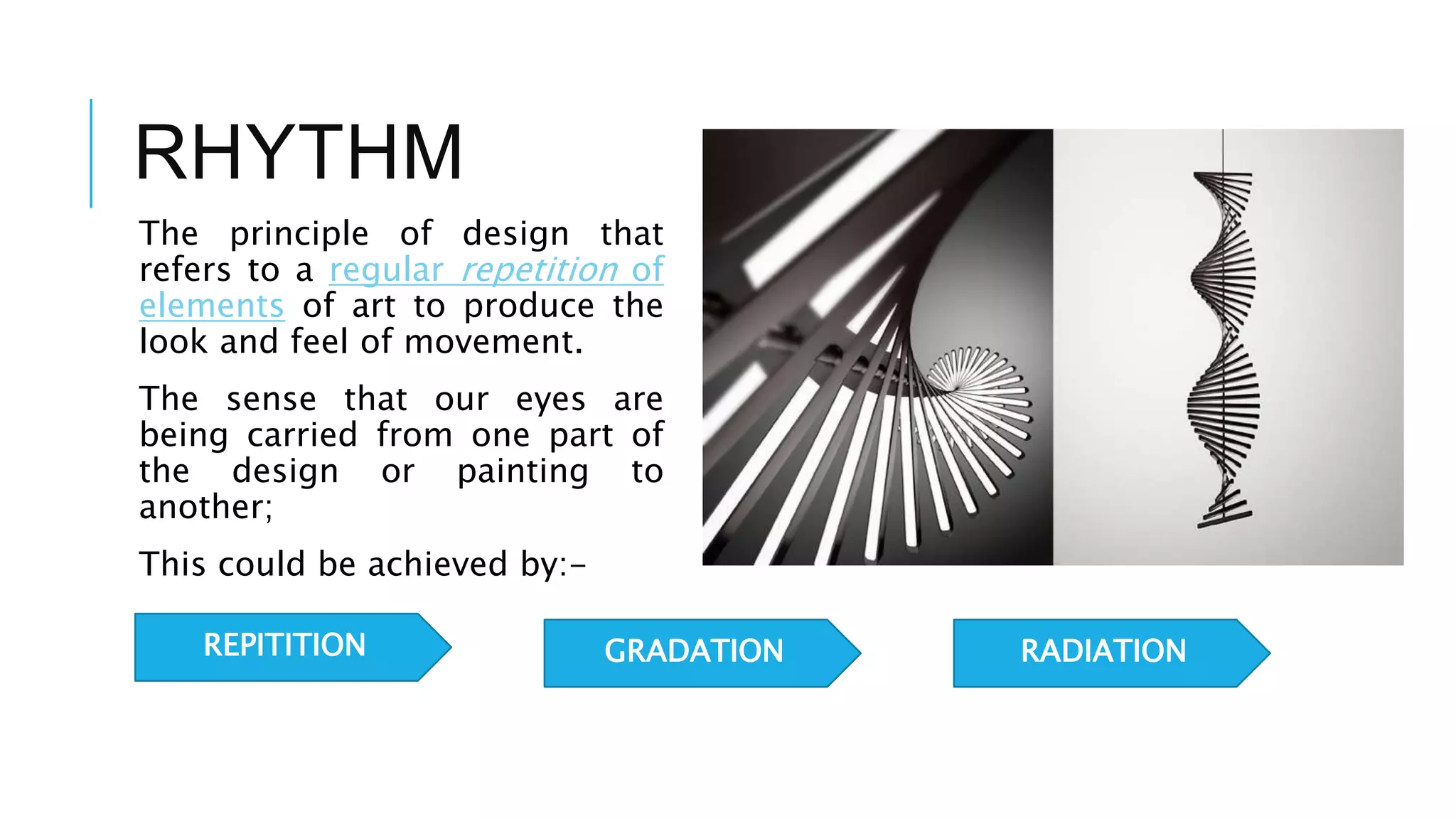
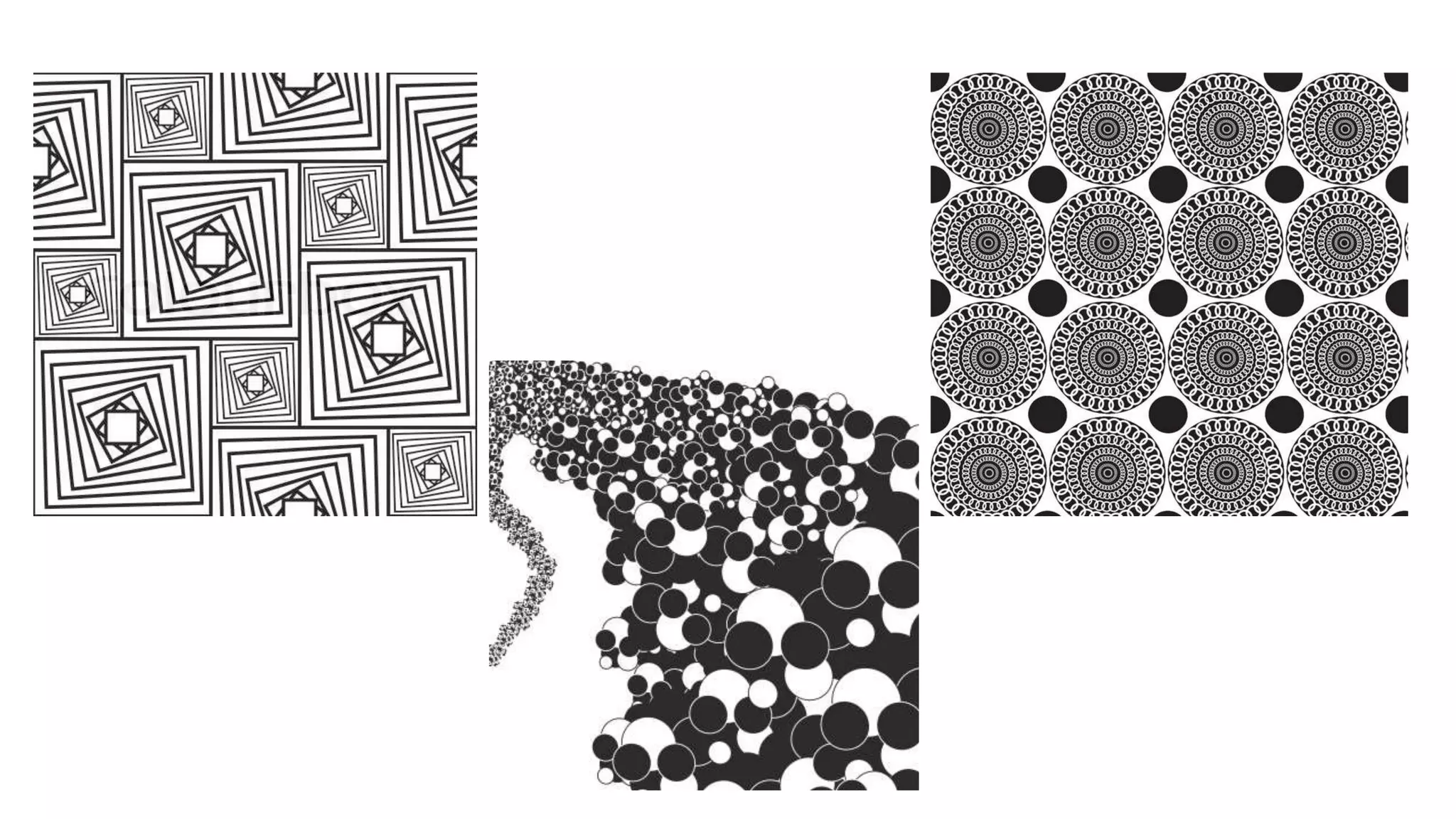
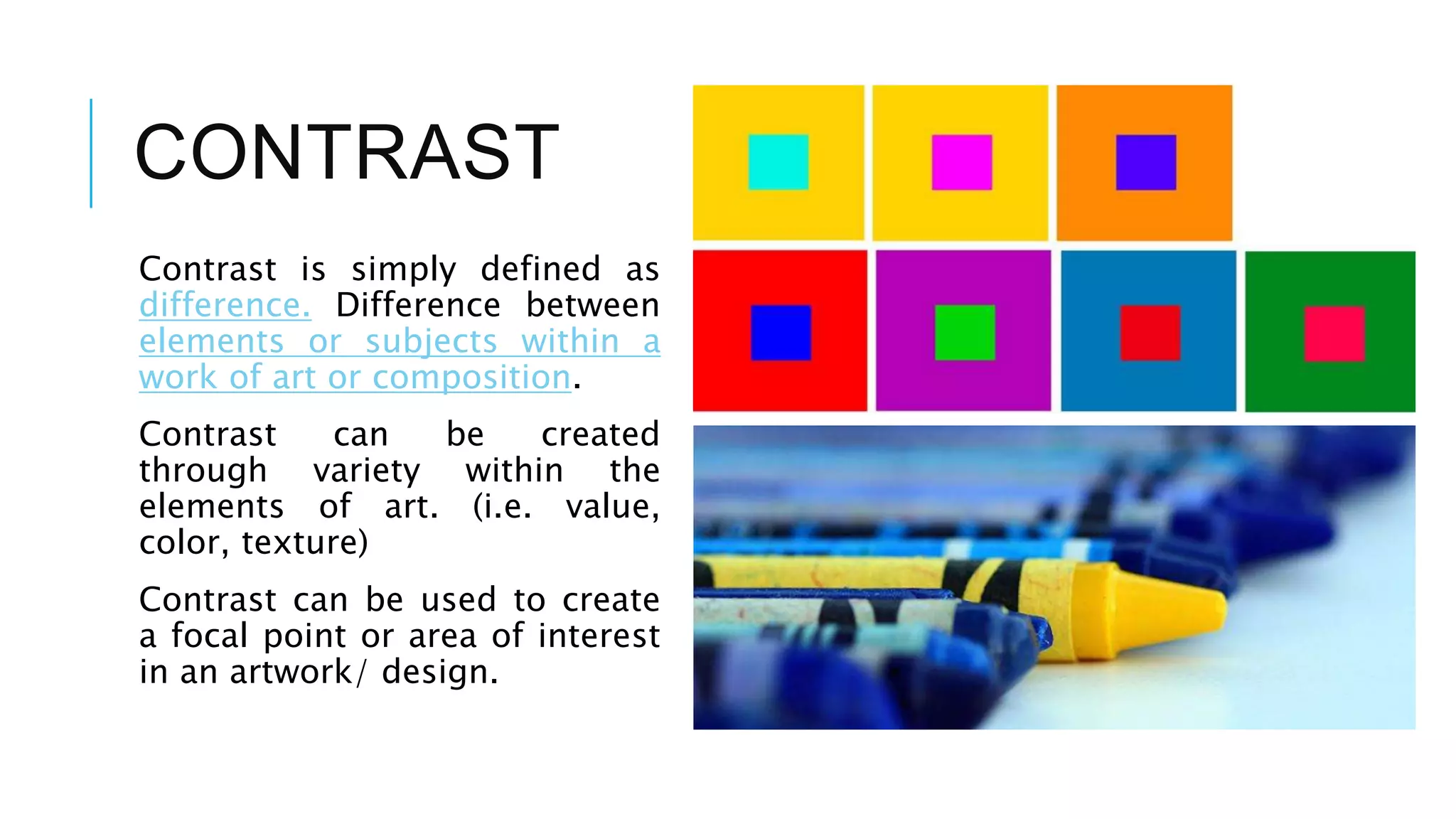
The document discusses principles of design that guide how visual elements are arranged in an effective composition. It defines key principles such as balance, rhythm, emphasis, contrast, movement, and harmony. Balance refers to the visual weight distribution of elements and can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, or radial. Rhythm creates a sense of movement through repetition, gradation, or radiation of elements. Emphasis focuses attention on a central point. Contrast creates difference using elements like value and color. Movement guides the eye along a path. Harmony means all parts relate and complement through unity of idea or an interesting variety.