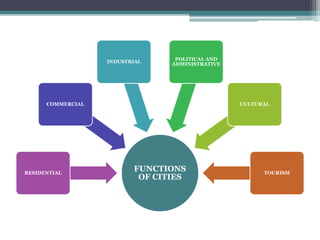
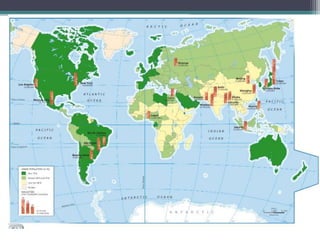
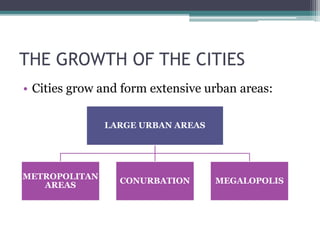
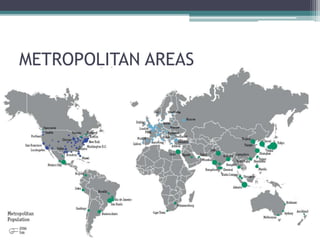
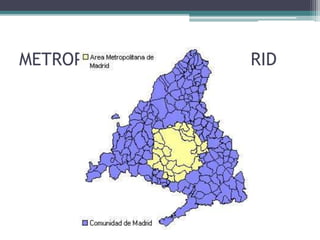
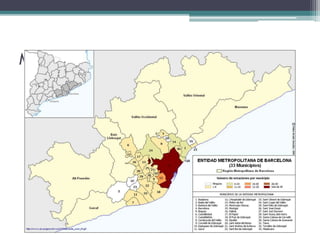
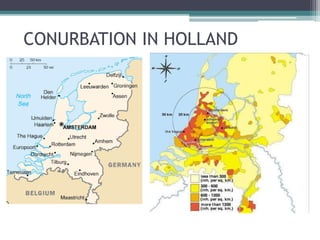
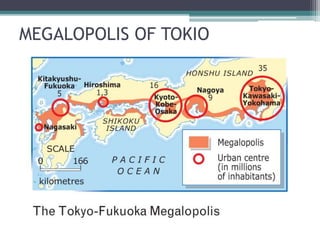
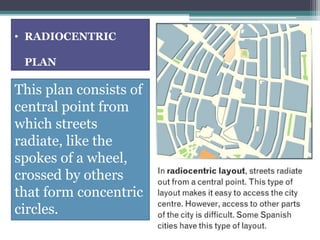
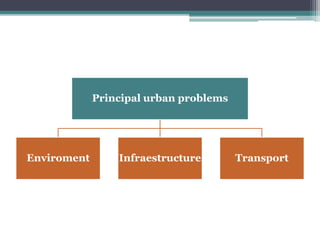
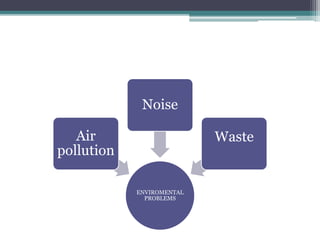
This document discusses various topics related to urban settlement and the growth of cities. It describes how most people live in towns and medium-sized cities, but the number of megacities with over 10 million inhabitants has increased. Cities grow and form large urban areas, metropolitan areas, and megalopolises. The urban hierarchy ranks cities from world metropolises down to smaller cities. The document also examines the analysis of cities in terms of location, urban plans like orthogonal and radiocentric, and types of urban construction such as old buildings, blocks, and single-family homes.