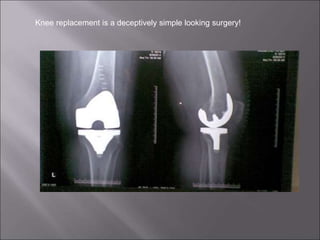
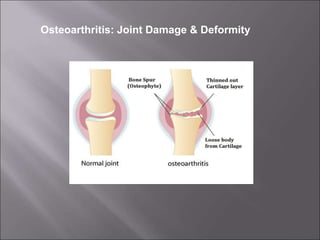
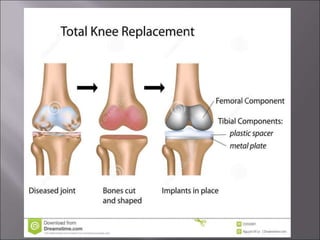
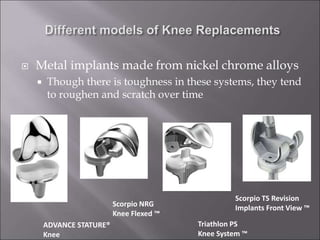
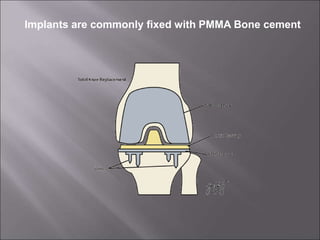
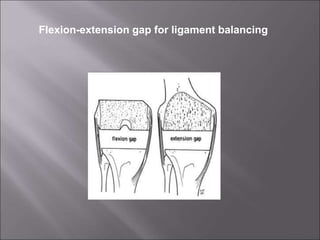
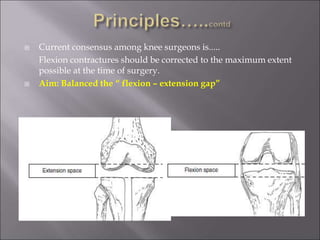
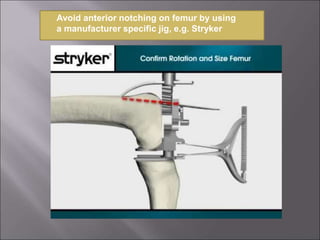
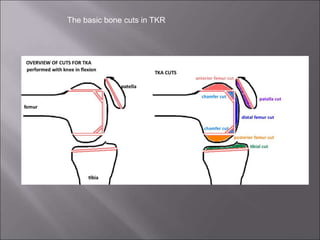
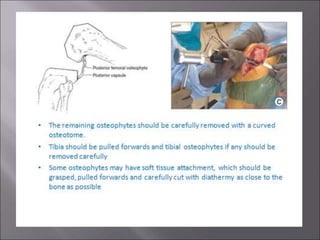
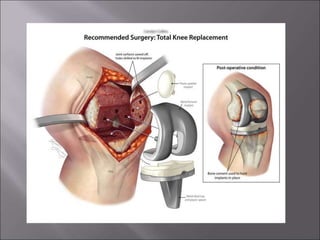
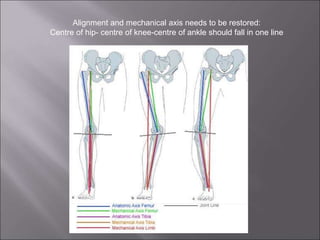
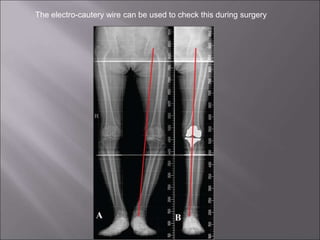
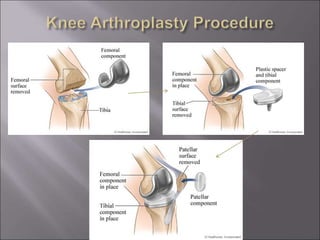
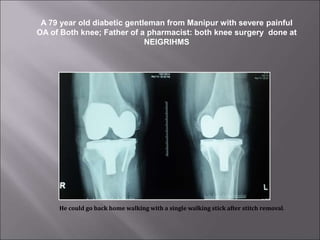
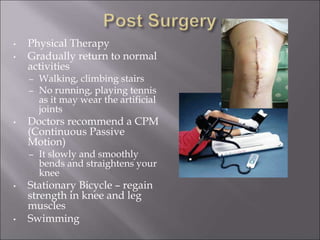
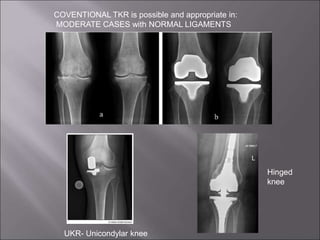
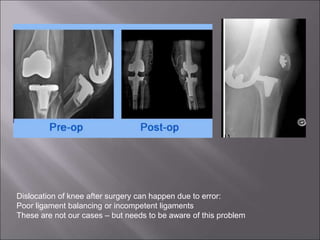
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a highly successful surgical procedure aimed at relieving pain and improving knee function, particularly in elderly patients suffering from advanced osteoarthritis. The procedure involves precise balancing of the knee joint, with methods including both cemented and cementless implants, and has been successfully performed at Neigrihms since 2010. Post-operative care involves rehabilitation strategies and physical therapy to ensure patients regain strength and mobility.