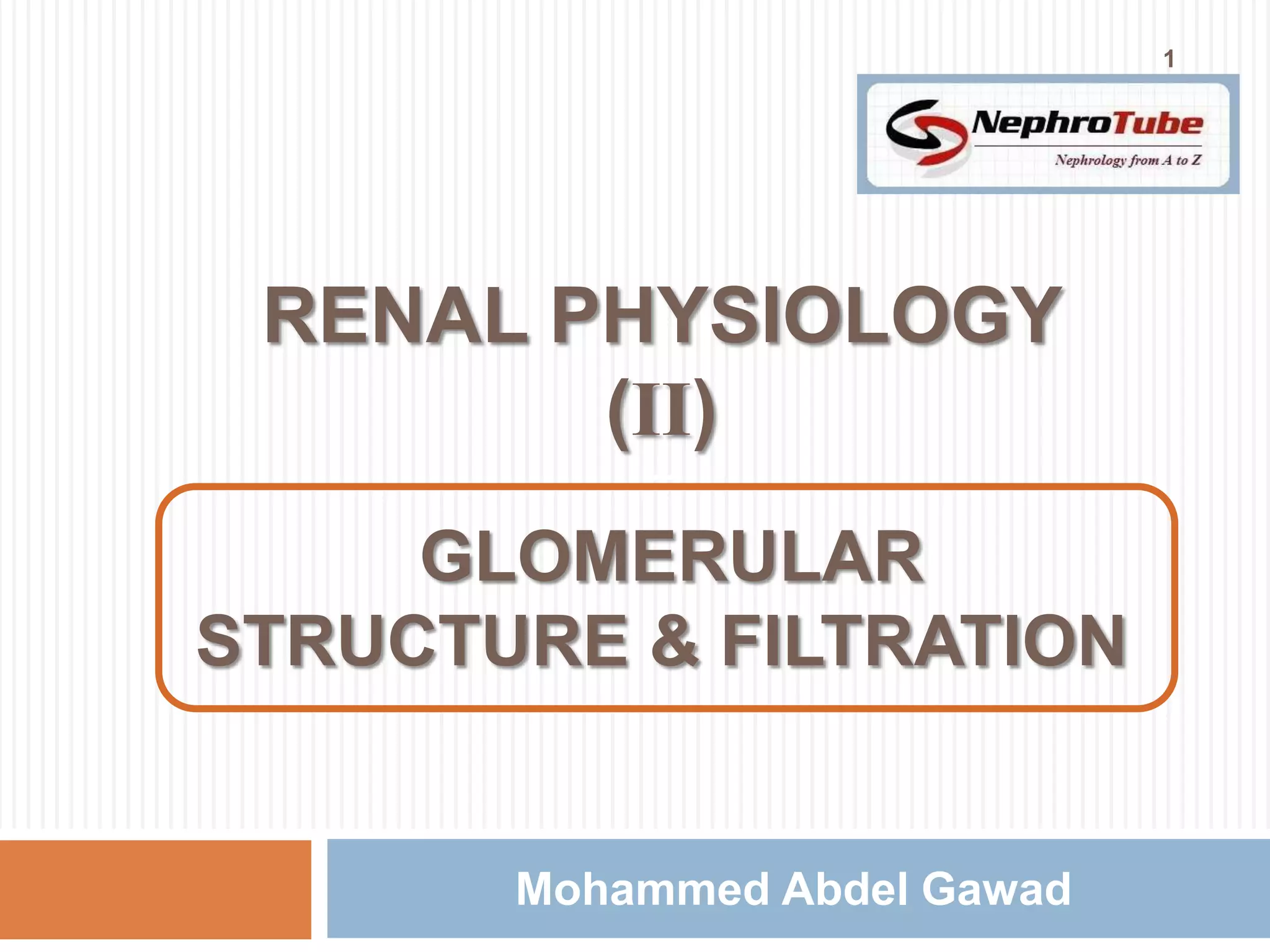
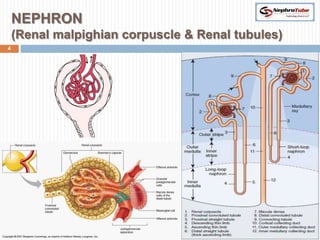
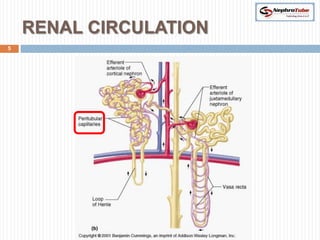
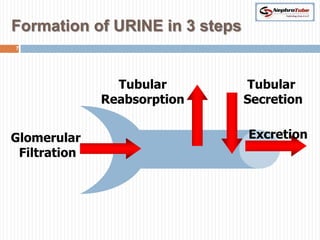
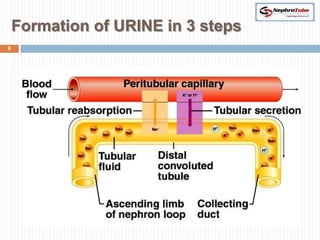
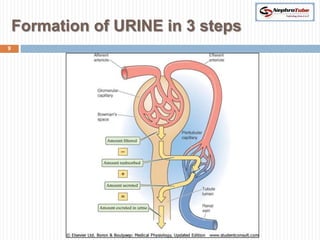
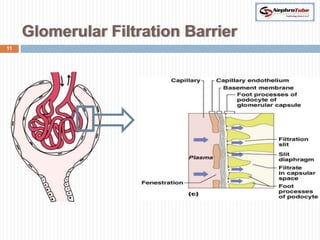
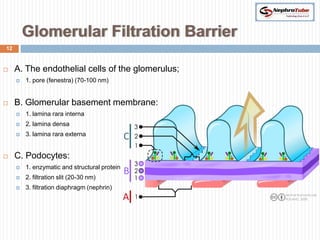
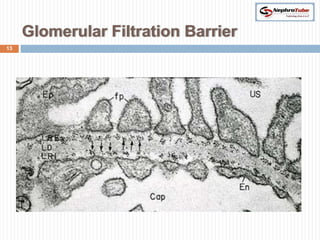
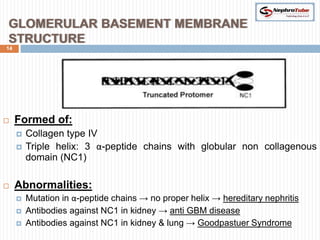
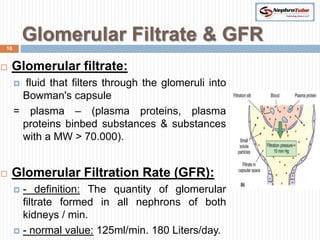
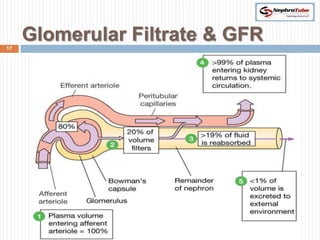
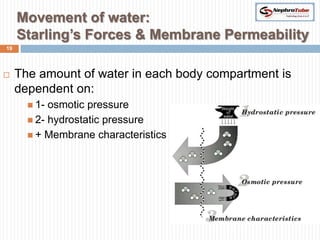
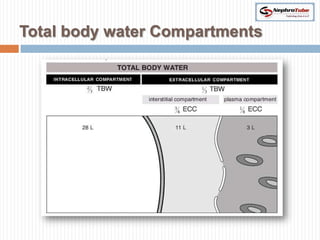
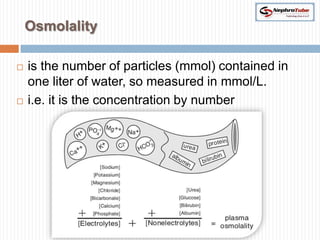
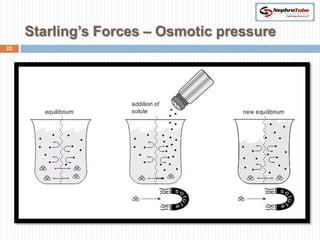
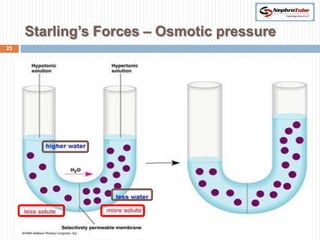
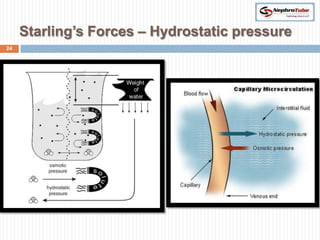
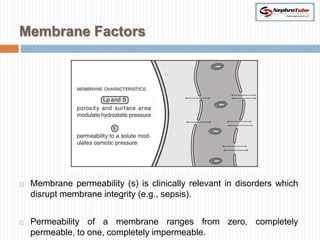
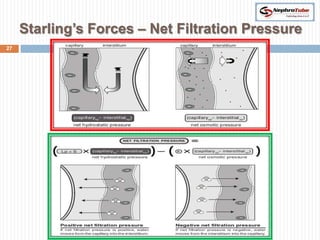
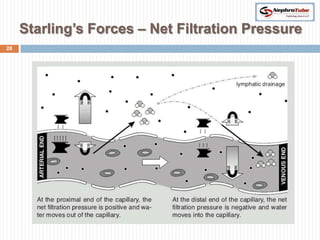
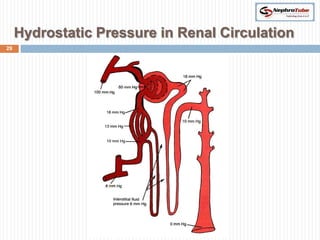
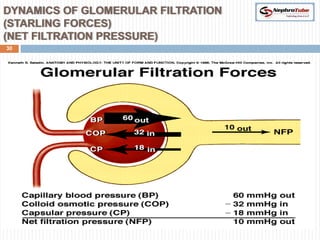
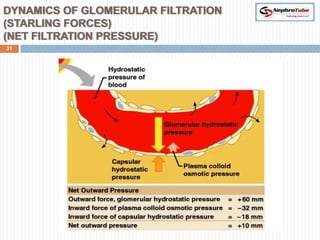
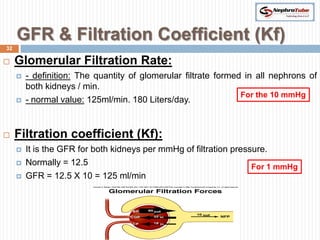
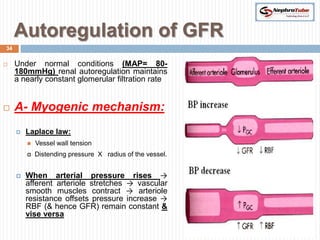
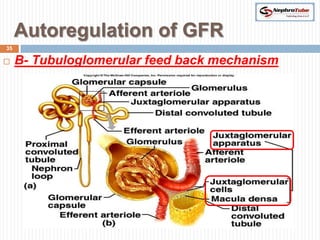
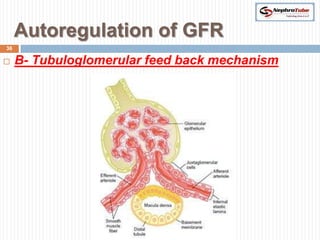
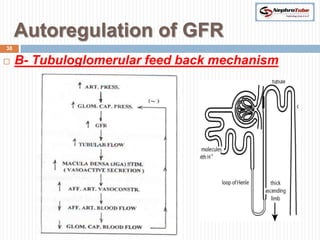
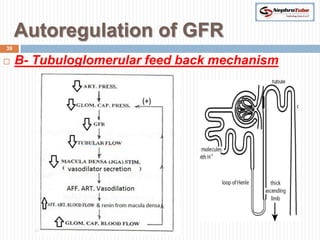
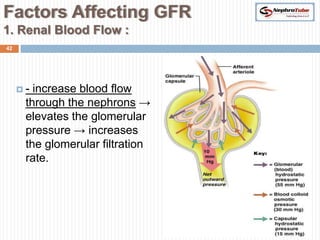
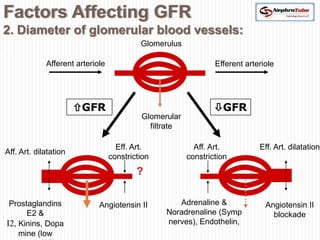
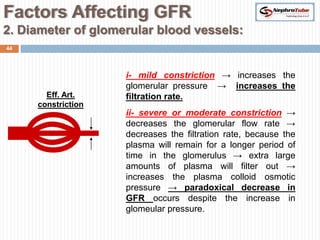
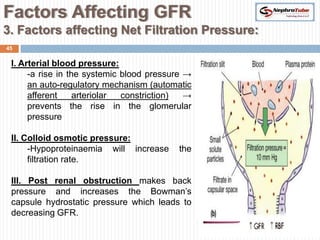
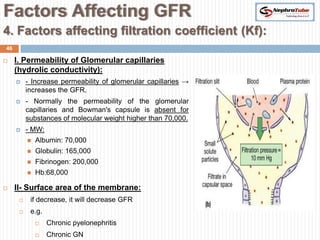
The document covers key concepts in renal physiology, focusing on nephron structure, renal circulation, and urine formation through glomerular filtration. It describes the glomerular filtration barrier, the composition and dynamics of glomerular filtrate, and factors affecting glomerular filtration rate (GFR) including autoregulation mechanisms. Additionally, it highlights the importance of Starling’s forces and membrane permeability in renal function.