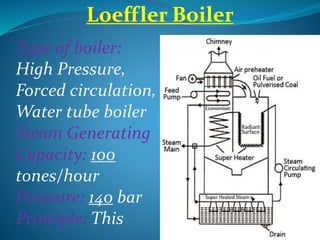
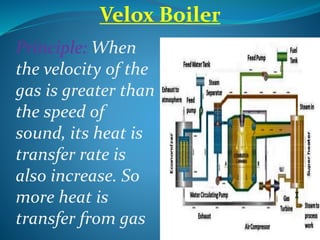
A boiler is a closed vessel that heats water or another fluid to produce steam or heated fluid. High pressure boilers operate above 80 bars and produce steam with pressures up to 160 bars and temperatures up to 540°C. Several types of high pressure boilers are described, including La-Mont, Loeffler, Benson, Schmidt-Hartmann, and Velox boilers. Key advantages of high pressure boilers include increased heat transfer rates, compact size, higher efficiencies, and ability to quickly change loads. Challenges include preventing scale buildup and bubble formation in tubes.