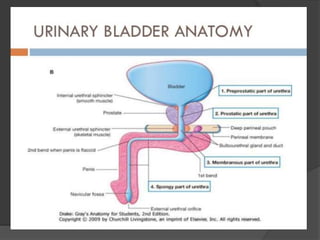
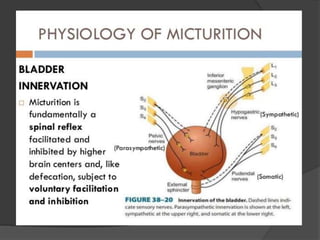
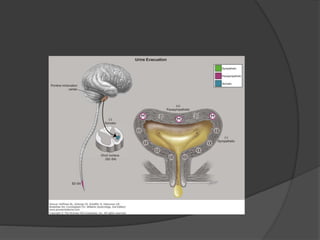
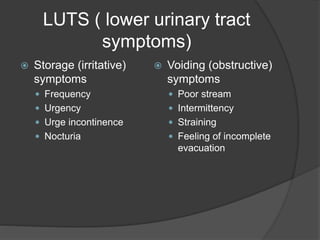
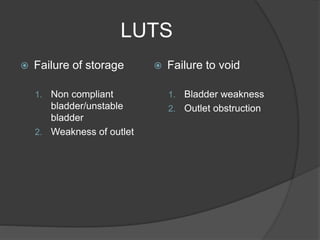
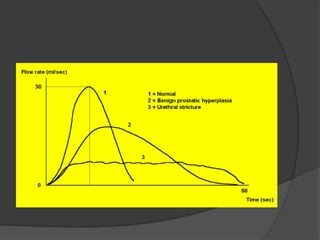
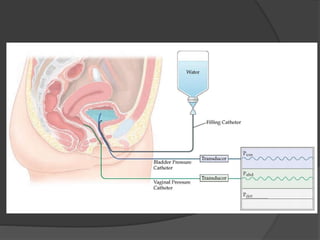
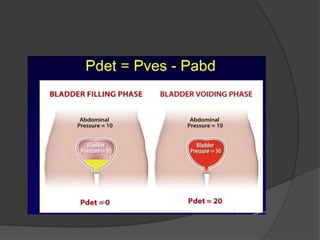
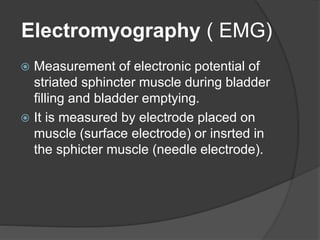
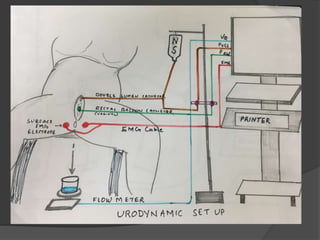
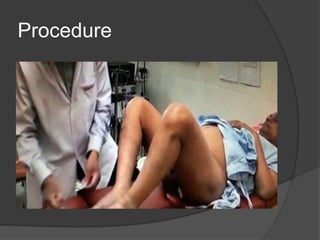
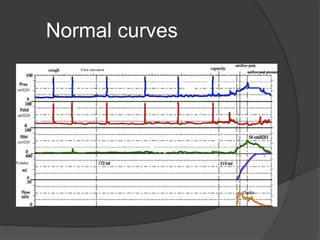
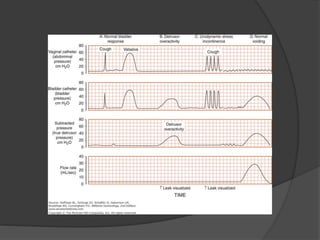
This document discusses urodynamics, which involves testing to evaluate lower urinary tract symptoms. It describes the components of a urodynamic study including uroflowmetry, cystometrography, and pressure flow study. Common indications for urodynamics include evaluating young males with untreated LUTS, neurogenic bladder issues, and mixed urinary incontinence. The document outlines the procedure, parameters evaluated, normal values, and how urodynamics can help guide appropriate treatment.