Jimmy Carter's presidency was marked by several key events and challenges:
1) He brokered the historic Camp David Accords between Egypt and Israel in 1978.
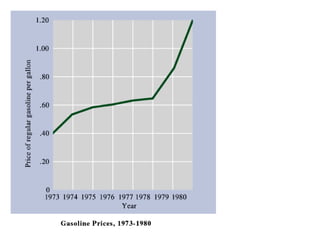
2) However, his presidency was hampered by stagflation, the Iran hostage crisis, and the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan.
3) He lost his bid for reelection in 1980 to Ronald Reagan in a landslide as Americans had lost confidence in his leadership.