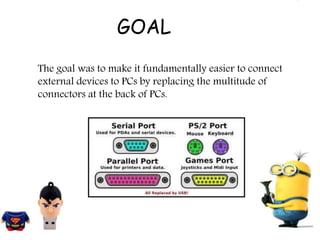
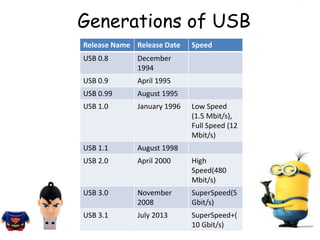
USB was developed in 1994 by seven companies to make connecting external devices to PCs easier by standardizing connectors. It has since gone through several revisions to increase speed, with USB 3.0 providing speeds up to 5Gbps and USB 3.1 providing 10Gbps. USB has a tiered star topology centered on a host controller, usually the PC chipset, and uses pipes to manage communication between devices. It supports various transfer types and has become ubiquitous due to its convenience, high speeds, and ability to hot-plug devices without rebooting.