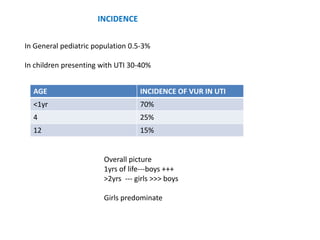
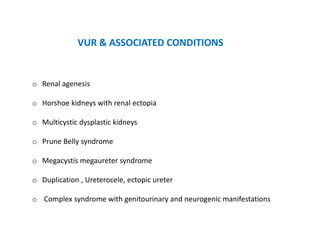
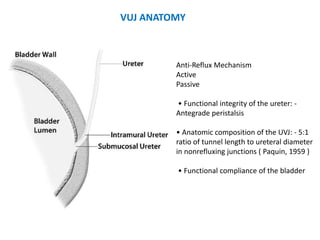
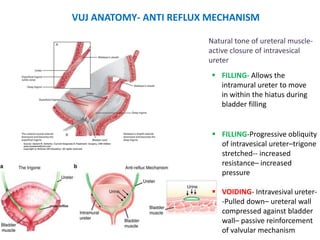
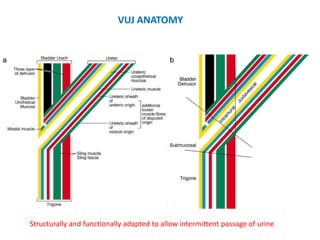
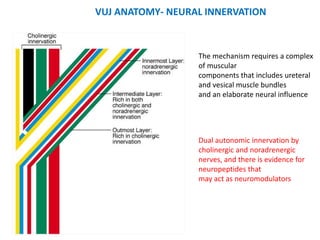
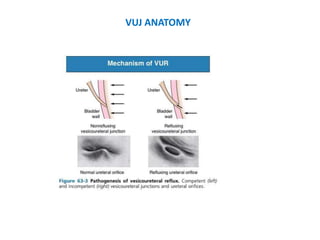
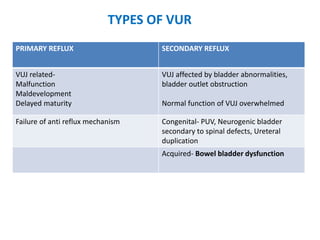
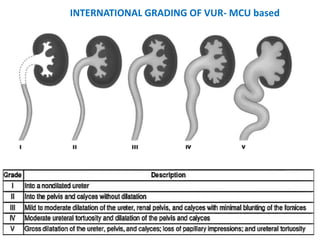
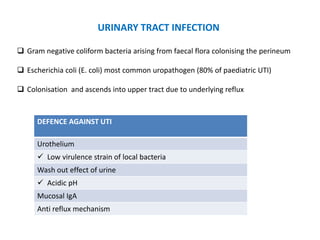
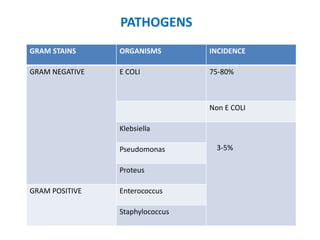
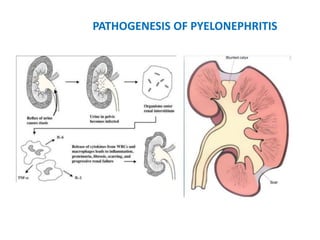
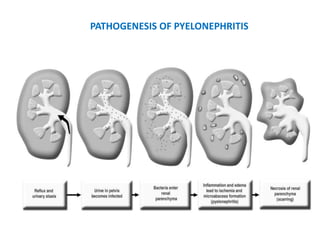
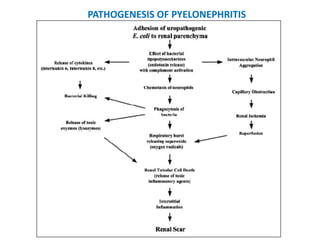
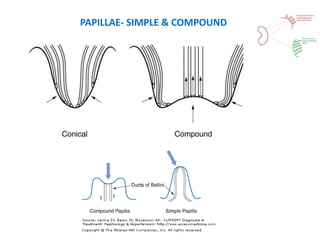
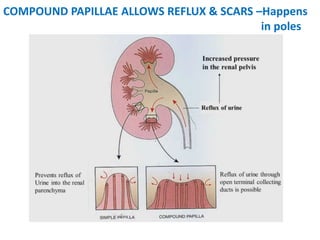
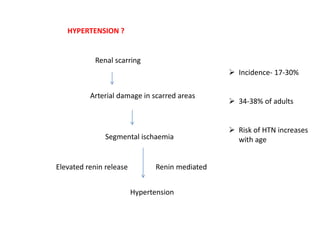
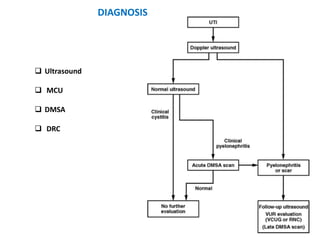
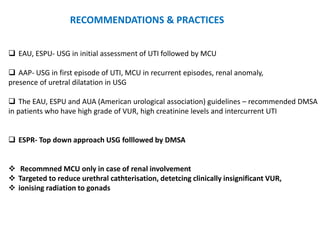
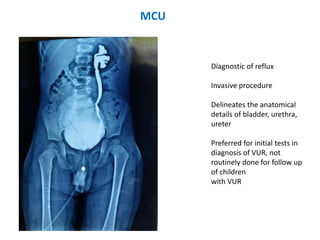
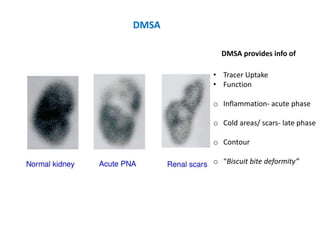
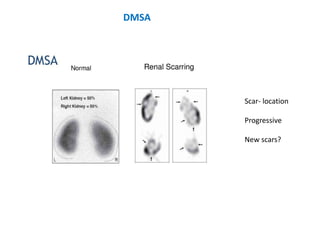
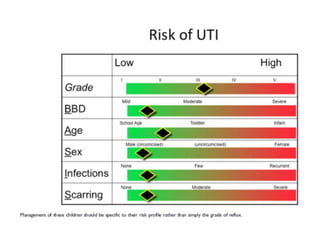
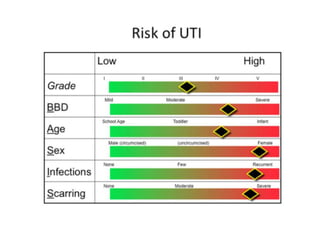
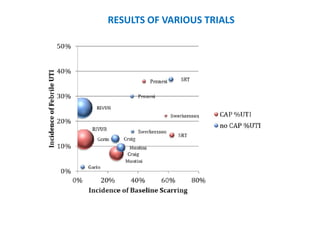
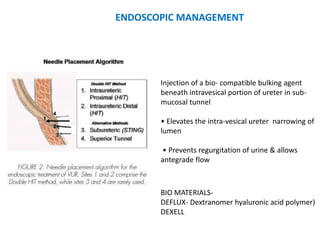
Vesicoureteric reflux (VUR) is a common condition in children where urine flows backward from the bladder into the ureters or kidneys. It can lead to urinary tract infections and renal scarring. The document discusses the anatomy, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of VUR. Management involves continuous antibiotic prophylaxis, endoscopic injection, or open surgical correction depending on the grade of reflux and individual patient factors. Spontaneous resolution is more likely for lower grades of reflux and in younger children. Bowel and bladder dysfunction can complicate management and decrease resolution rates.