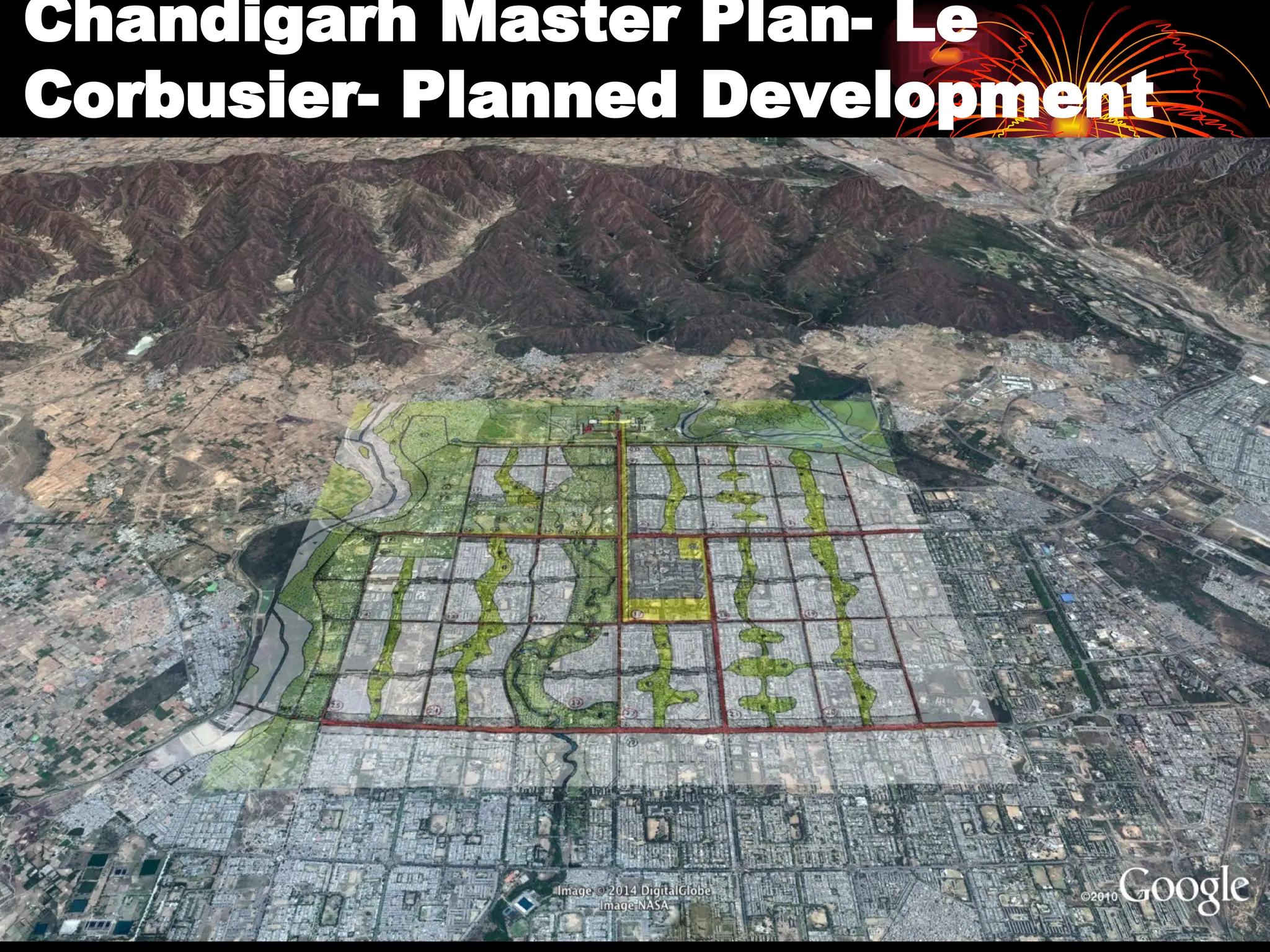
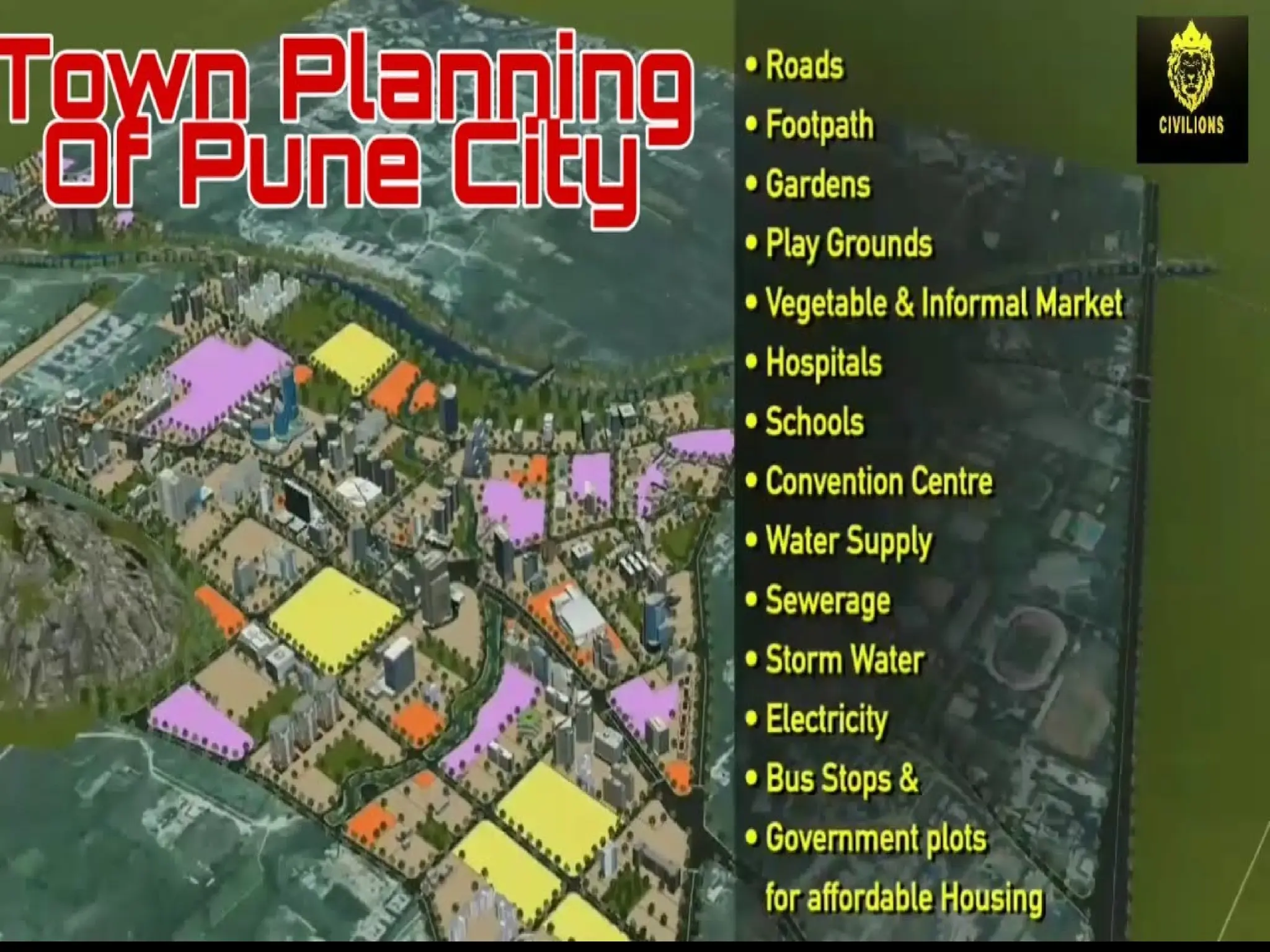
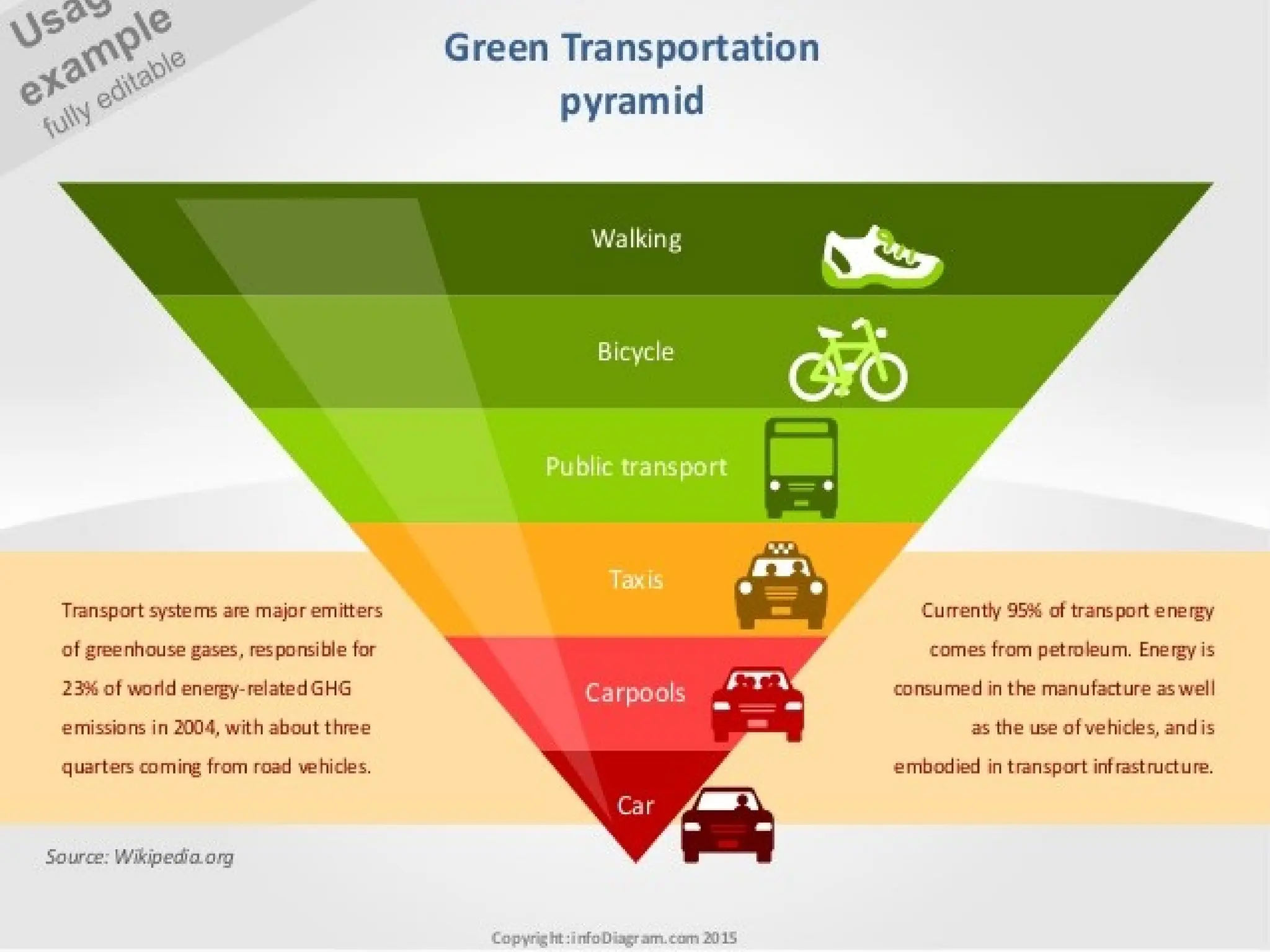
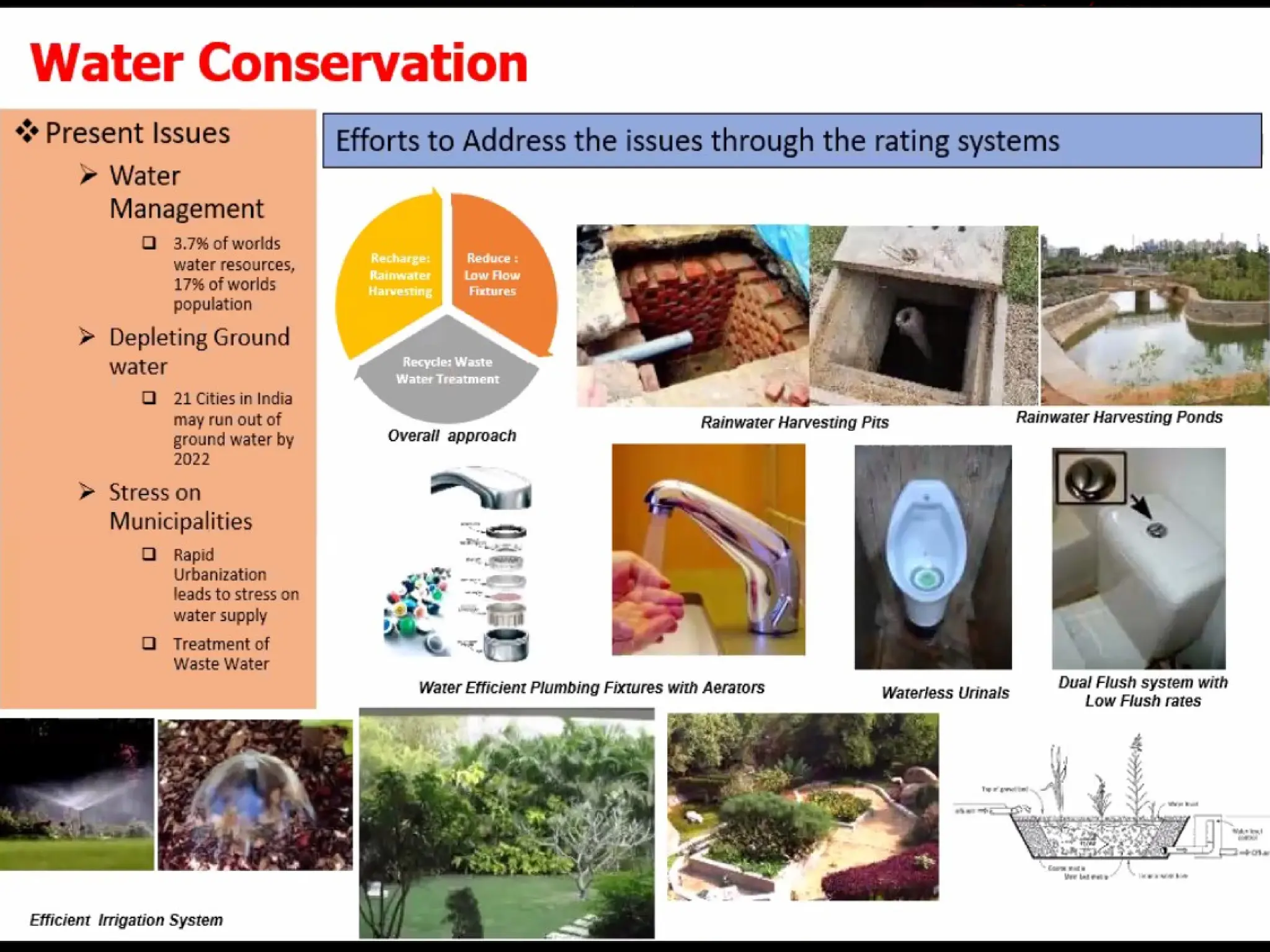
The document discusses the rapid urbanization of India, projecting significant population increases and emphasizing the critical role of infrastructure in supporting urban growth and development. It highlights challenges such as unplanned growth, inadequate infrastructure, and poverty, while outlining the need for sustainable urban planning, investment, and governance. The document also emphasizes the importance of public-private partnerships and innovative practices to improve infrastructure and the quality of life in urban areas.