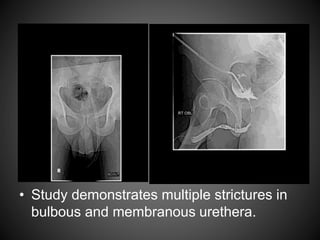
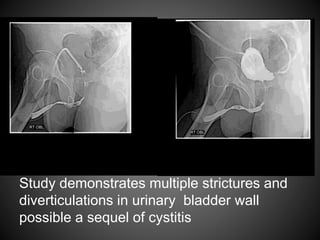
A 32-year-old male presented with a history of urinary retention and difficult catheterization. An antegrade urethrography revealed multiple strictures in the bulbous and membranous urethra as well as diverticulations in the bladder wall. He was diagnosed with gonococcal urethritis likely caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to his history of multiple sexual partners. Complications of gonorrhea can include urethral strictures, prostatitis, and infertility.






![RISK FACTORS
• Risk factors for gonorrhea include the following:
• Sexual exposure to an infected partner without barrier protection
(eg, failure to use a condom or condom failure) [13]
• Multiple sex partners
• Male homosexuality
• Low socioeconomic status
• Minority status - Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans have the
highest rates in the United States
• History of concurrent or past STDs
• Exchange of sex for drugs or money
• Use of crack cocaine
• Early age of onset of sexual activity
• Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) - Use of an intrauterine device
(IUD)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/urethro-160808101538/85/Urethro-9-320.jpg)









