This document provides guidance on the management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). It outlines the following key points:
1. Initial steps include assessing hemodynamic stability, IV access, monitoring, fluid resuscitation, and basic lab tests. Endoscopy within 24 hours is critical for diagnosis and treatment.
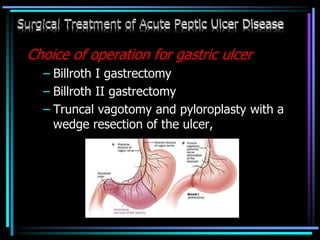
2. For non-variceal bleeding, endoscopic therapies like injection, thermal coagulation, and clipping are first-line. Refractory or high-risk bleeding may require surgery.
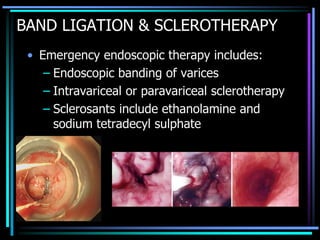
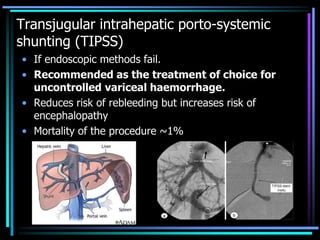
3. Variceal bleeding requires urgent endoscopic ligation or sclerotherapy. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting or surgical shunting may be needed if initial measures