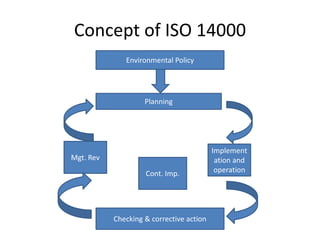
The ISO is an international organization for standardization established in 1942 that aims to coordinate and unify international standards. It is made up of national standards bodies from over 150 countries. ISO standards like ISO 9000 for quality management systems and ISO 14000 for environmental management systems provide requirements and guidance to help organizations ensure quality and minimize environmental impact. Auditing is used to evaluate conformity with ISO standards and drive continual improvement.