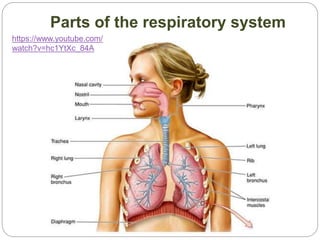
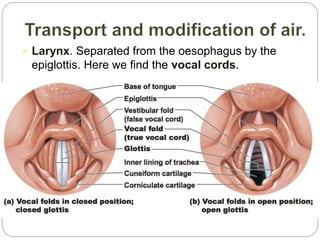
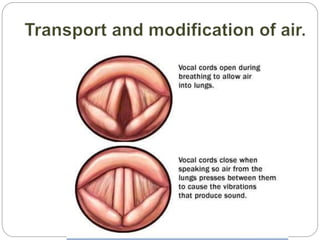
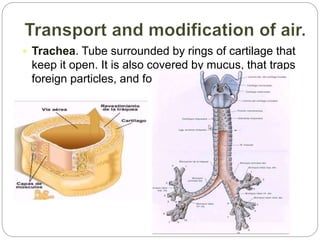
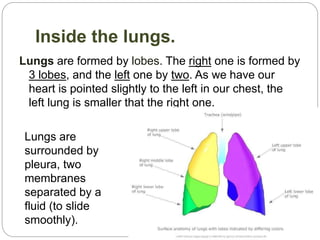
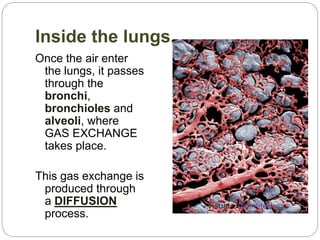
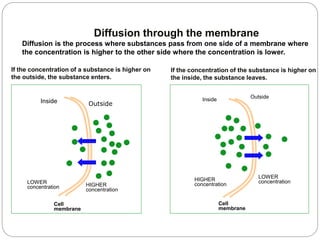
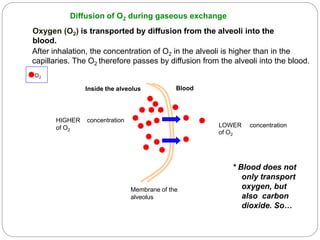
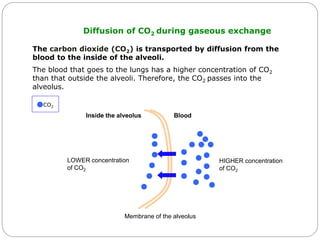
The document discusses the respiratory and digestive systems and their roles in obtaining energy from nutrients. The respiratory system works with the digestive system to transform nutrients into energy. It obtains oxygen needed for cellular respiration to release energy from nutrients and expels the resulting carbon dioxide waste. The respiratory system consists of the airways and lungs. In the lungs, gas exchange occurs via diffusion - oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.