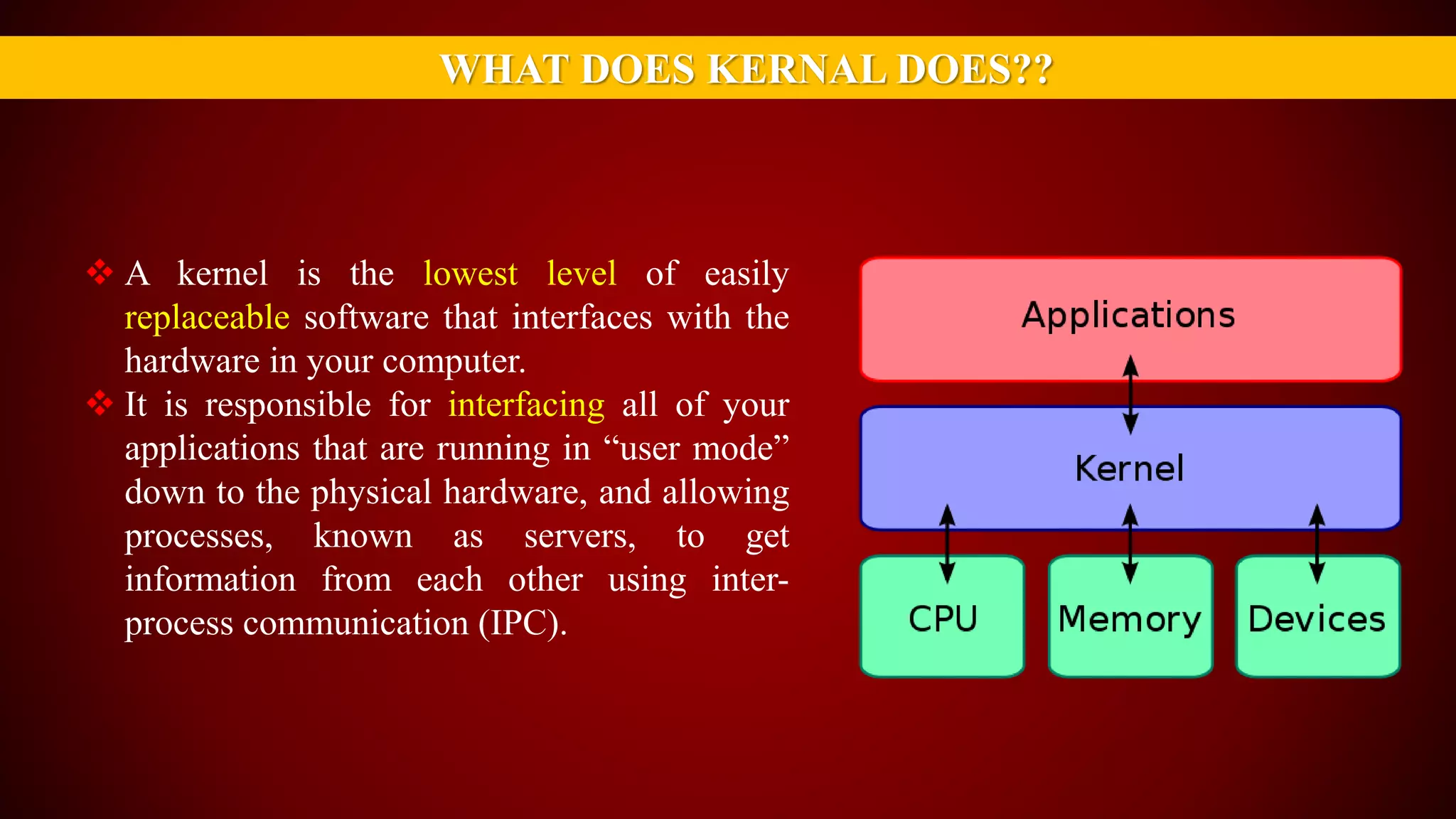
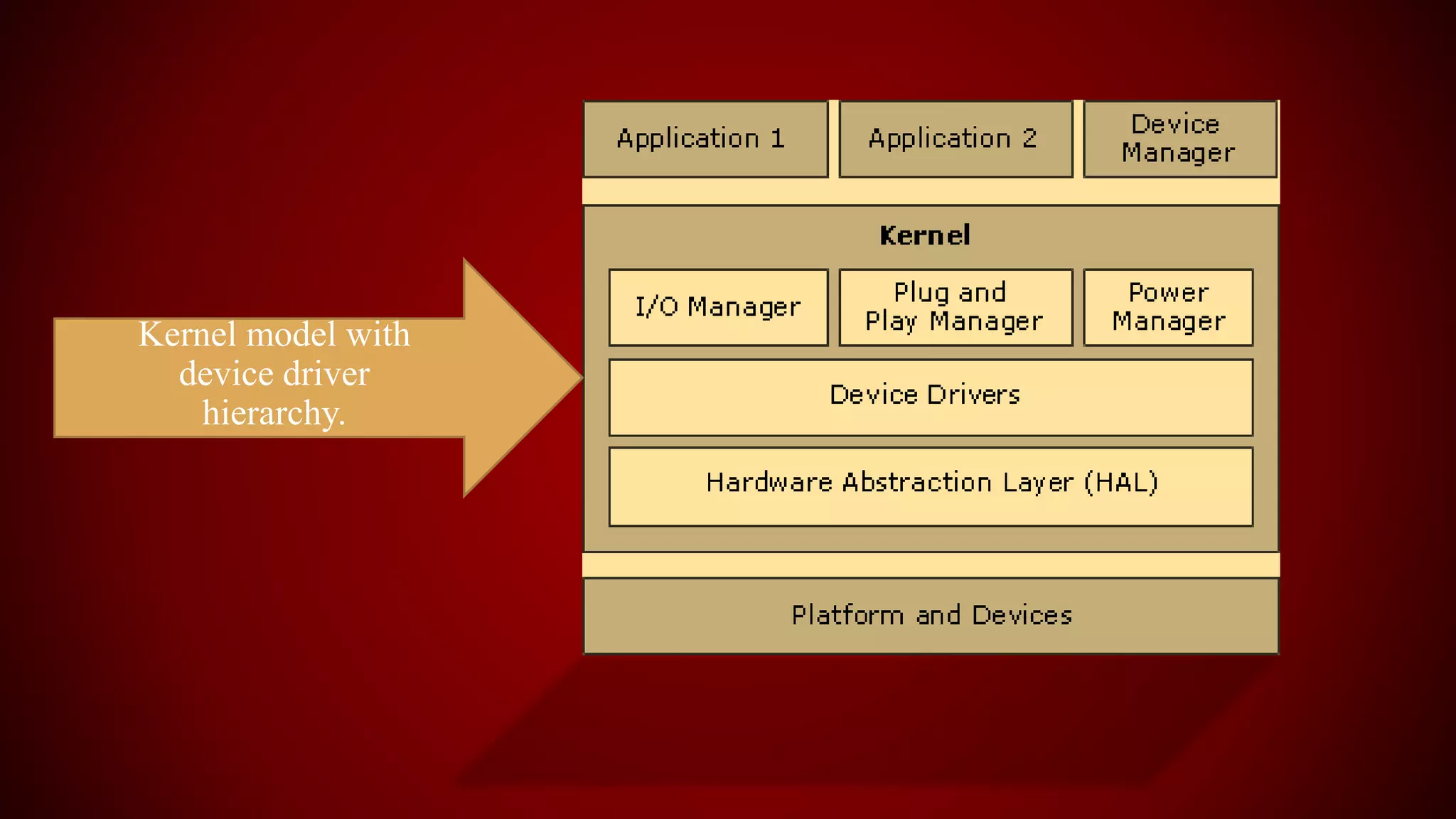
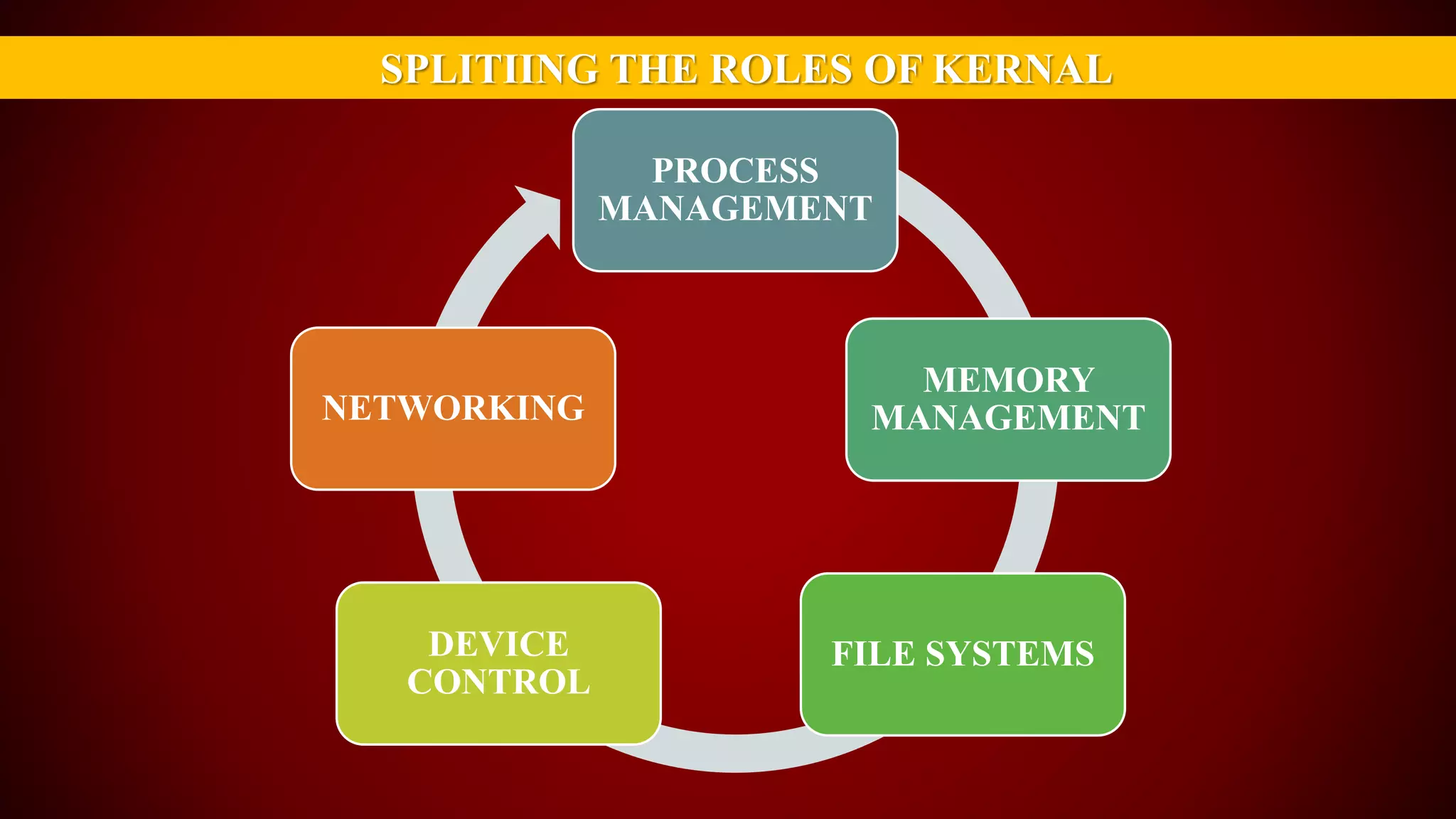
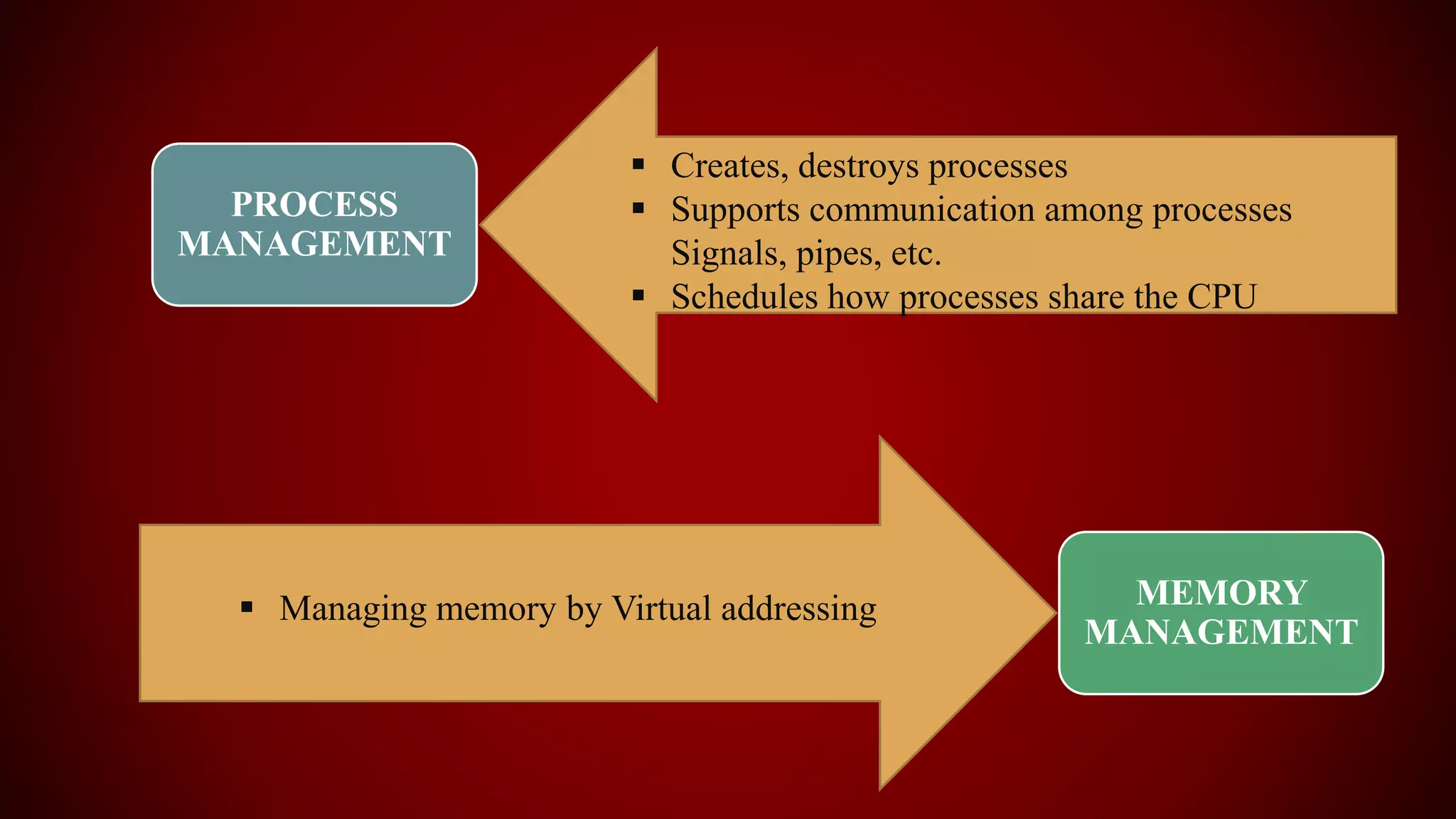
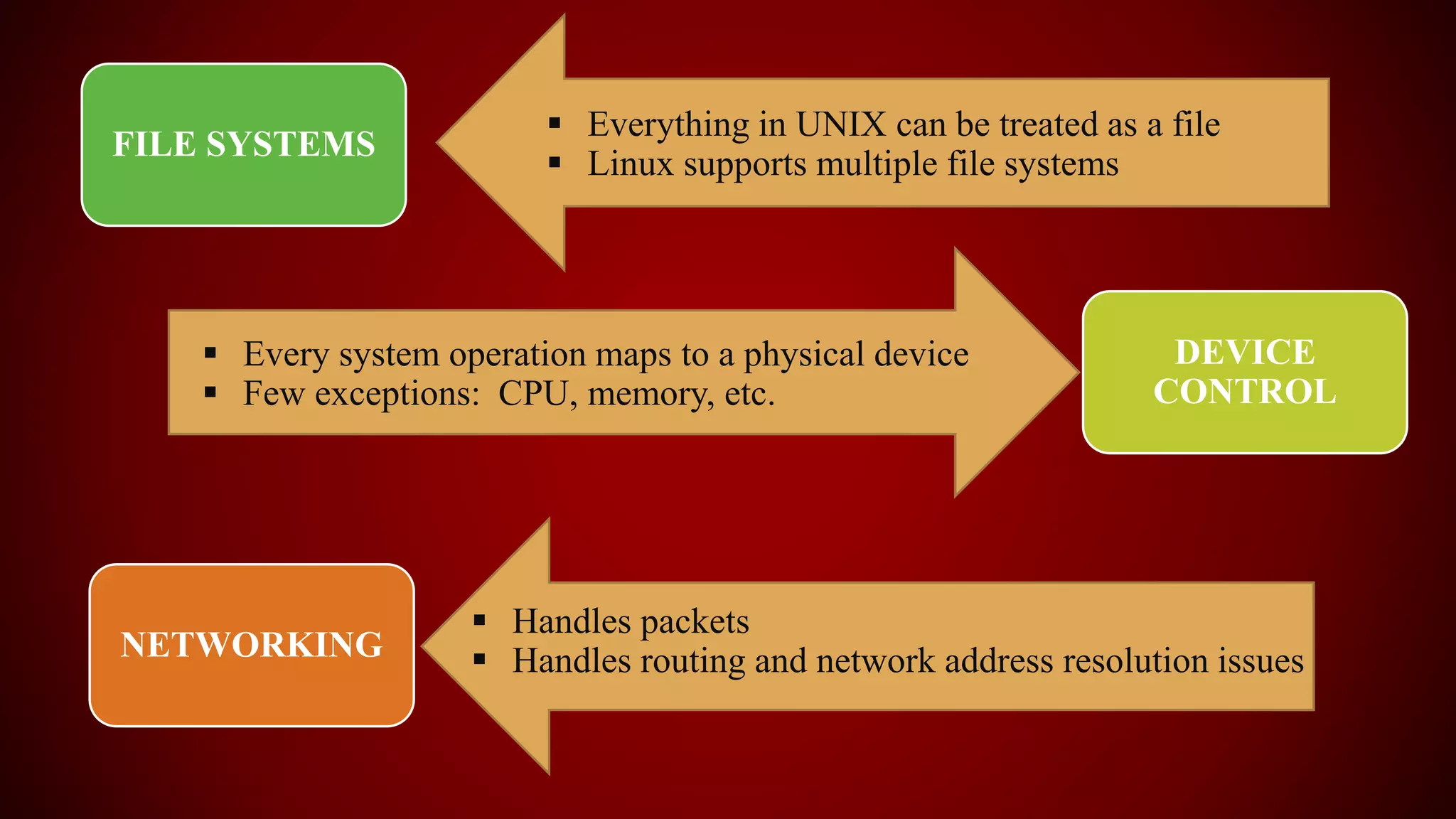
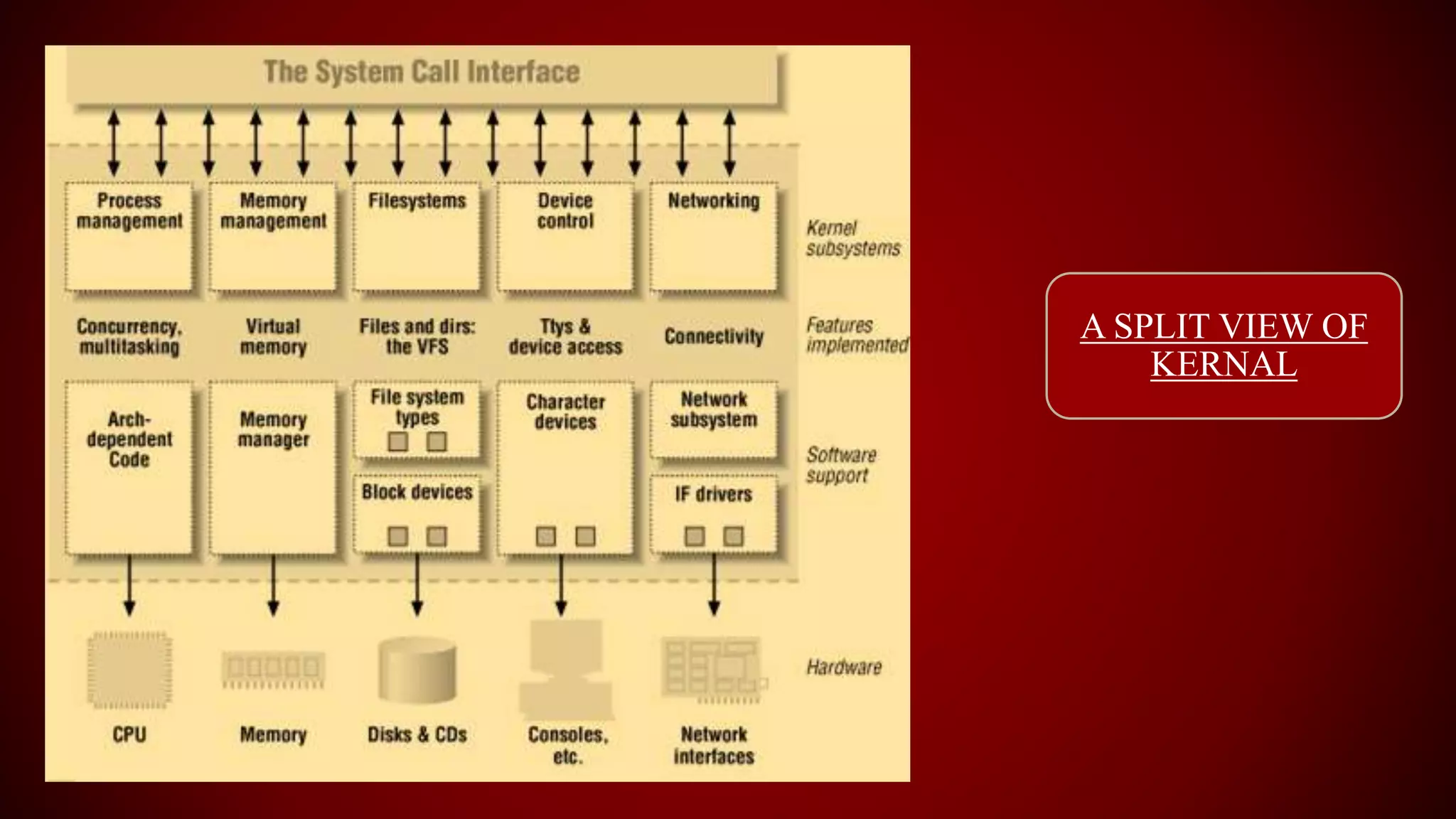
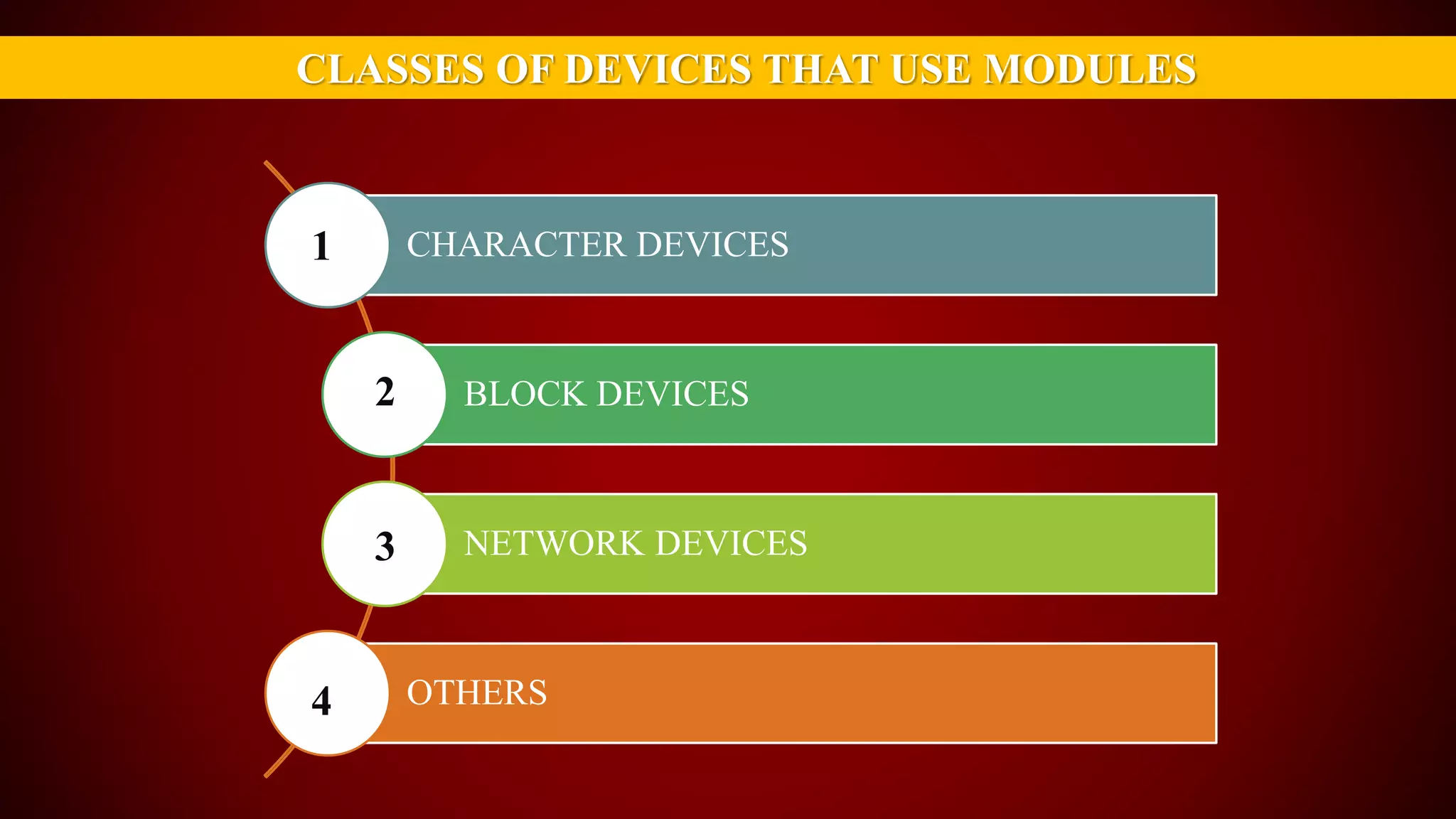
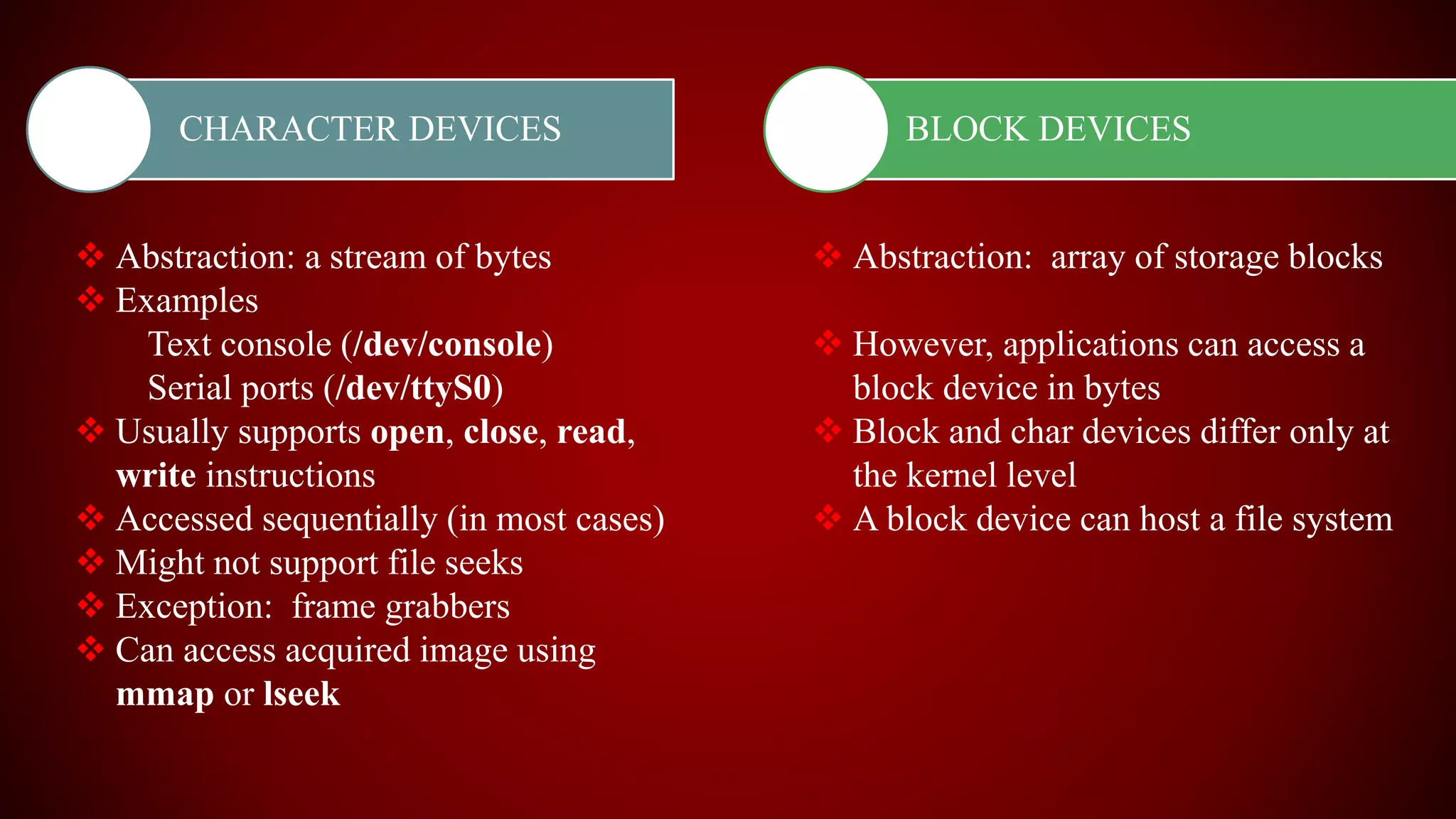
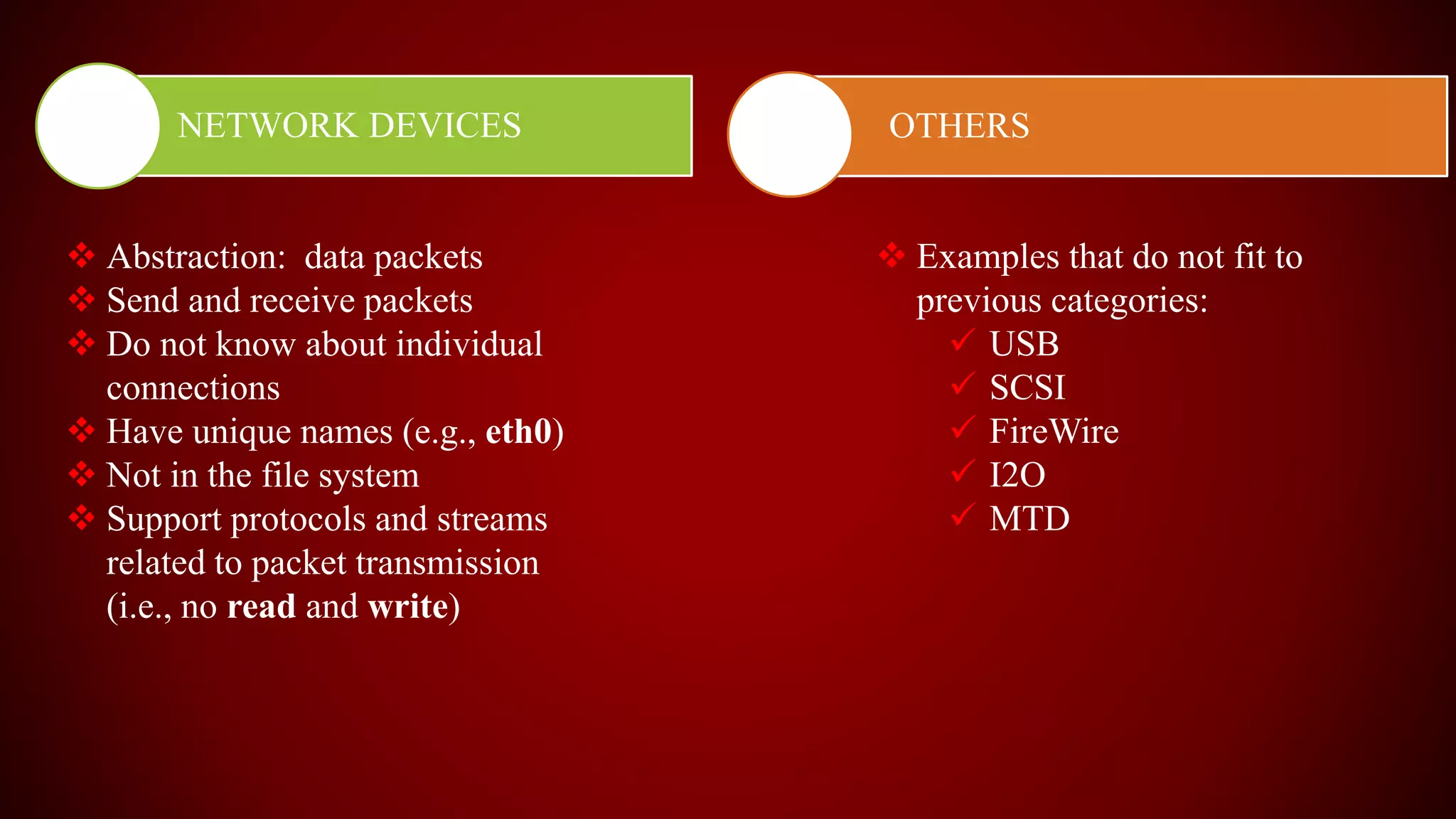
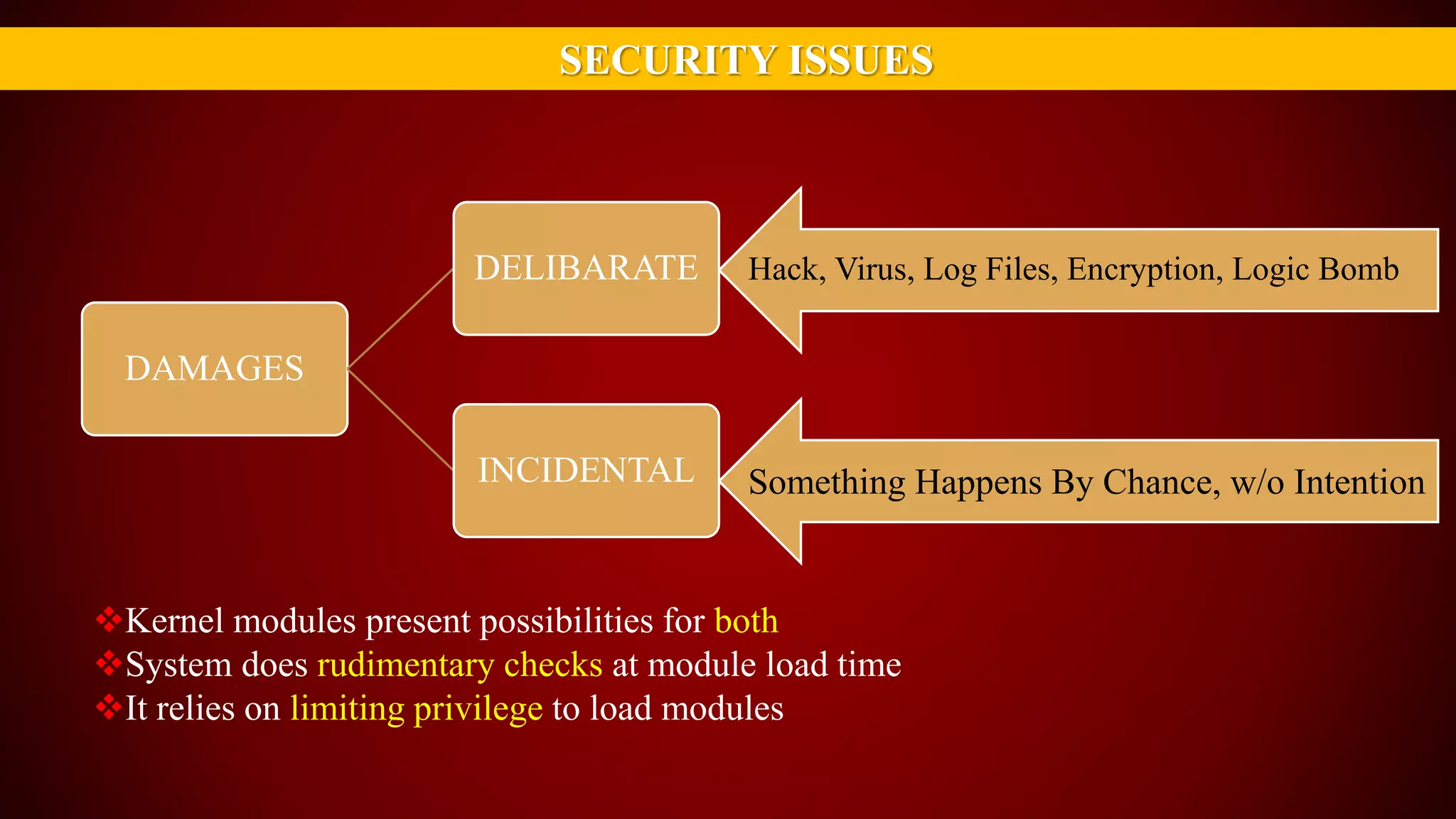
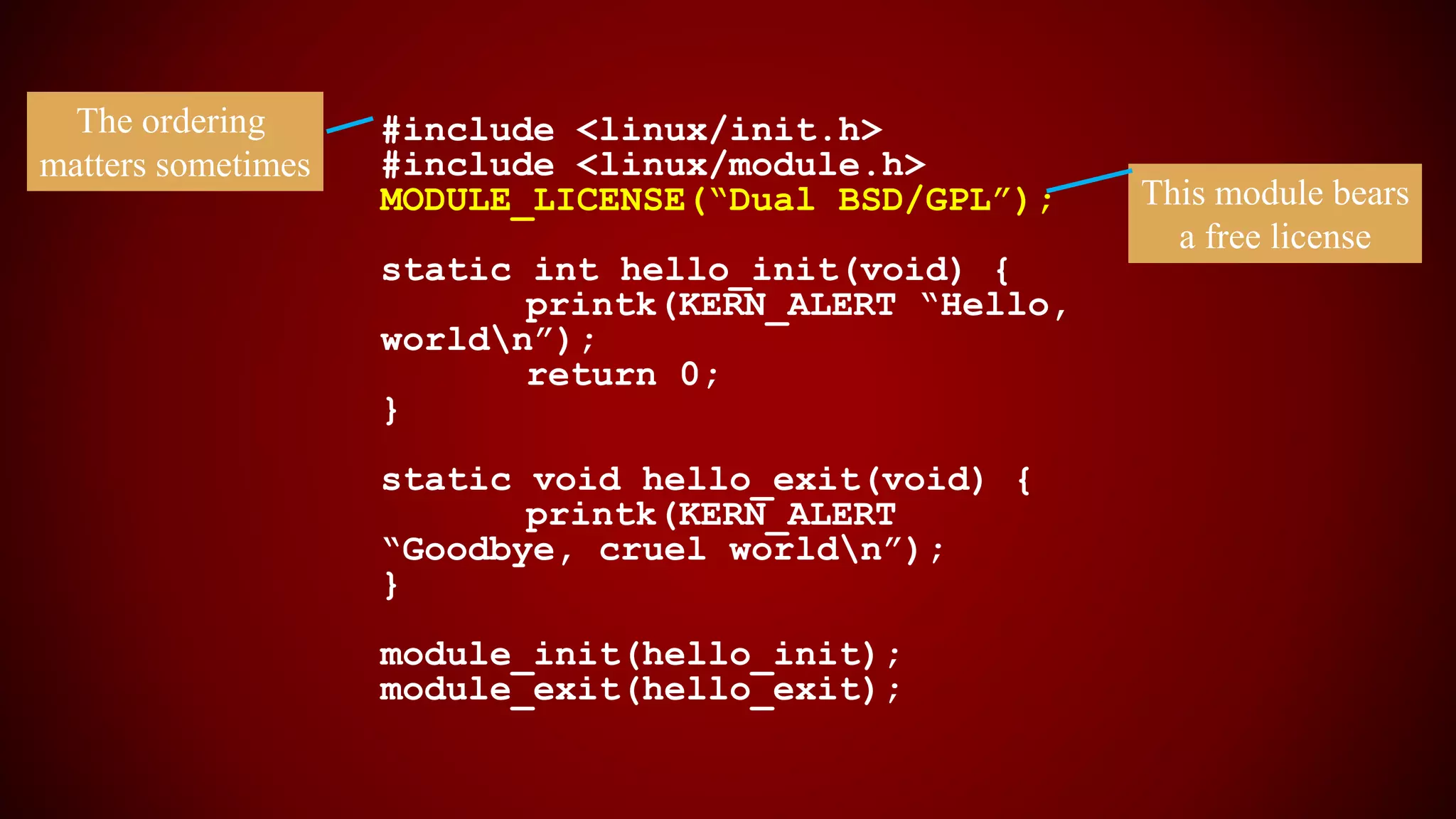
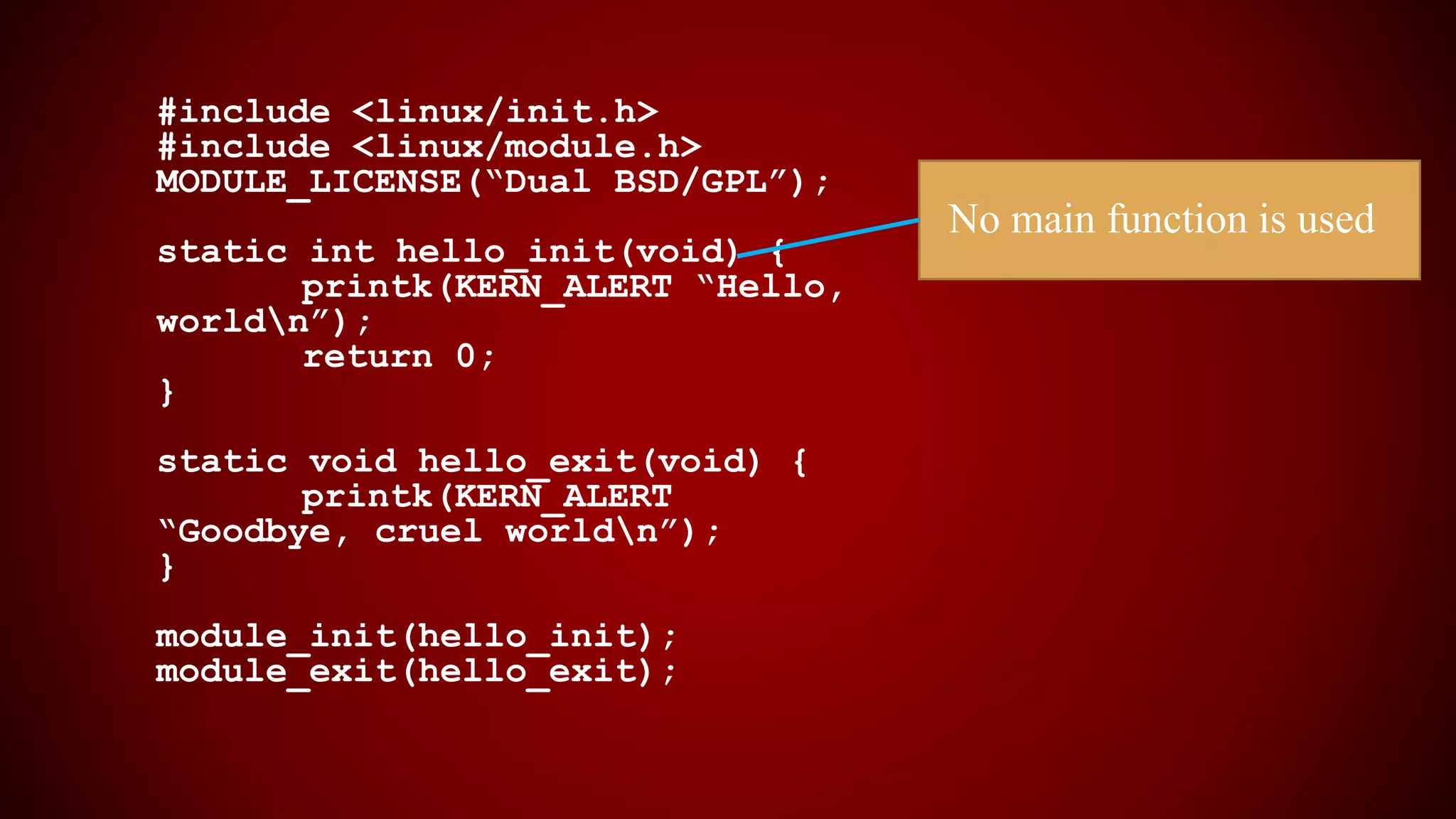
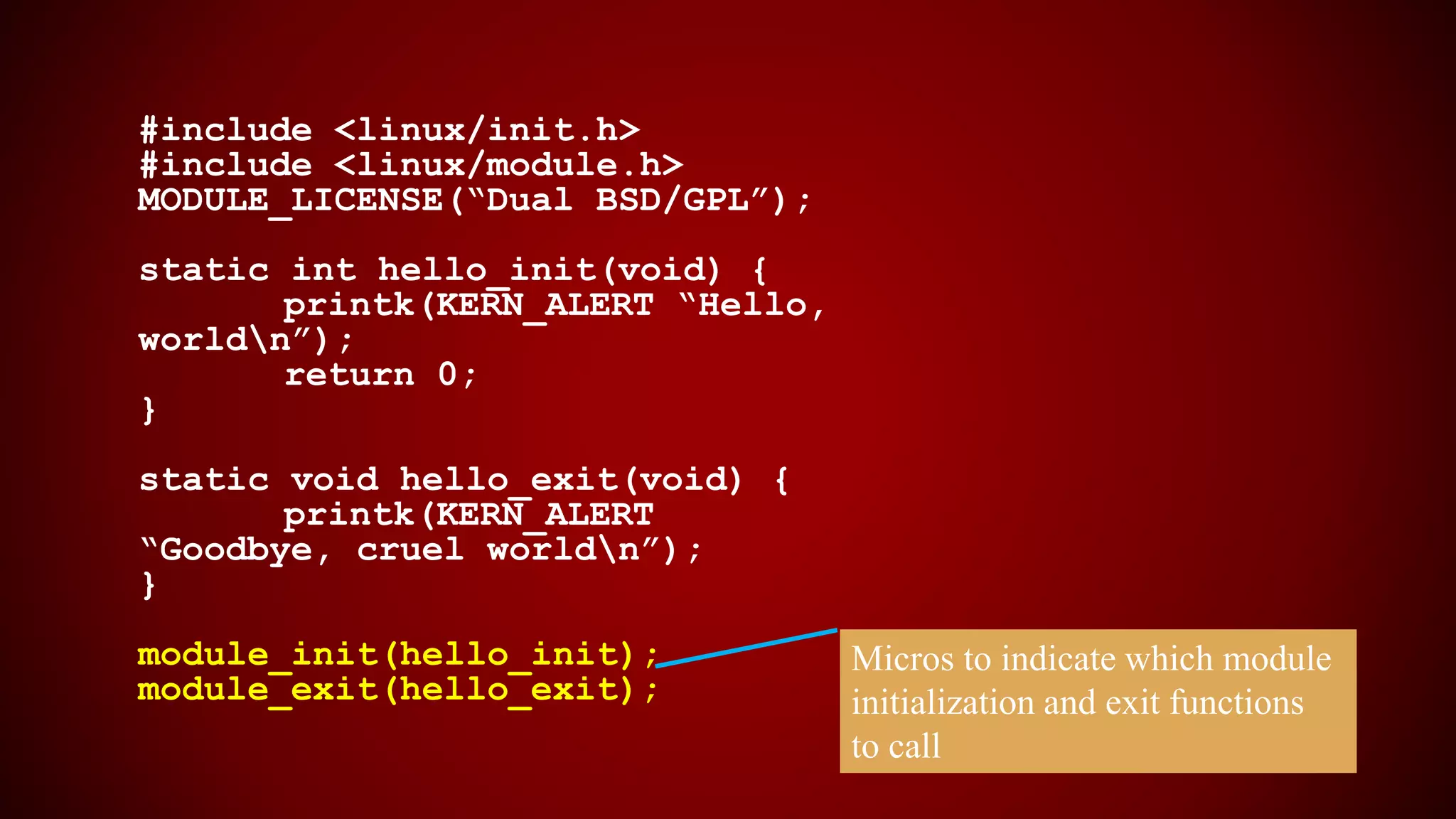
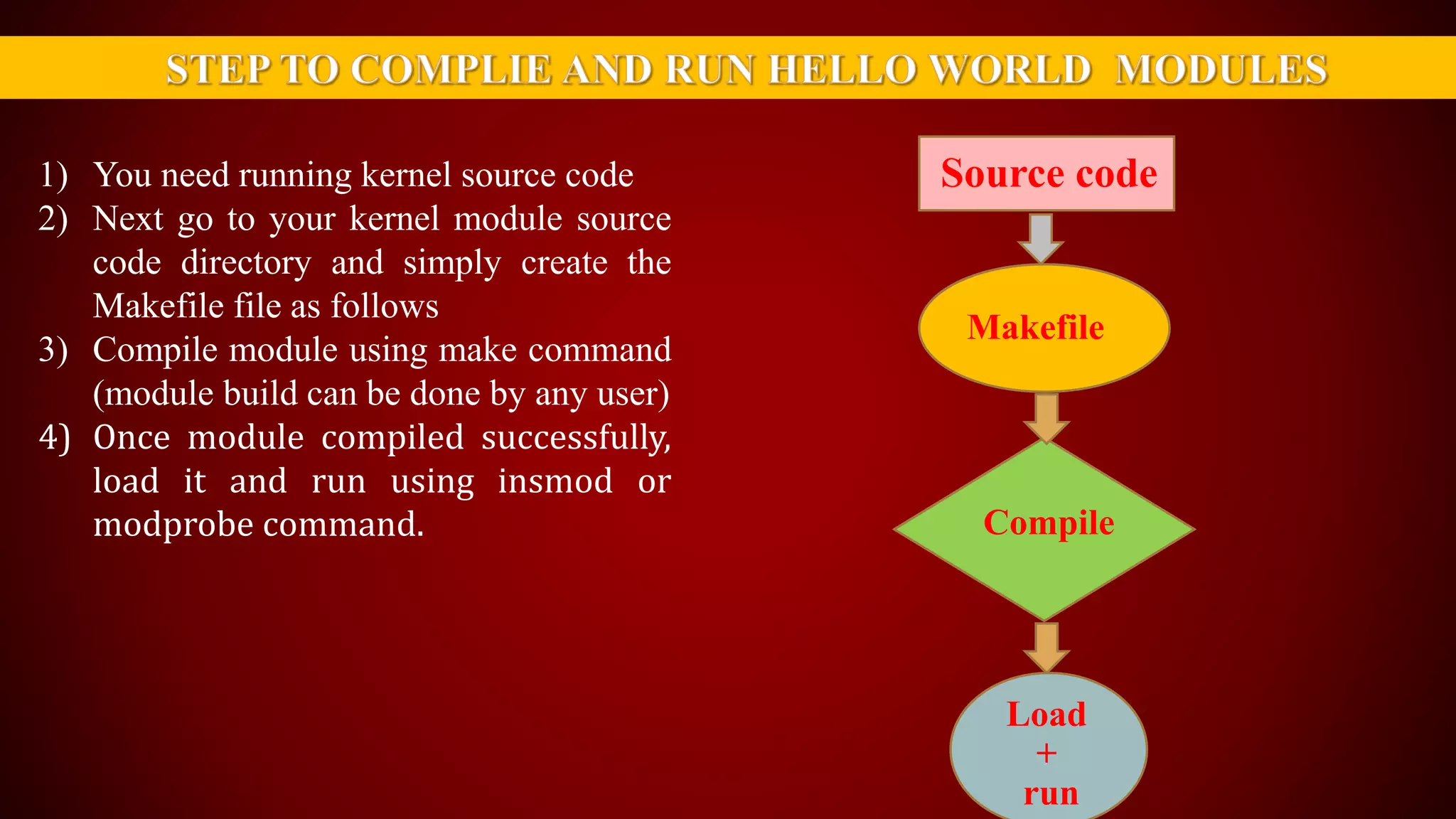
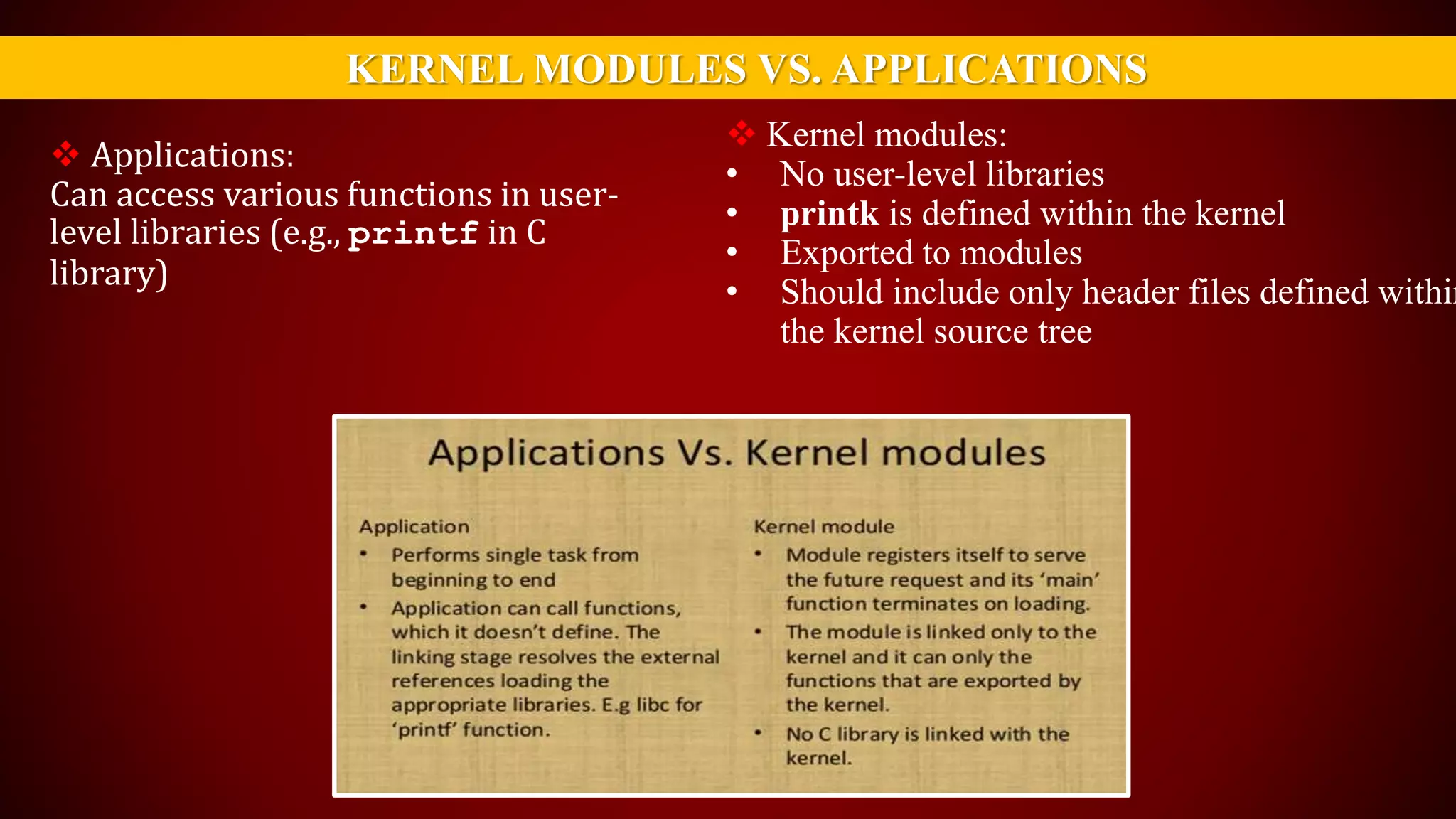
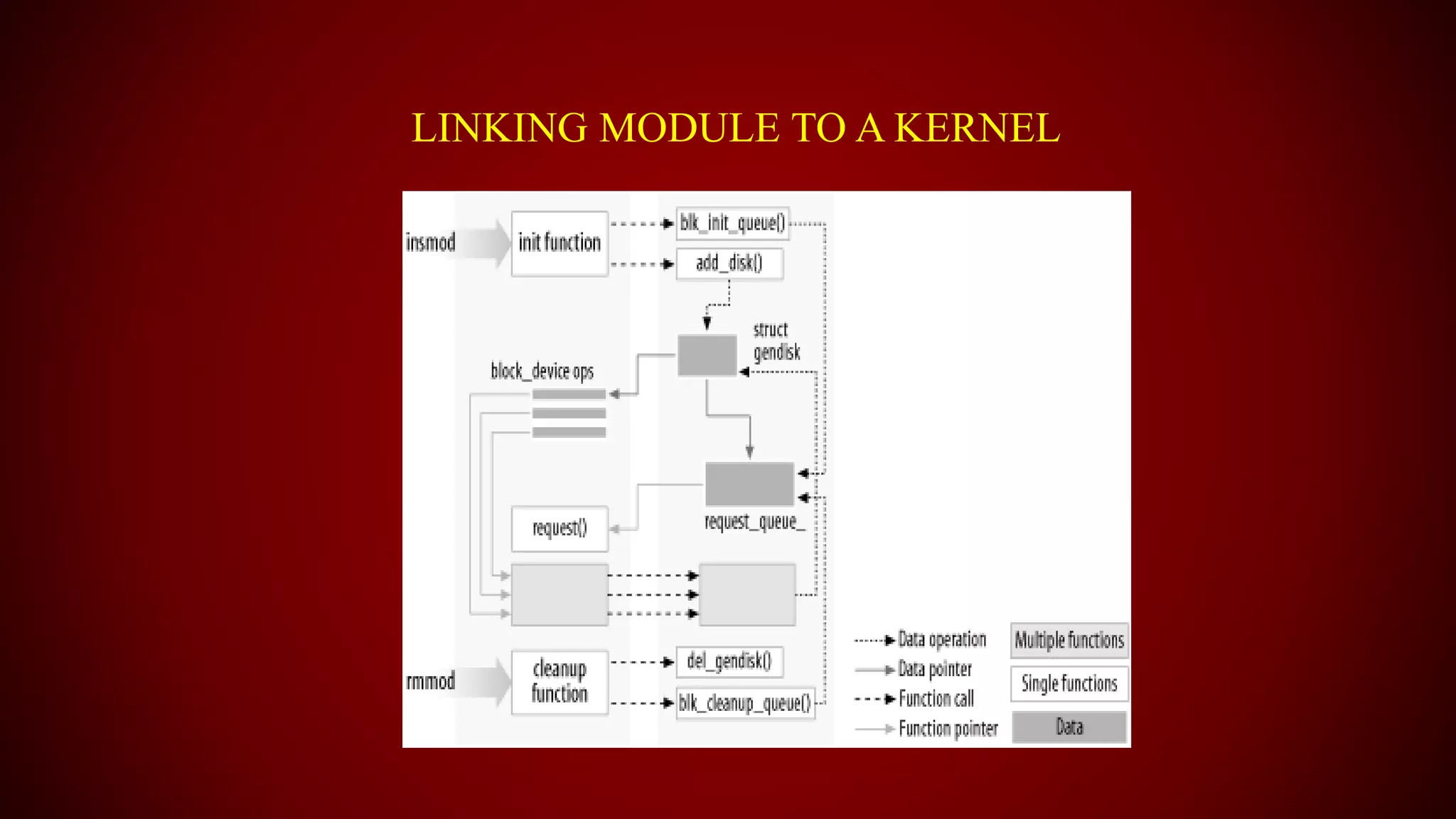
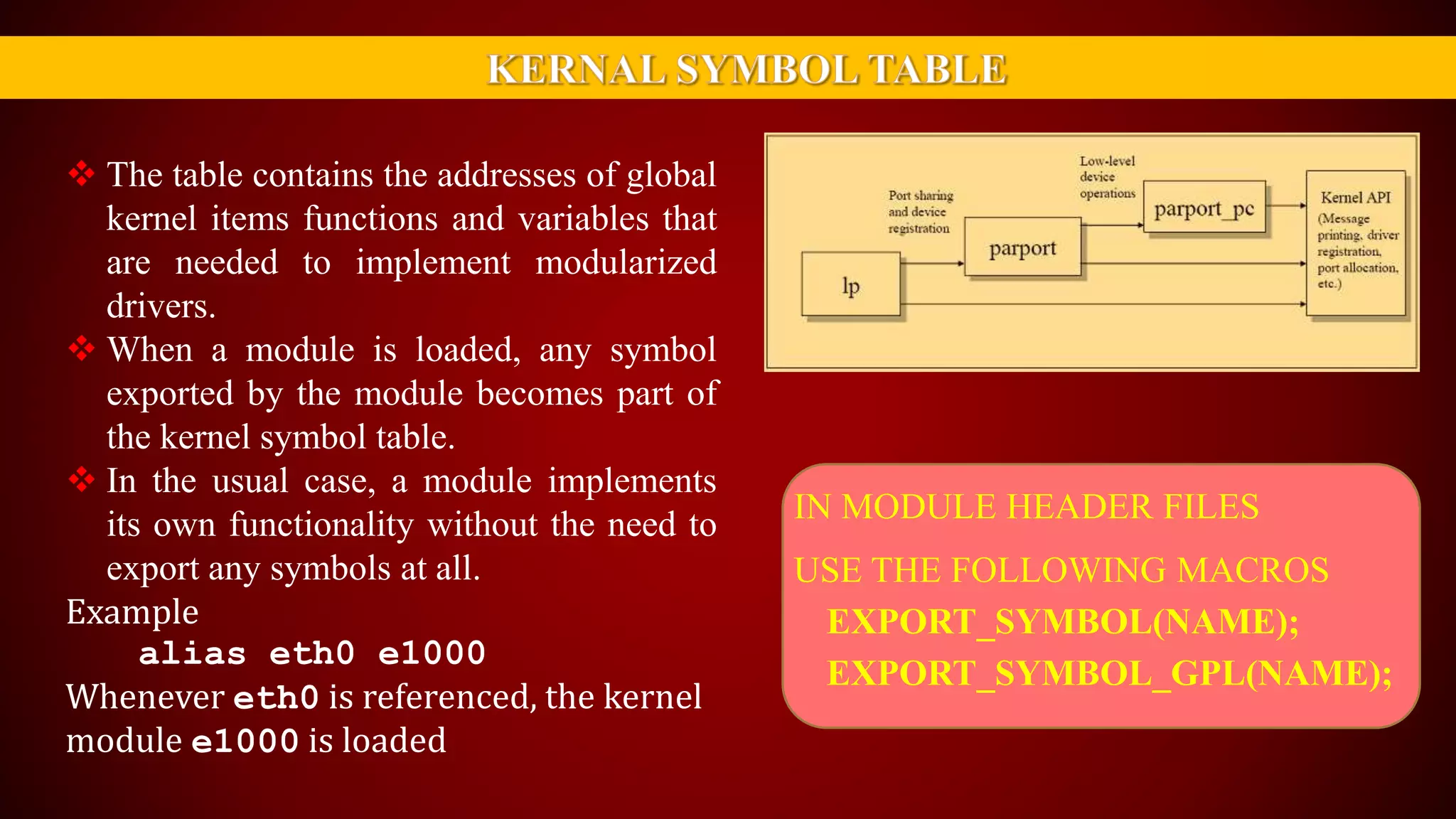
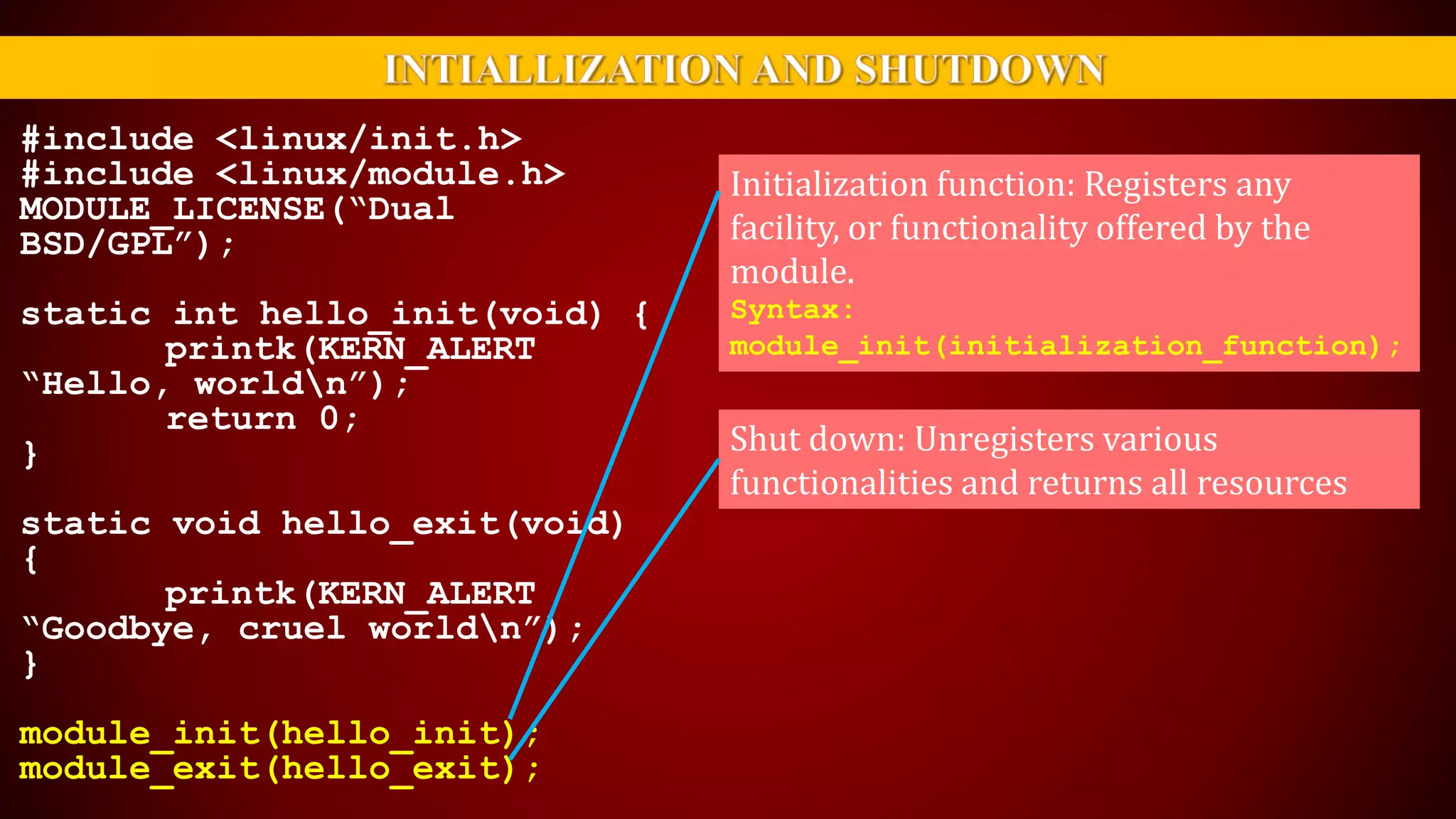
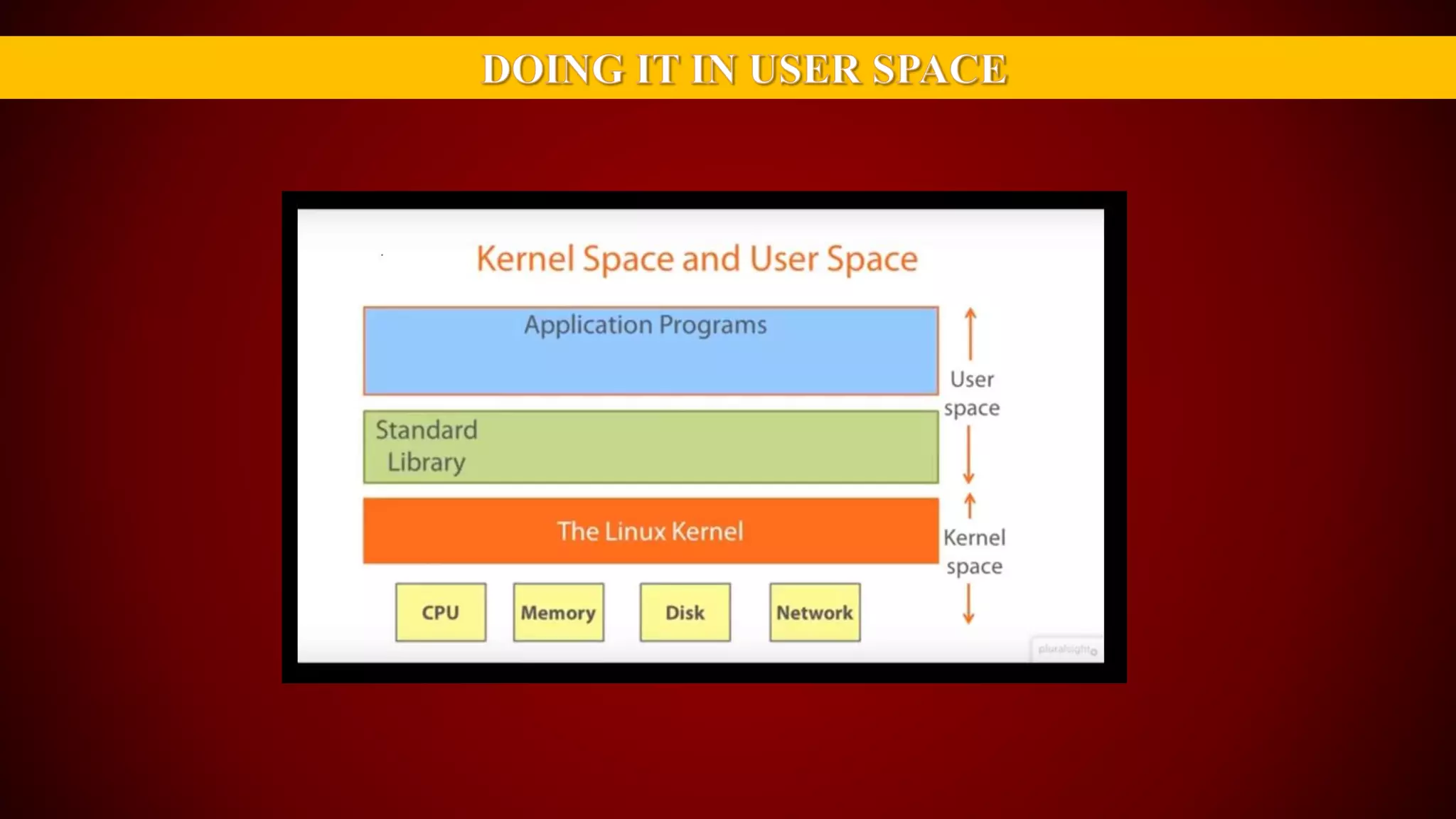
The document provides an overview of the Linux kernel, focusing on device drivers and their roles in managing hardware interactions. It discusses various types of device drivers, including character, block, and network devices, along with their functionalities and relationships within the kernel framework. Additionally, it touches on security concerns, versioning, and how to implement and load kernel modules.