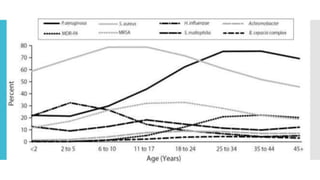
The document discusses the advantages of nebulised antibiotics for treating respiratory infections, particularly in cystic fibrosis, highlighting their ability to deliver high local drug concentrations while minimizing systemic exposure and toxicity. It outlines the treatment protocols for managing infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria, including specific inhaled antibiotics and dosages. Additionally, it emphasizes the potential off-label use of inhaled antibiotics in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis and the need for further studies on optimal antibiotic choices.