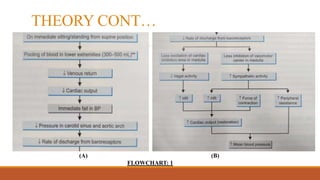
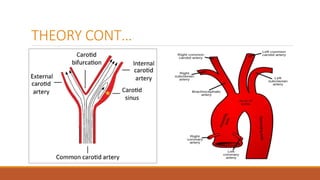
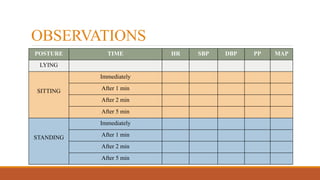
The document explores the effects of postural changes on blood pressure and heart rate, highlighting how gravity causes fluid redistribution, resulting in decreased venous return and blood pressure when a person changes position. It outlines a procedural method for measuring these changes with specific apparatus and precautions, emphasizing the clinical significance in assessing autonomic nervous system integrity and identifying postural hypotension. The findings are particularly relevant for individuals in professions requiring prolonged standing, advising measures to enhance venous return.