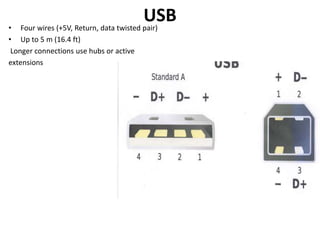
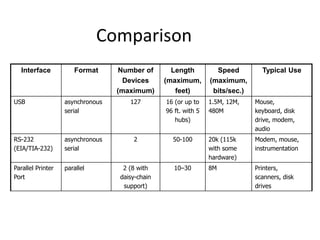
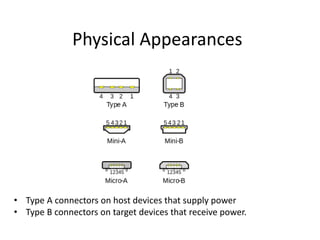
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a standard interface that allows devices to connect to computers and other electronic devices. USB provides a serial bus for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, printers, and more. It offers benefits like ease of use, automatic configuration, hot pluggability, and sometimes not requiring separate power for low-power devices. USB has evolved through several generations, starting with USB 1.0 in 1994 and increasing speeds with USB 2.0 and 3.0. It uses different connector types on hosts and targets and can connect up to 127 devices through hubs.