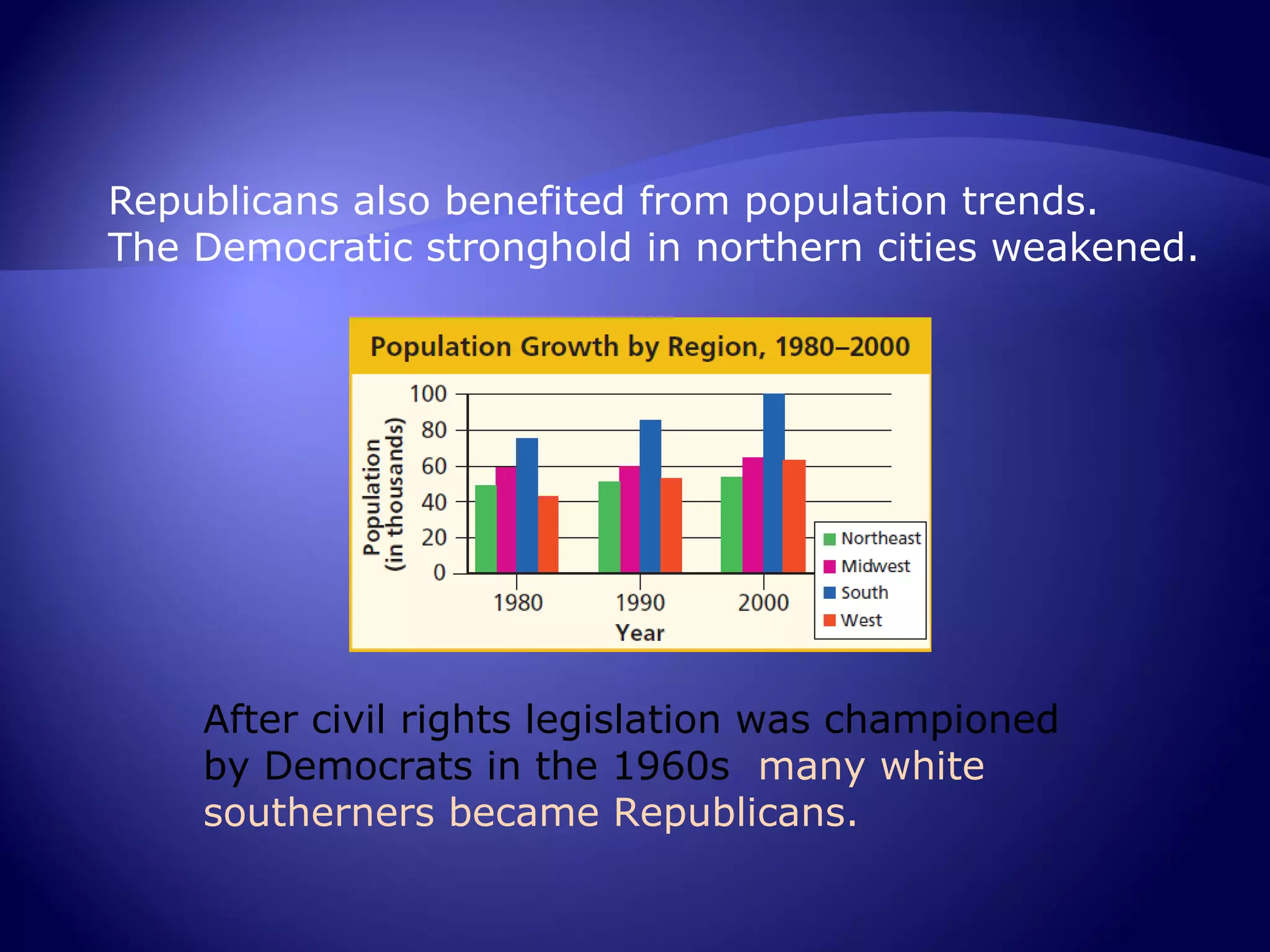
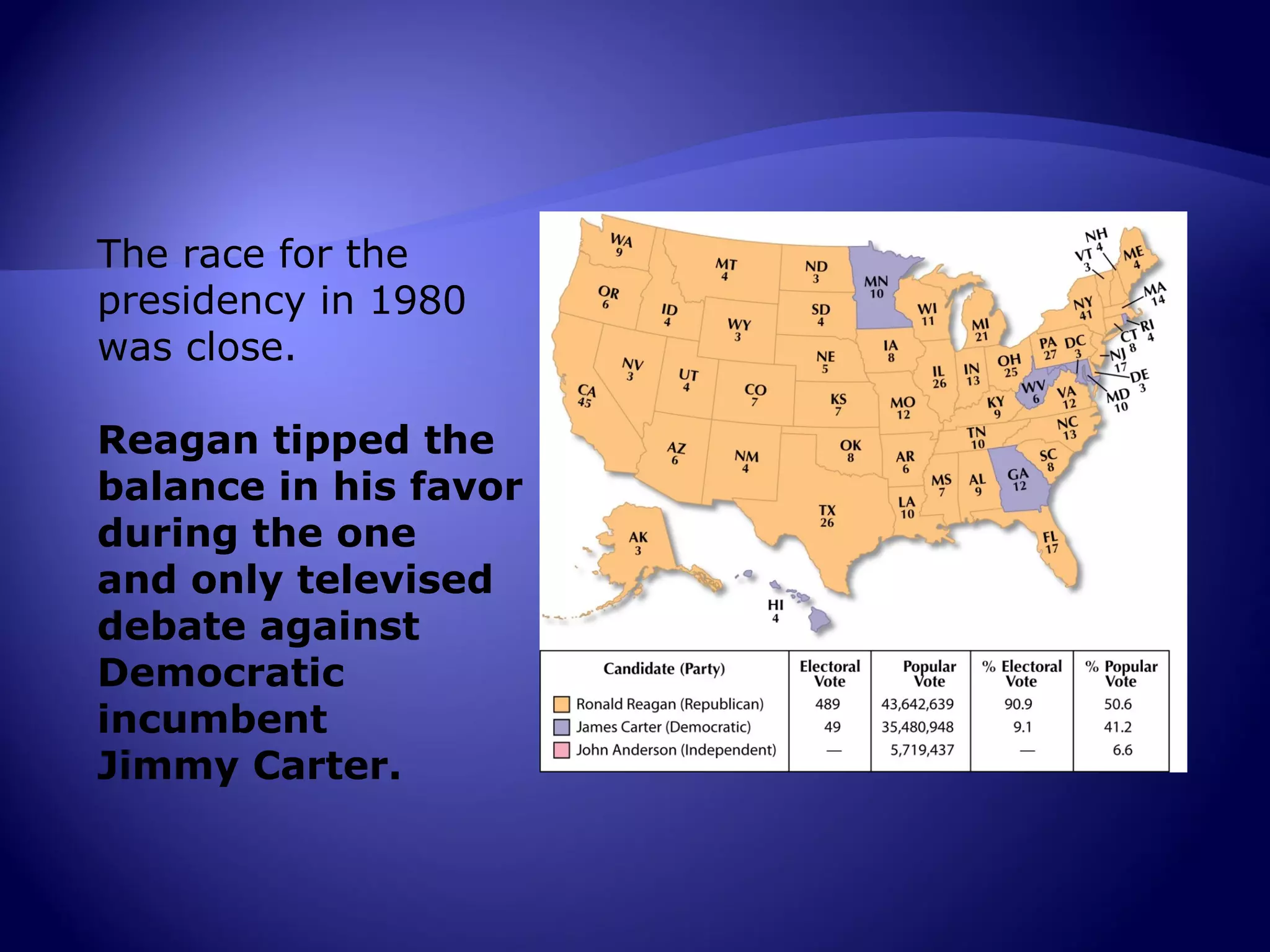
The rise of conservatism in the early 1980s was fueled by public discontent with liberal social programs and economic issues like high taxes and inflation during the 1970s. Conservatives argued for limited government, lower taxes, and traditional social values. Ronald Reagan successfully tapped into this conservative movement and was elected president in 1980, representing a significant shift toward more conservative policies that shaped the nation for decades. His election marked the ascendance of the modern conservative movement in American politics.