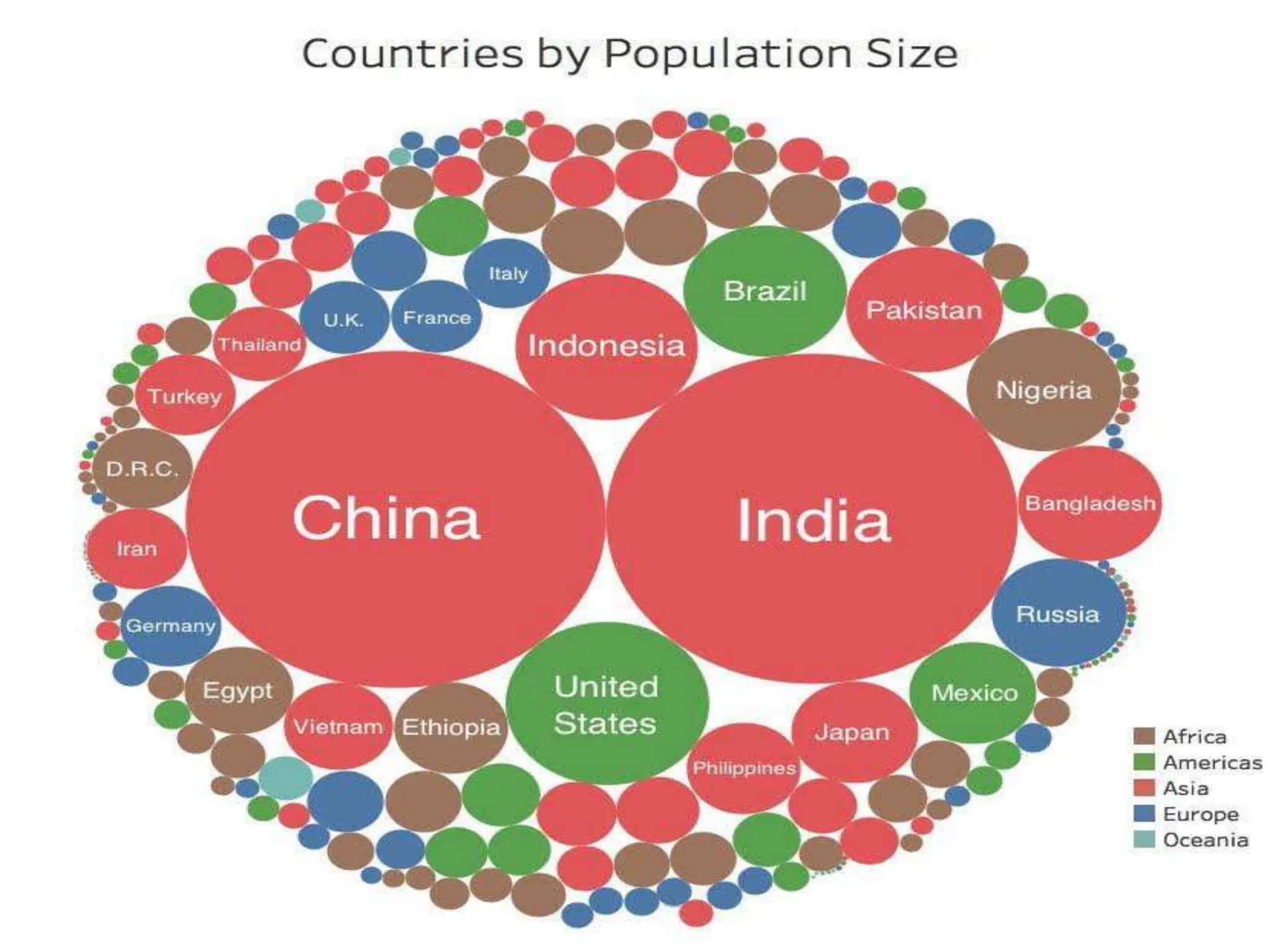
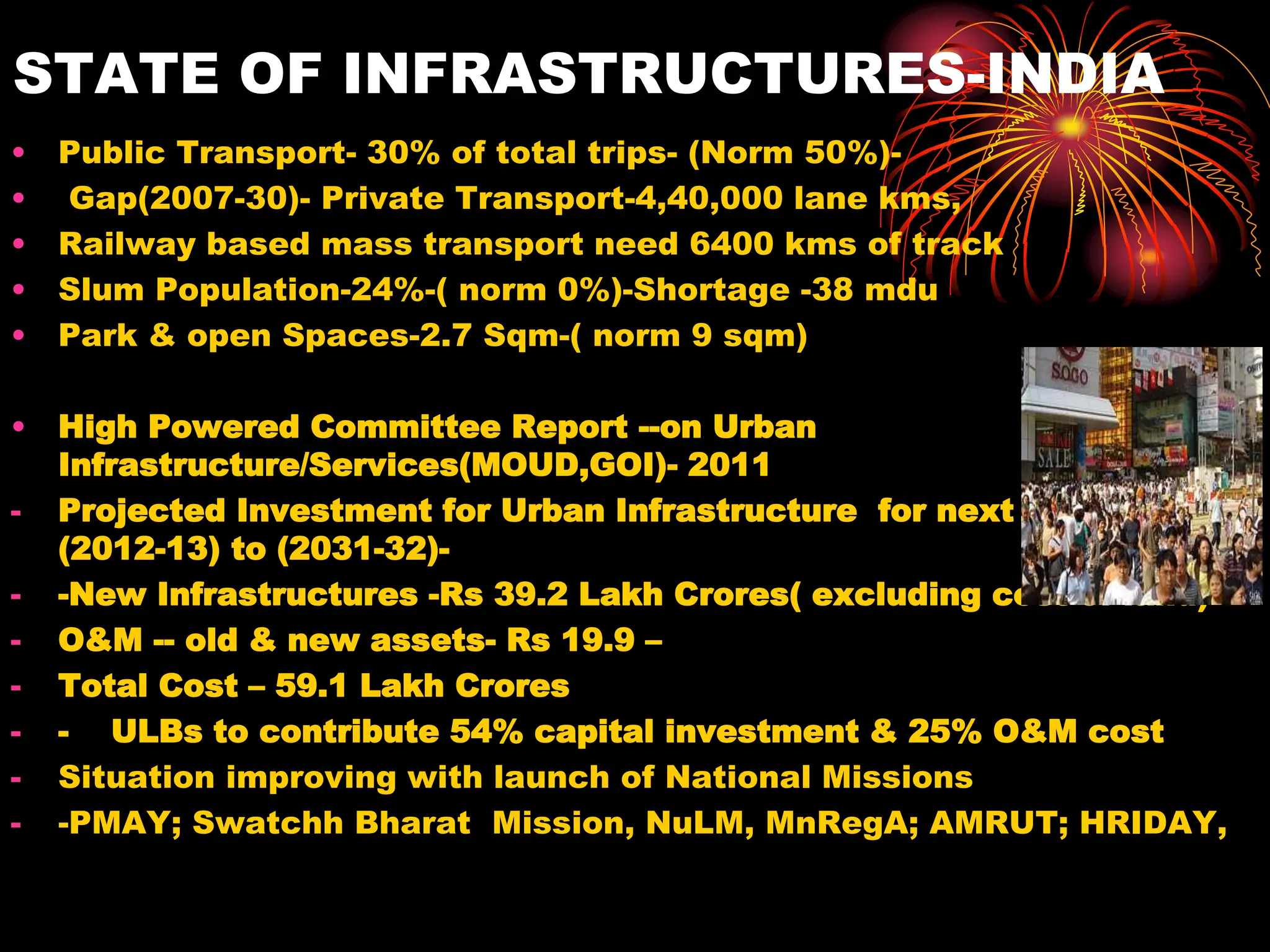
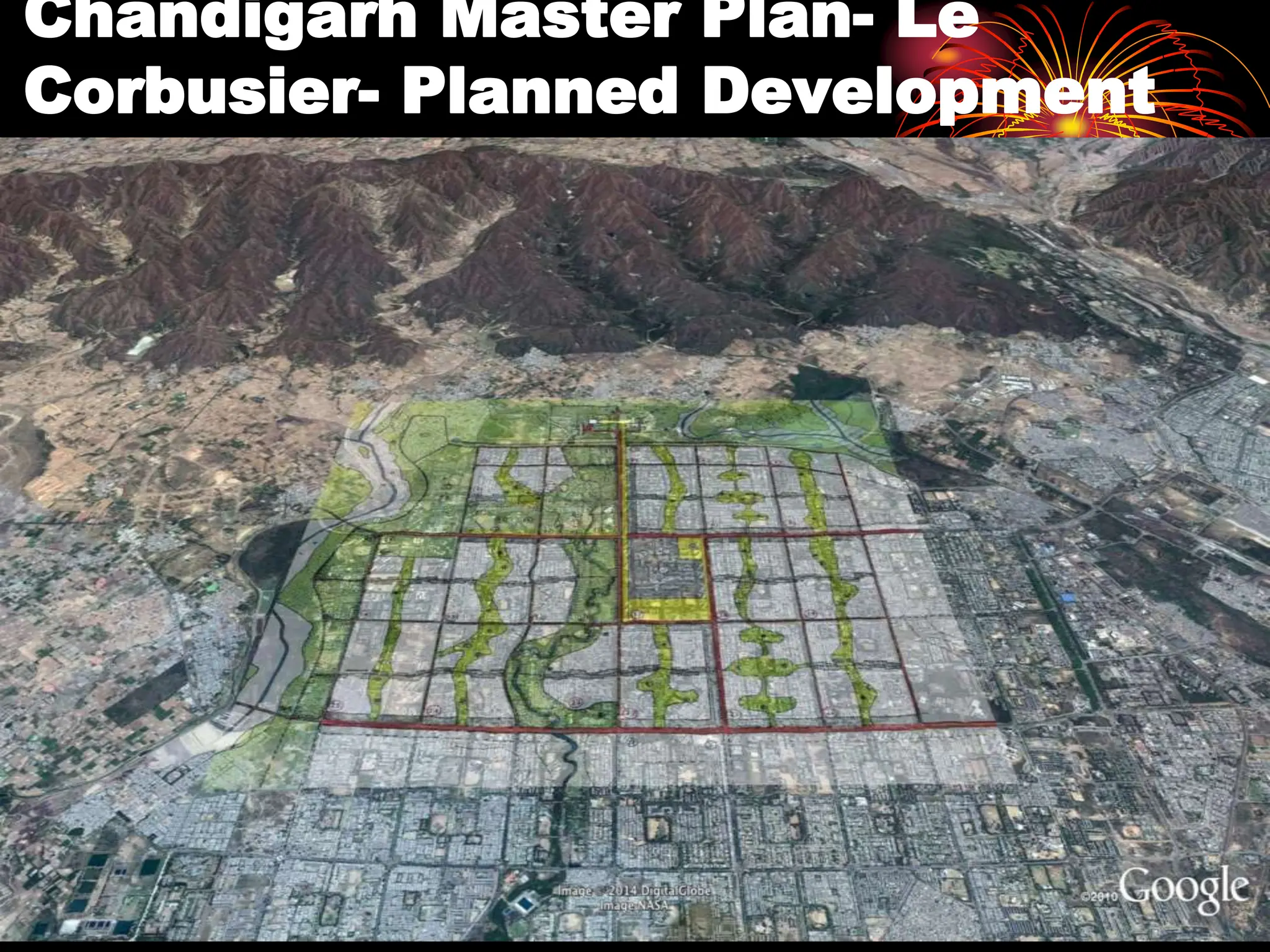
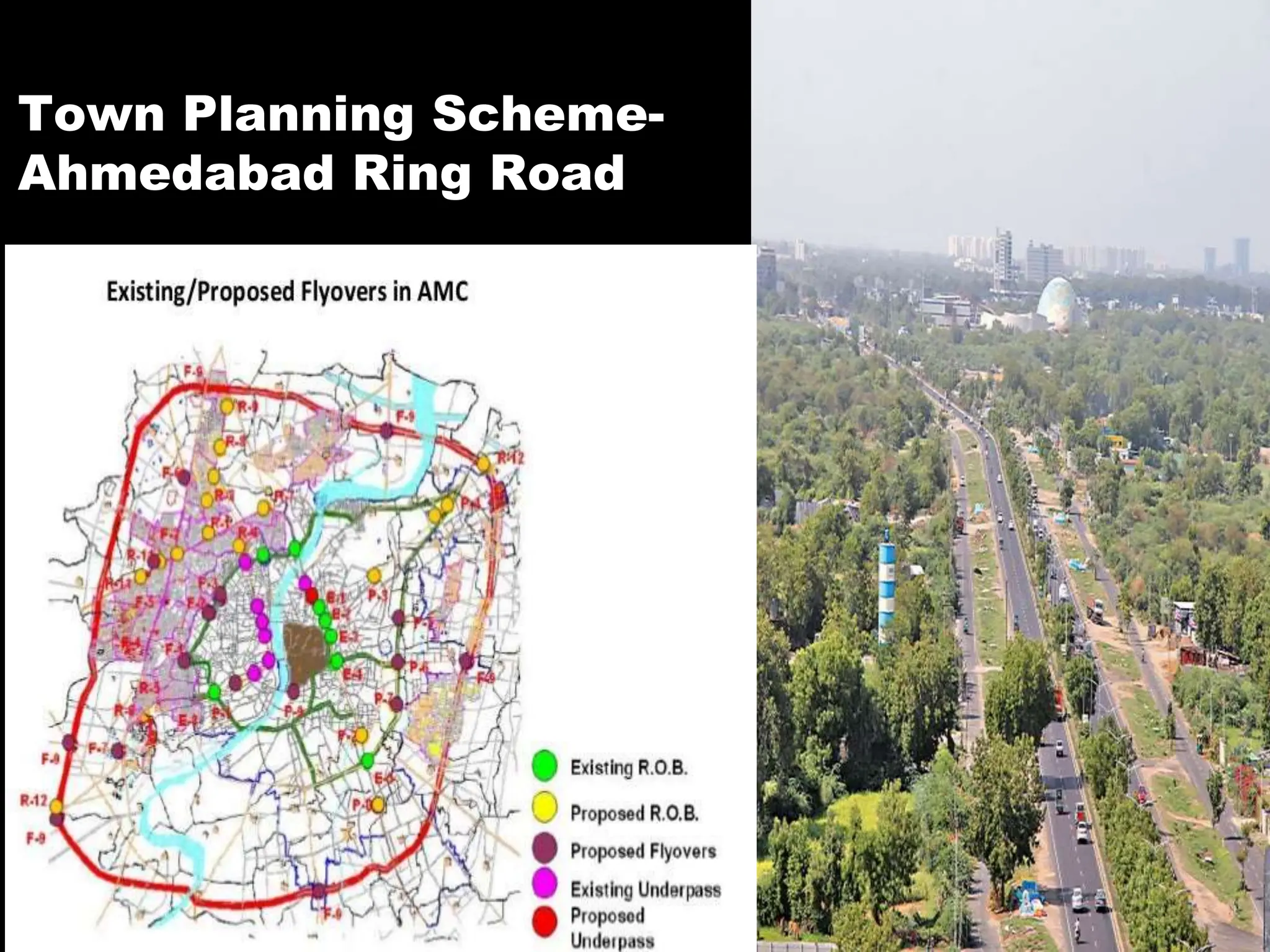
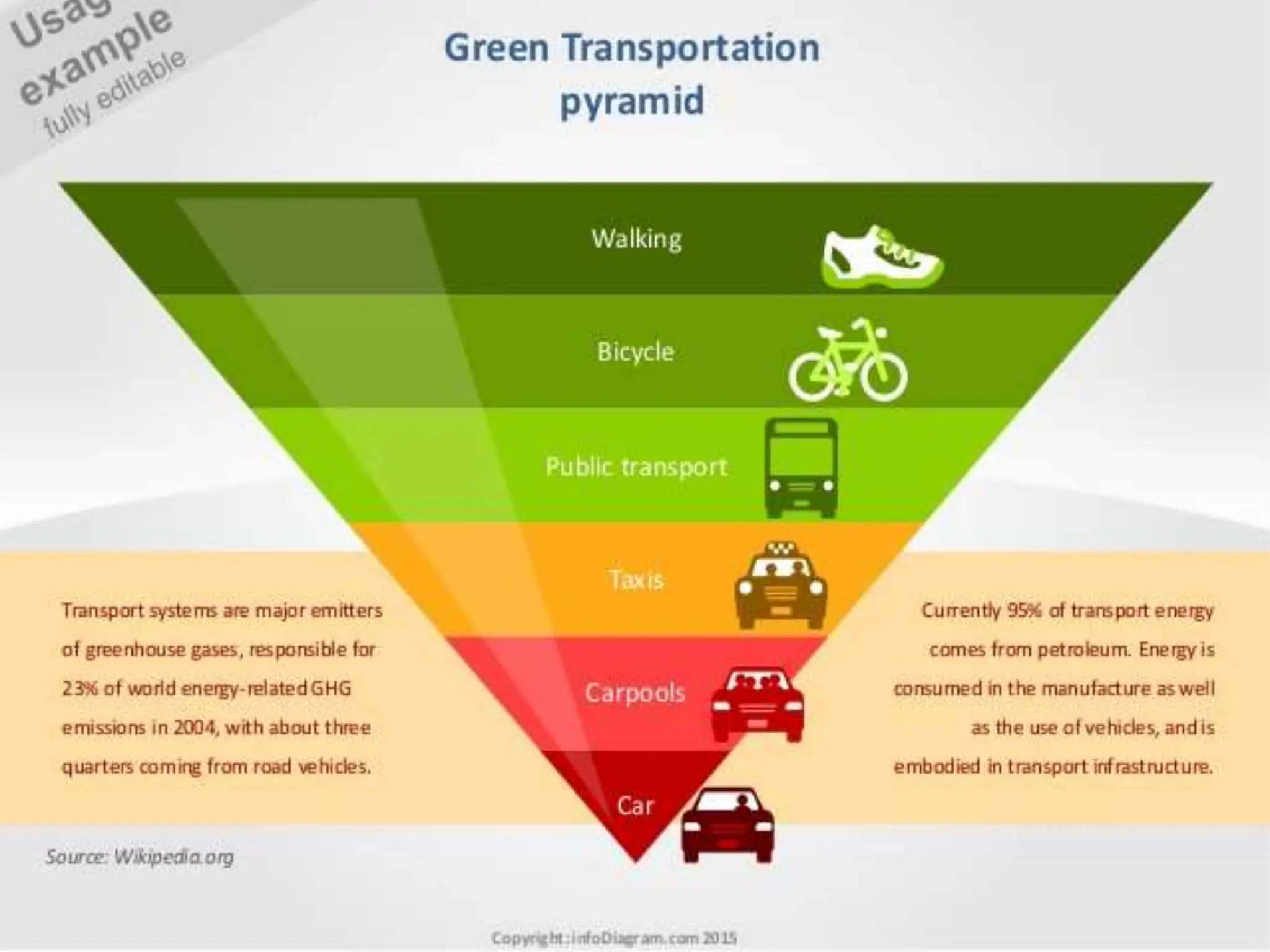
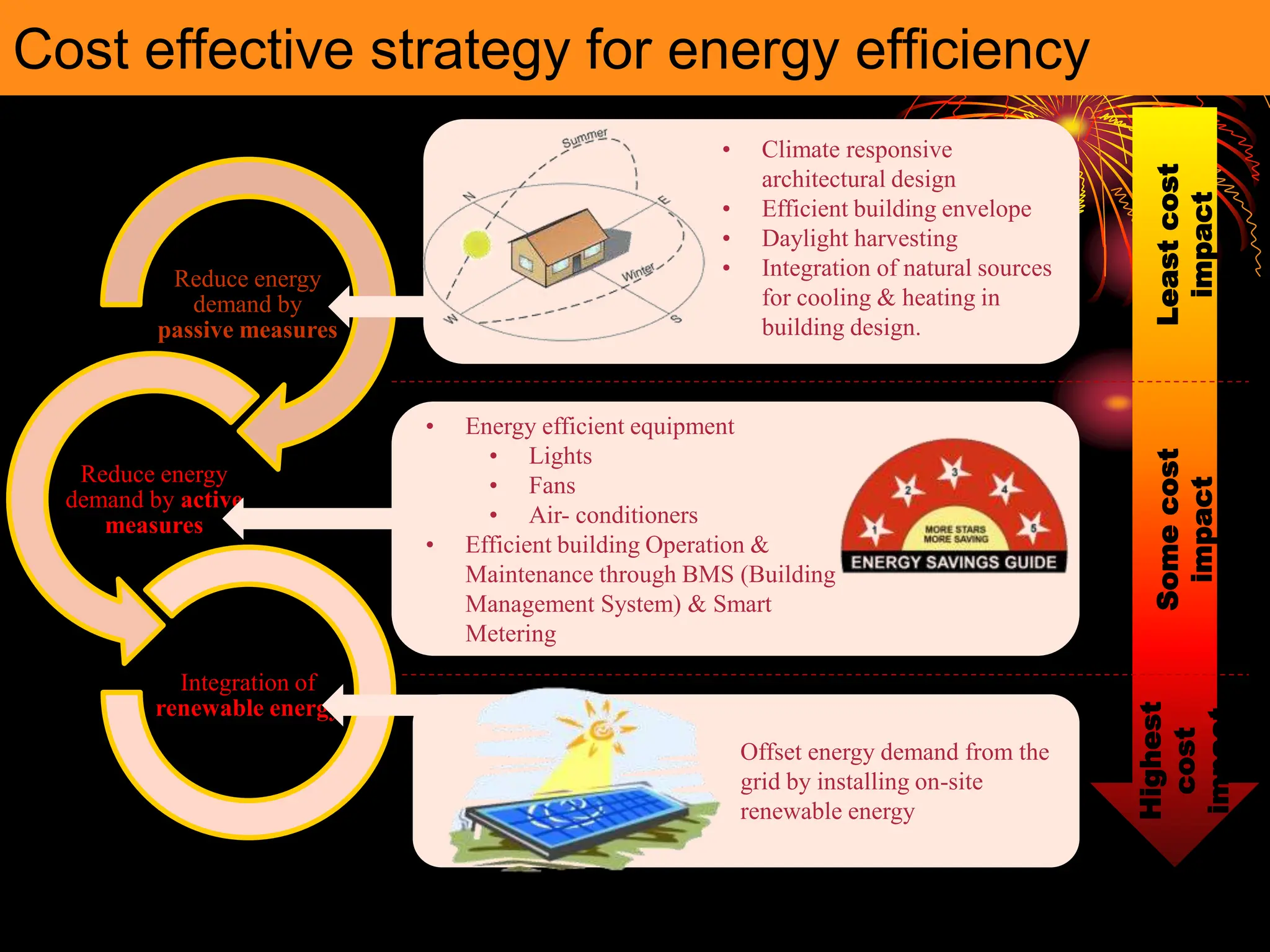
The document discusses the issues and options related to urban infrastructure in India, highlighting the rapid urbanization and growth of cities, which necessitates improved infrastructure for sustainable development. It emphasizes the importance of planned urban growth, the challenges of inadequate services, and the need for investment in both hard and soft infrastructure to enhance the quality of life. The text outlines future projections for urban populations and necessary infrastructure developments by 2030 to meet the needs of a growing and increasingly urbanized society.