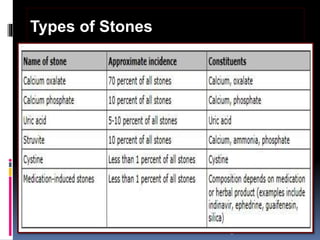
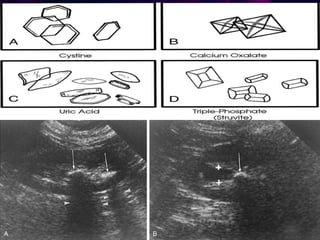
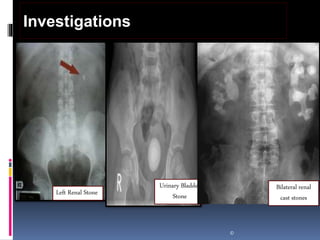
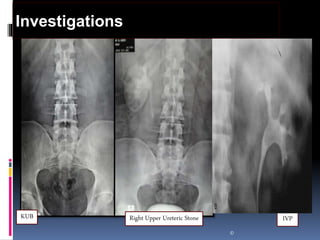
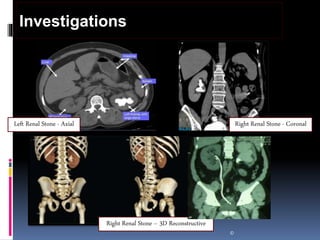
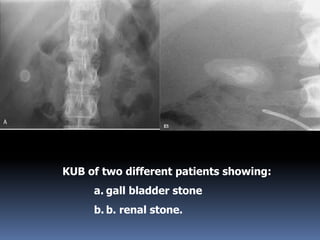
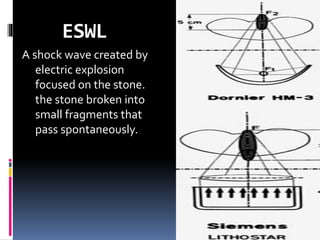
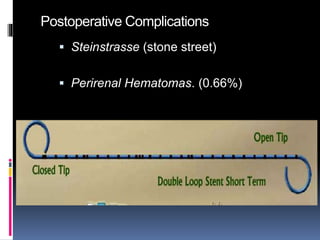
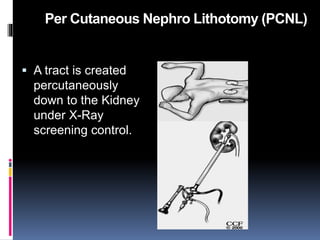
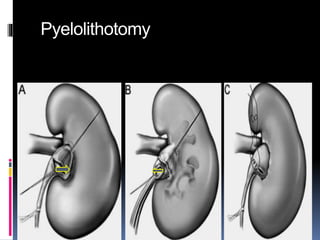
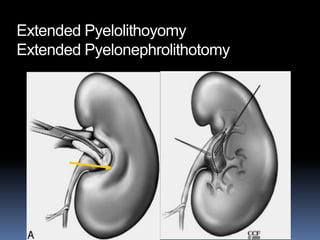
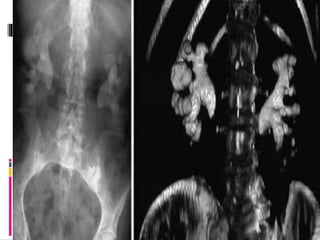
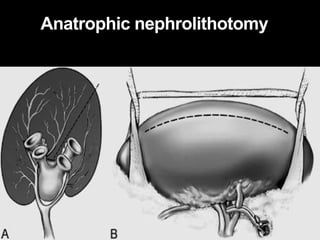
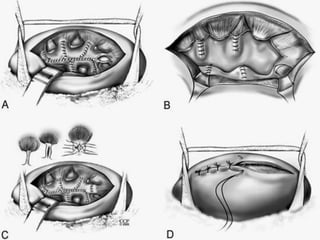
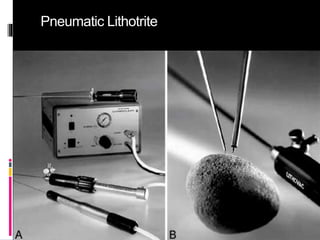
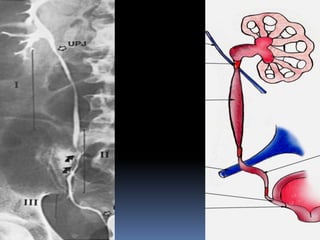
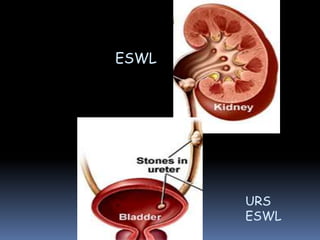
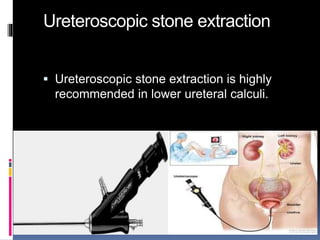
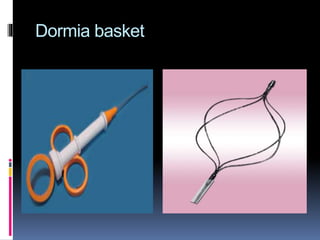
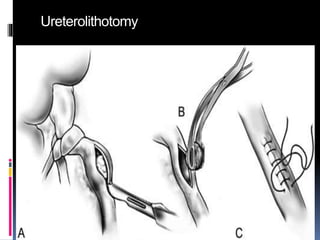
This document summarizes urolithiasis (kidney stone disease). It discusses the epidemiology, risk factors, types of stones, clinical presentation, investigations, treatment options, and prevention strategies. The peak age for stones is 20-40 years. Risk factors include excess calcium, oxalate, or uric acid in the urine. Common stone types are calcium oxalate, uric acid, cystine, and struvite. Clinical symptoms depend on the location of the stone and include flank pain, hematuria, and obstruction. Investigations include imaging like CT, IVU, ultrasound and metabolic workup. Treatment involves medical expulsion therapy, ESWL, ureteroscopy, percutaneous neph