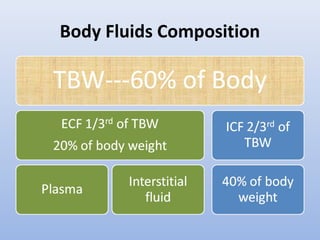
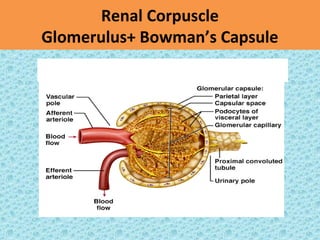
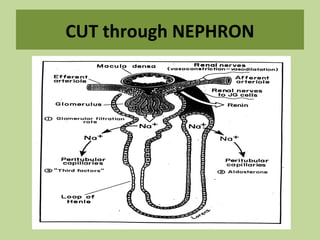
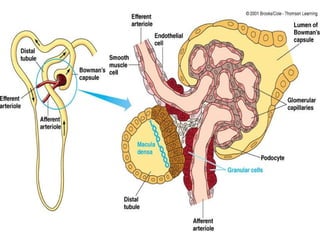
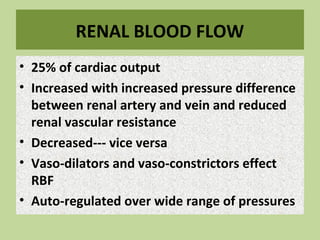
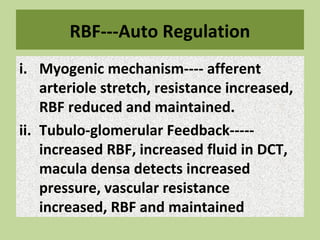
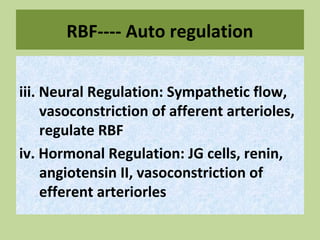
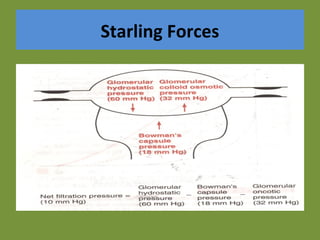
Urine is formed via glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion in the nephron. Glomerular filtration is the initial process where plasma is filtered from the renal bloodstream into Bowman's capsule through small pores in the glomerular capillaries. The glomerular filtration rate measures the volume of filtrate produced per unit of time and is a key indicator of kidney function. Filtration occurs due to Starling forces and other factors that allow plasma and solutes but not cells to pass through the glomerular membrane into the filtrate.