The document discusses USB (Universal Serial Bus). It provides details on the history and development of USB, including its features and versions. It describes USB cables, connectors, ports and their uses. It also discusses USB pen drives, their advantages for data transfer and storage, and the top five uses of pen drives including file transfer between devices, backup storage, and adding memory via ReadyBoost.





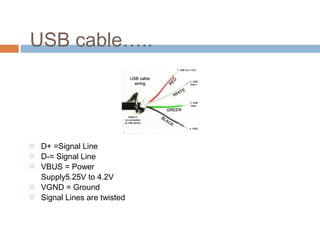



![USB system
USB system consist
of three units
1] USB host
2] USB Cable
3] USB DeviceHost Device
Cable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usb-130826060153-phpapp02/85/Usb-12-320.jpg)
![Fundamental packet
The host controller initiates and manages all USB
transfers.
A USB transfer consist of one or more transaction and
each transaction contains up to three packets.
There are 3 types of packets
1] Token 2] Data 3] Handshake
Each packet contains packet ID block of information and
error checking codes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usb-130826060153-phpapp02/85/Usb-15-320.jpg)








![USB ports…What can use
them?
Printer, Scanner, Keyboard, Mouse
Drives…Hard, Floppy, CD, Zip, Flash Drives
Wireless…”Bluetooth”, Keyboard, Mouse
Flash memory cards…Card Readers
Hubs…up to 127 Ports useable
Cameras…DigiCam, WebCam,
[no VideoCam]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usb-130826060153-phpapp02/85/Usb-24-320.jpg)









