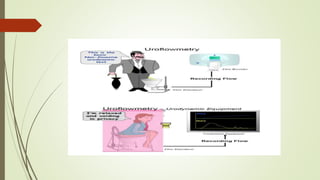
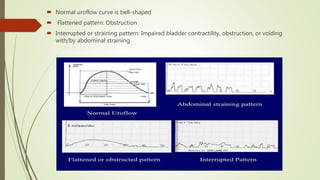
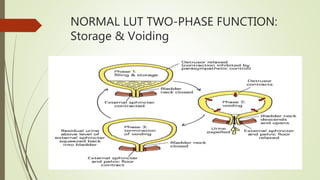
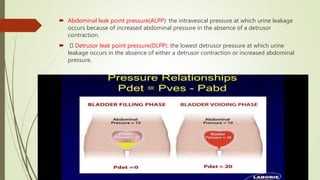
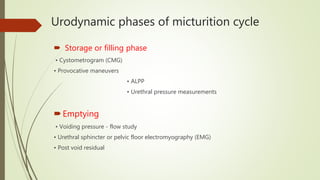
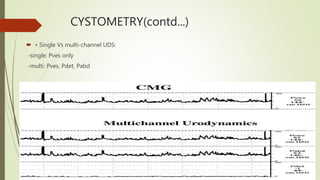
Urodynamics tests the storage and voiding functions of the lower urinary tract through various tests like cystometry, uroflowmetry, and pressure-flow studies. Cystometry measures pressure-volume relationships during bladder filling and looks at parameters like compliance, capacity, and detrusor activity. Uroflowmetry analyzes urine flow over time through variables like maximum flow rate and voiding time. Together these tests can characterize detrusor and outlet functions, diagnose neuropathies, and determine the cause of lower urinary tract symptoms when other evaluations are inconclusive. The tests are indicated for incontinence, outflow obstruction, neurogenic bladder dysfunction, and voiding problems in children.











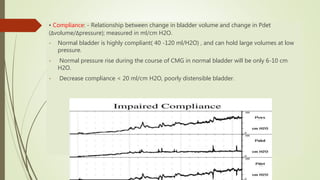
![Impaired compliance is seen in
• neurologic conditions: spinal cord injury/lesion, spina bifida, usually results from increased
outlet resistance (e.g., detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia [DESD]) or decentralization in
the case of lower motor neuron lesions,
• Long-term BOO (e.g., from benign prostatic obstruction),
• Structural changes- radiation cystitis or tuberculosis.
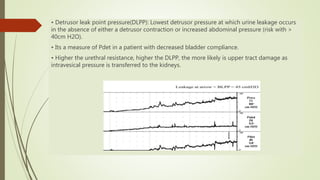
• Impaired compliance with prolonged elevated storage pressures is a urodynamic risk
factor and needs treatment to prevent renal damage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftpowerpoint-211126201102/85/Urodynamics-17-320.jpg)