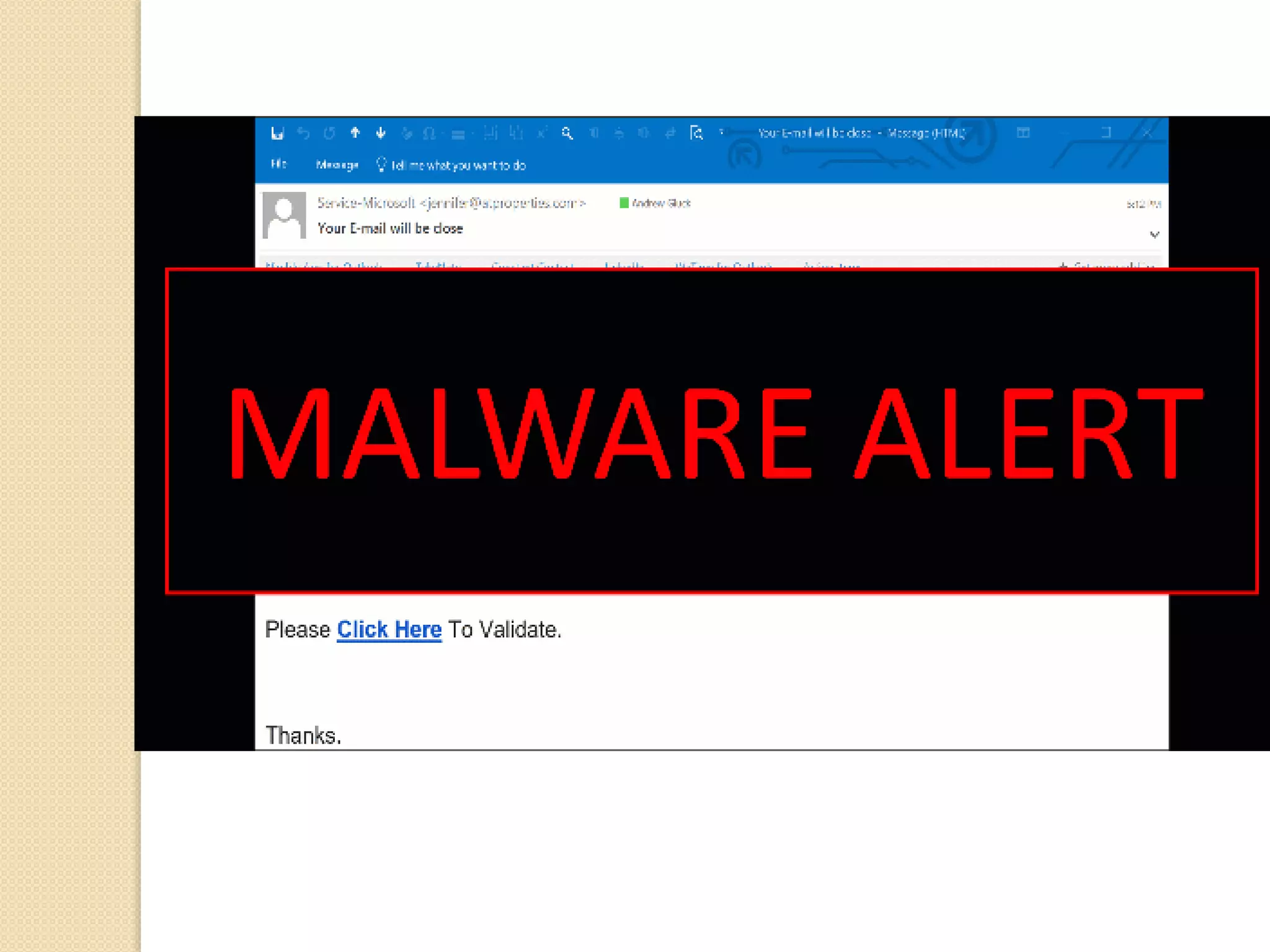
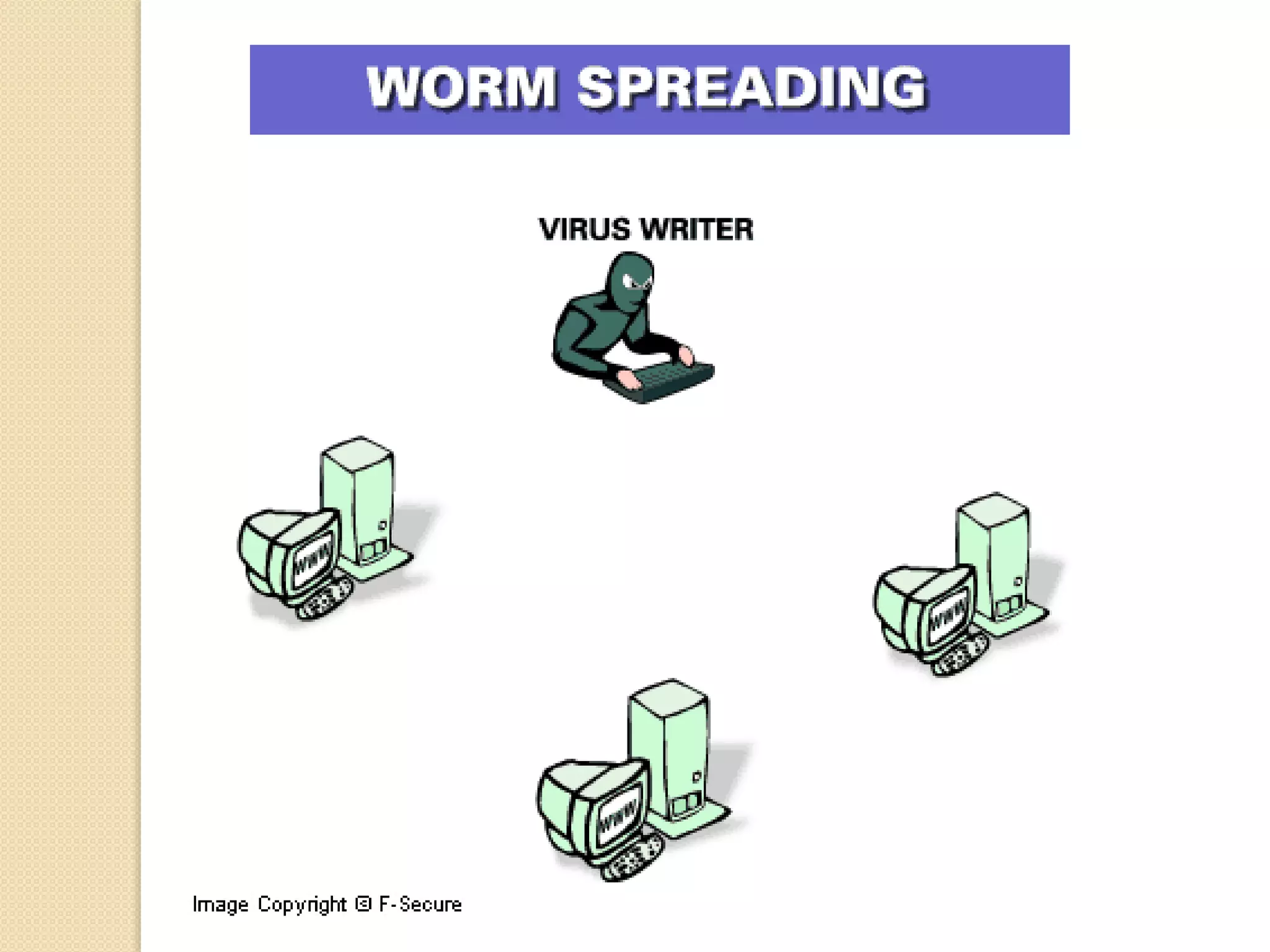
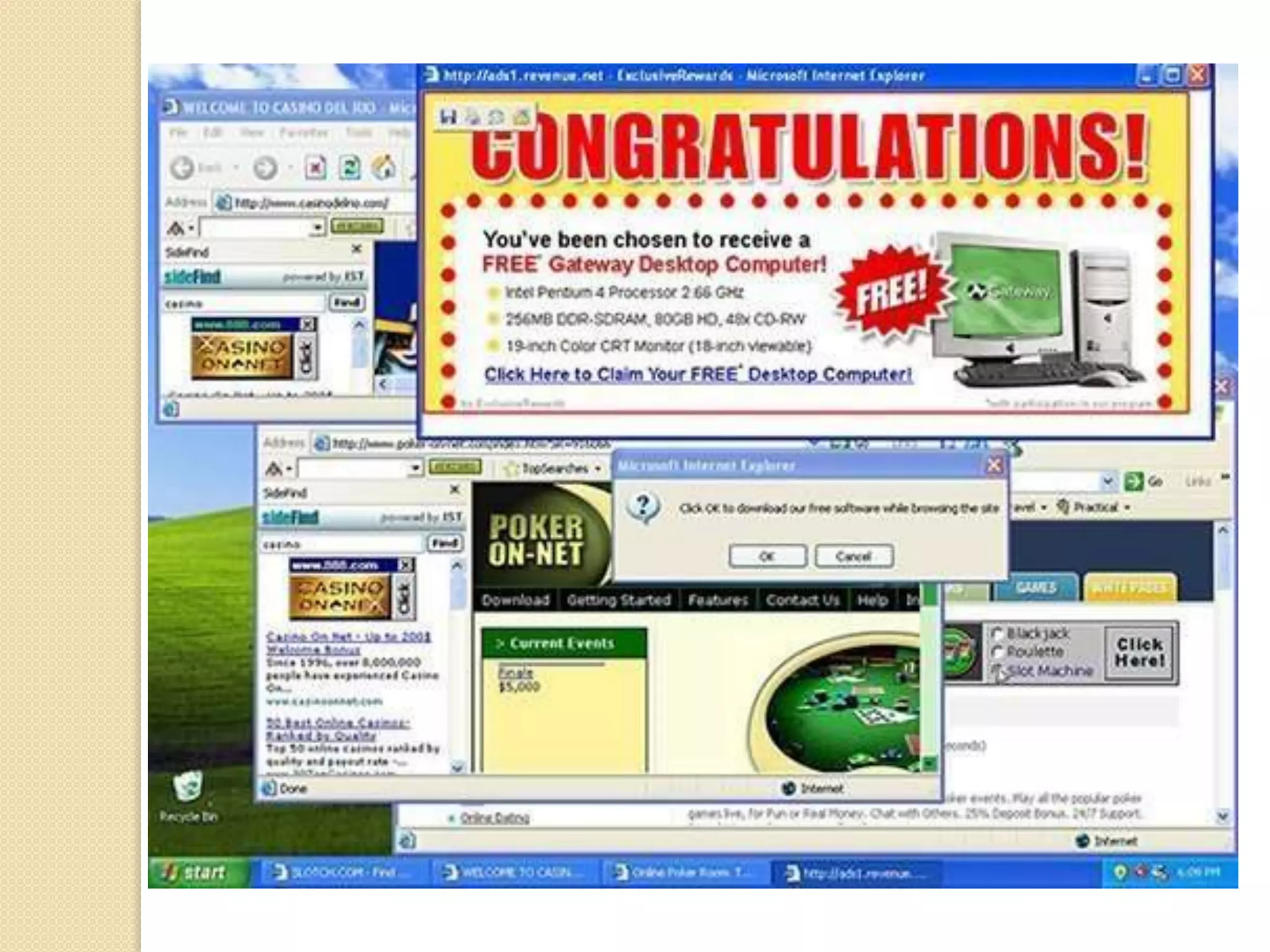
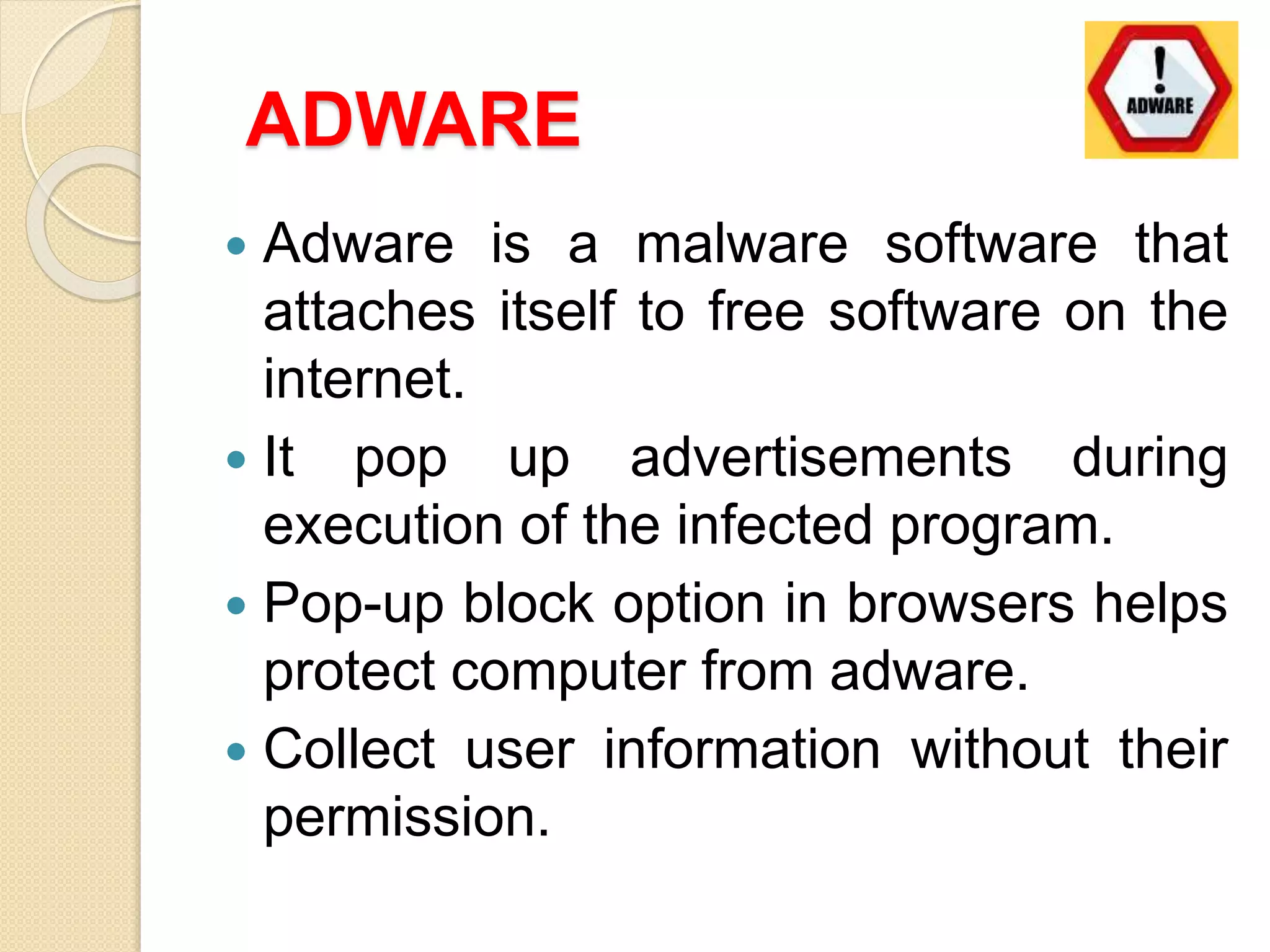
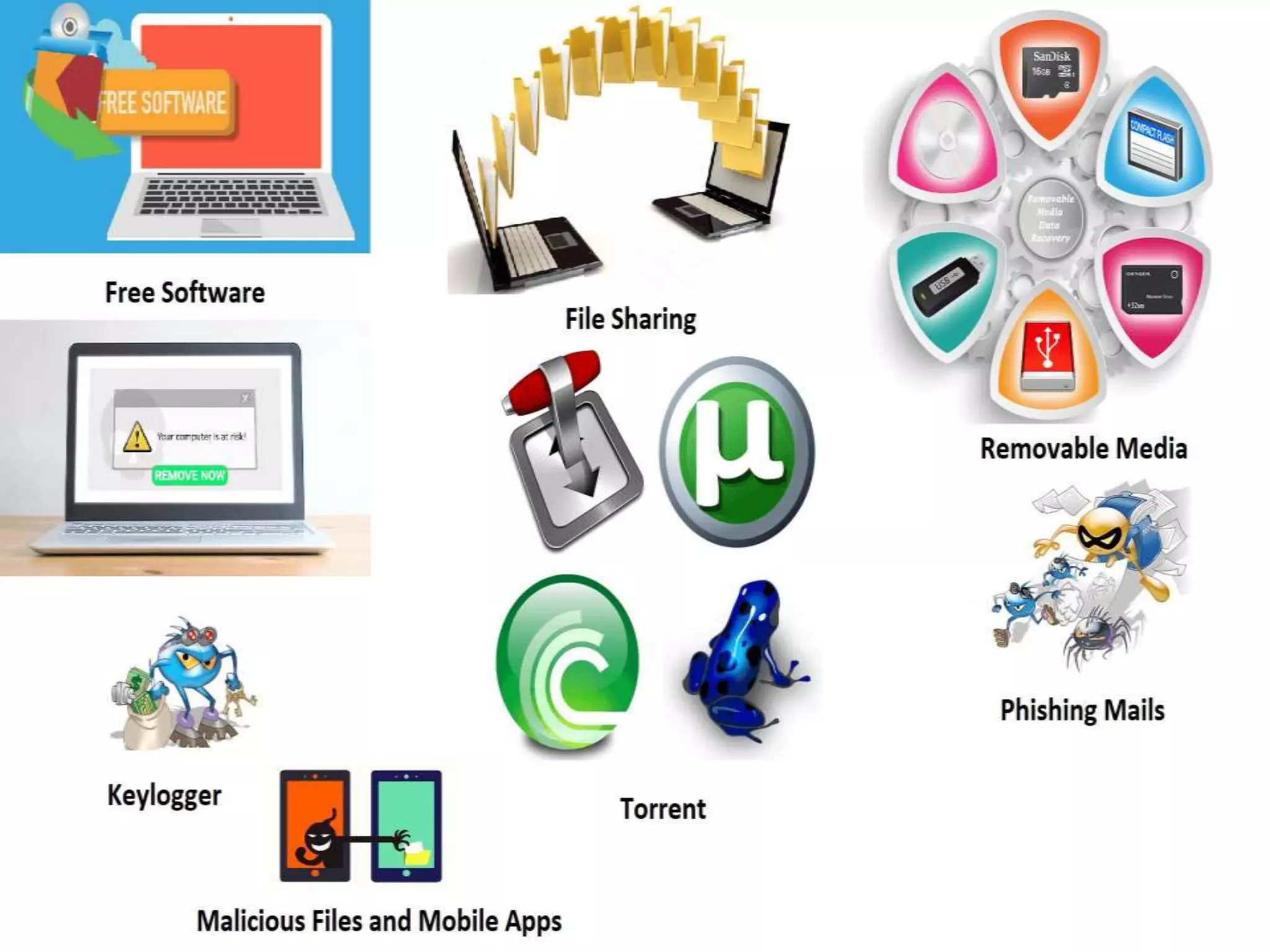
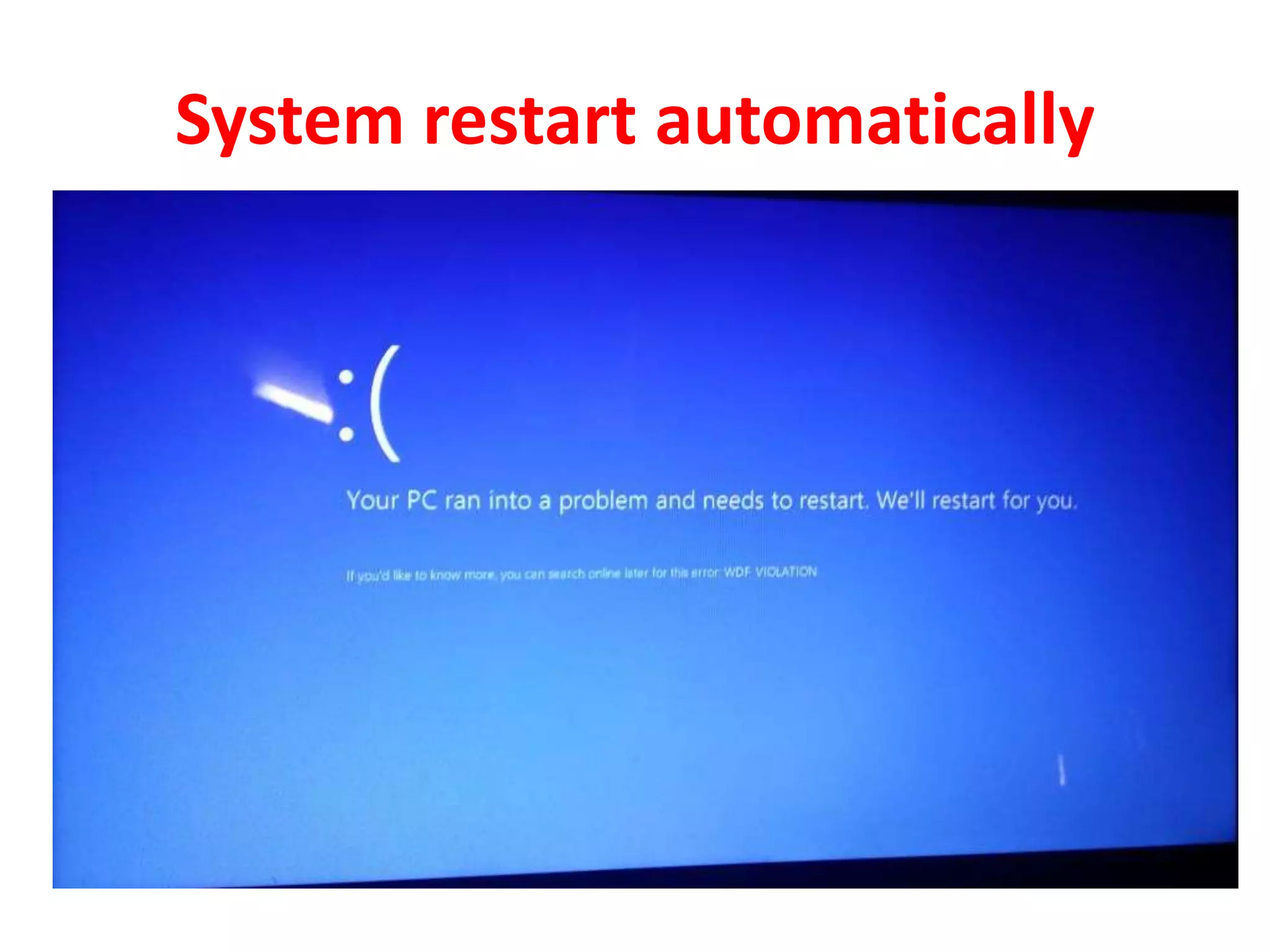
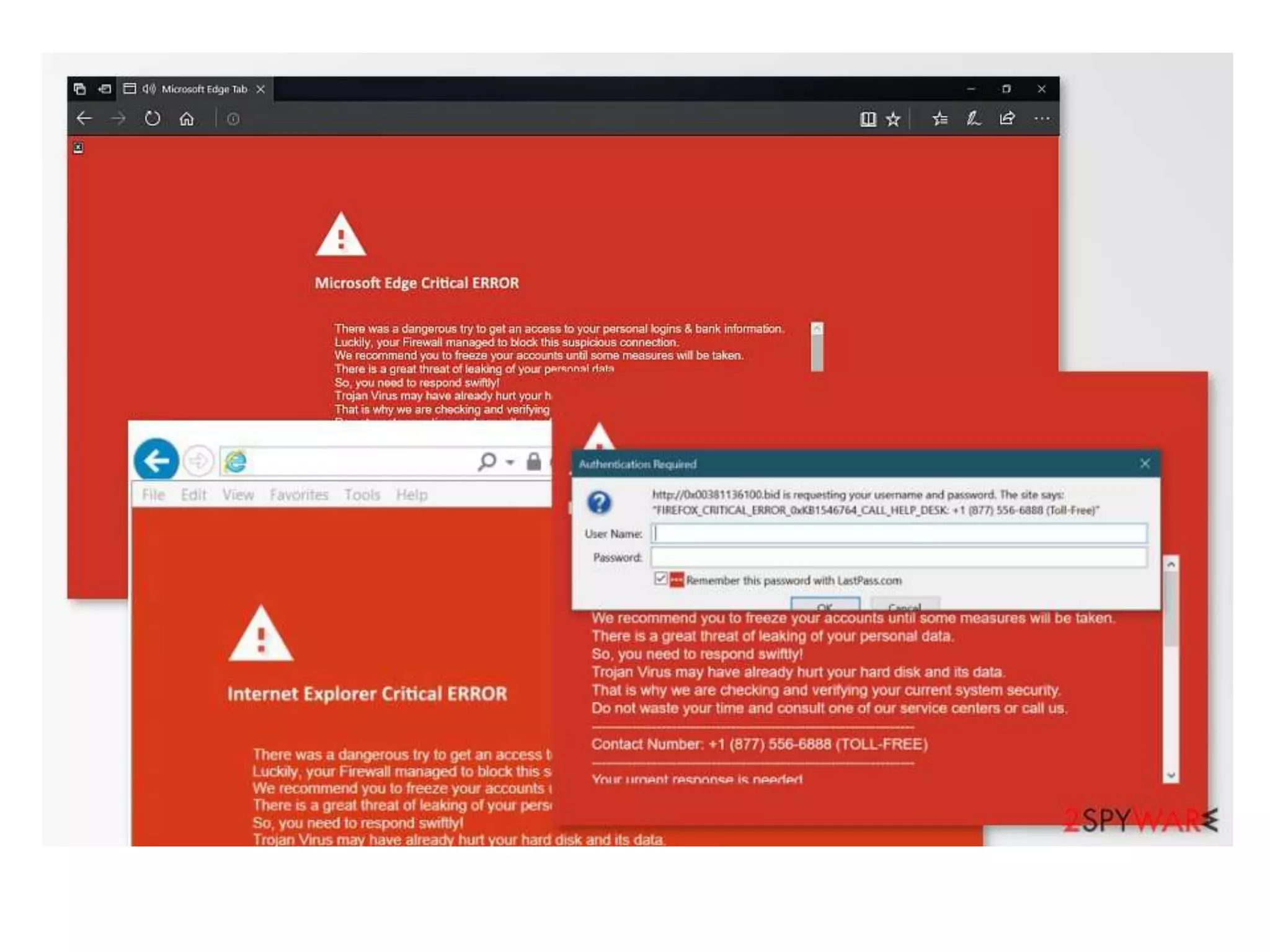
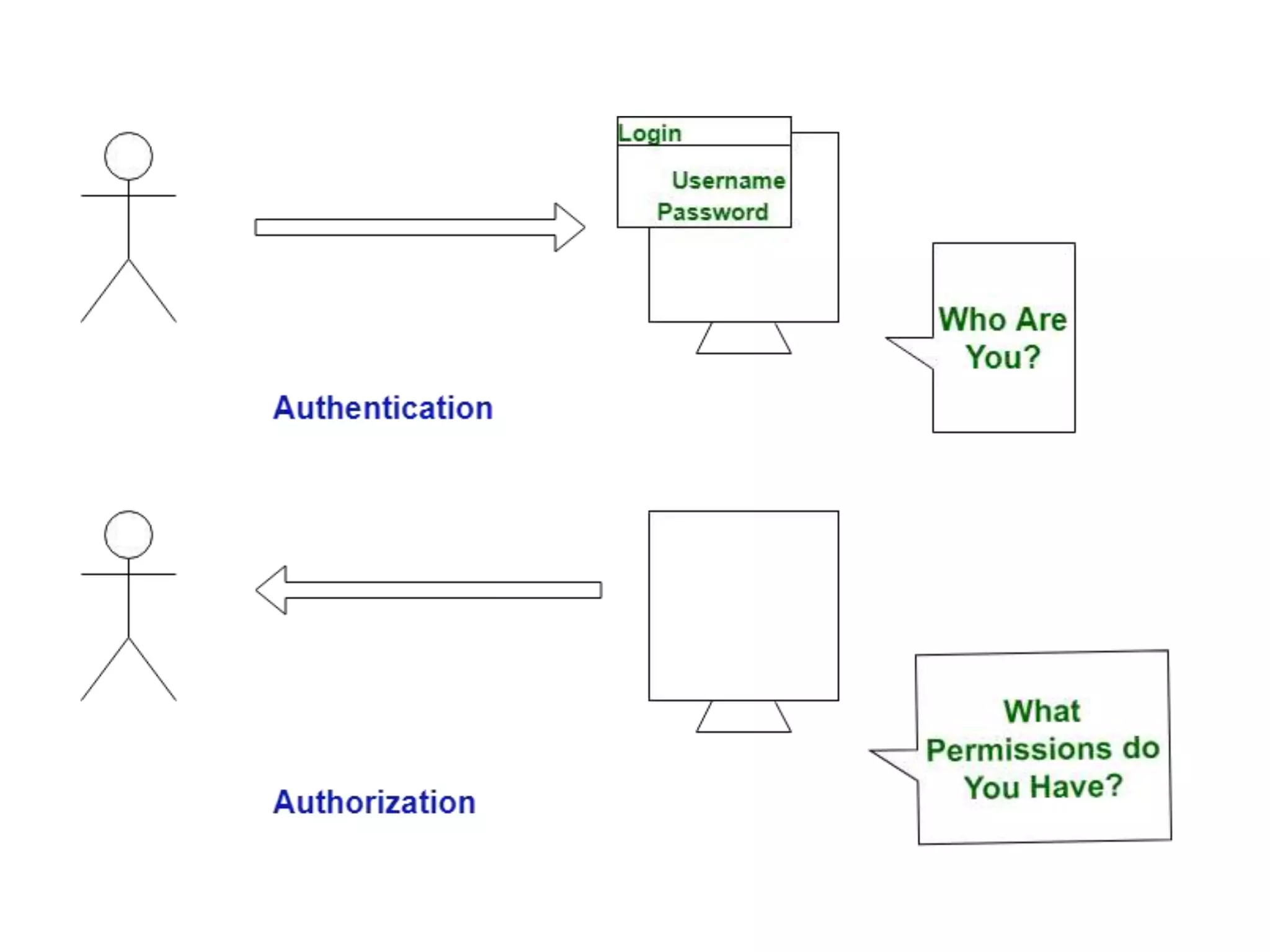
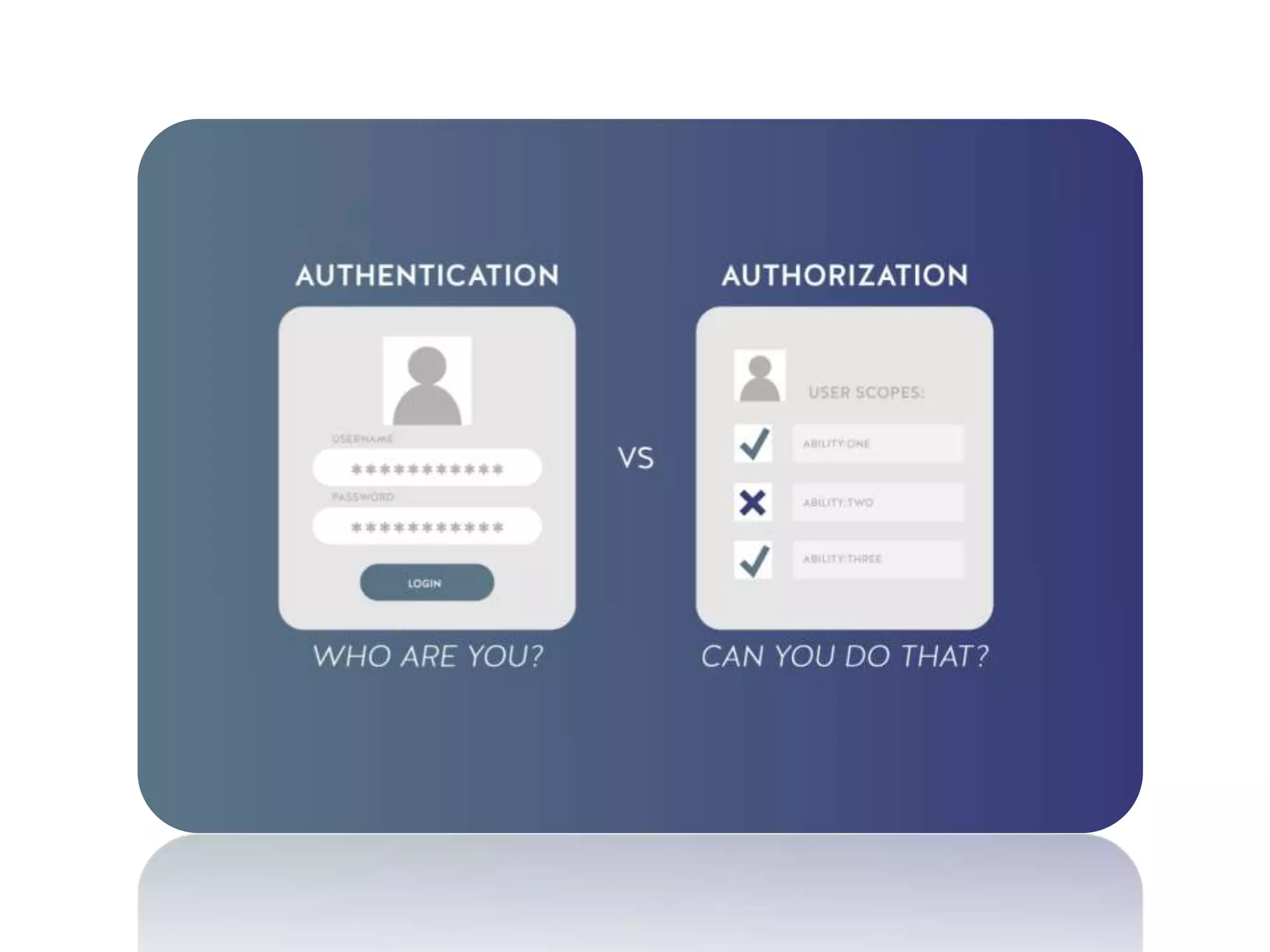
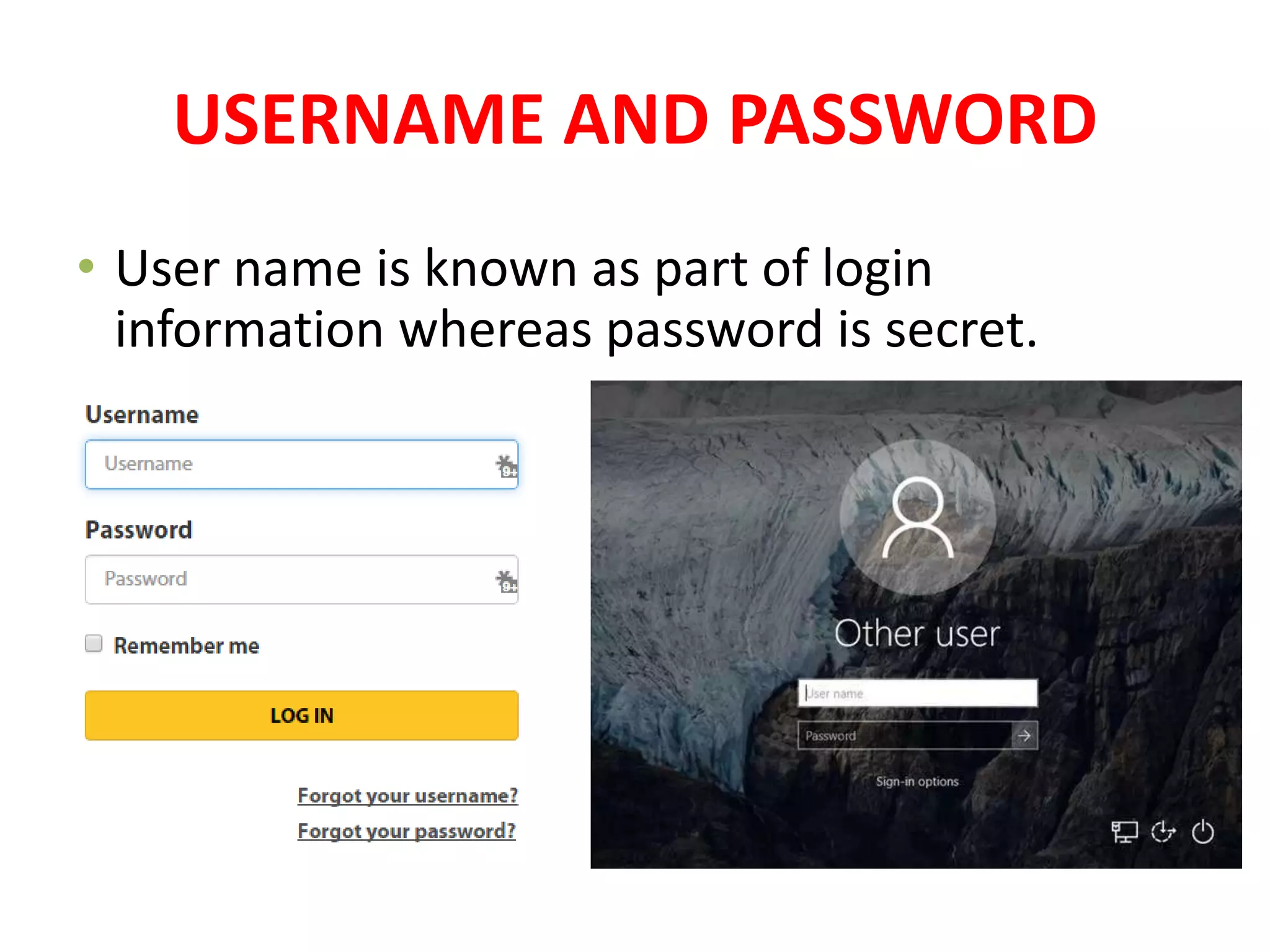
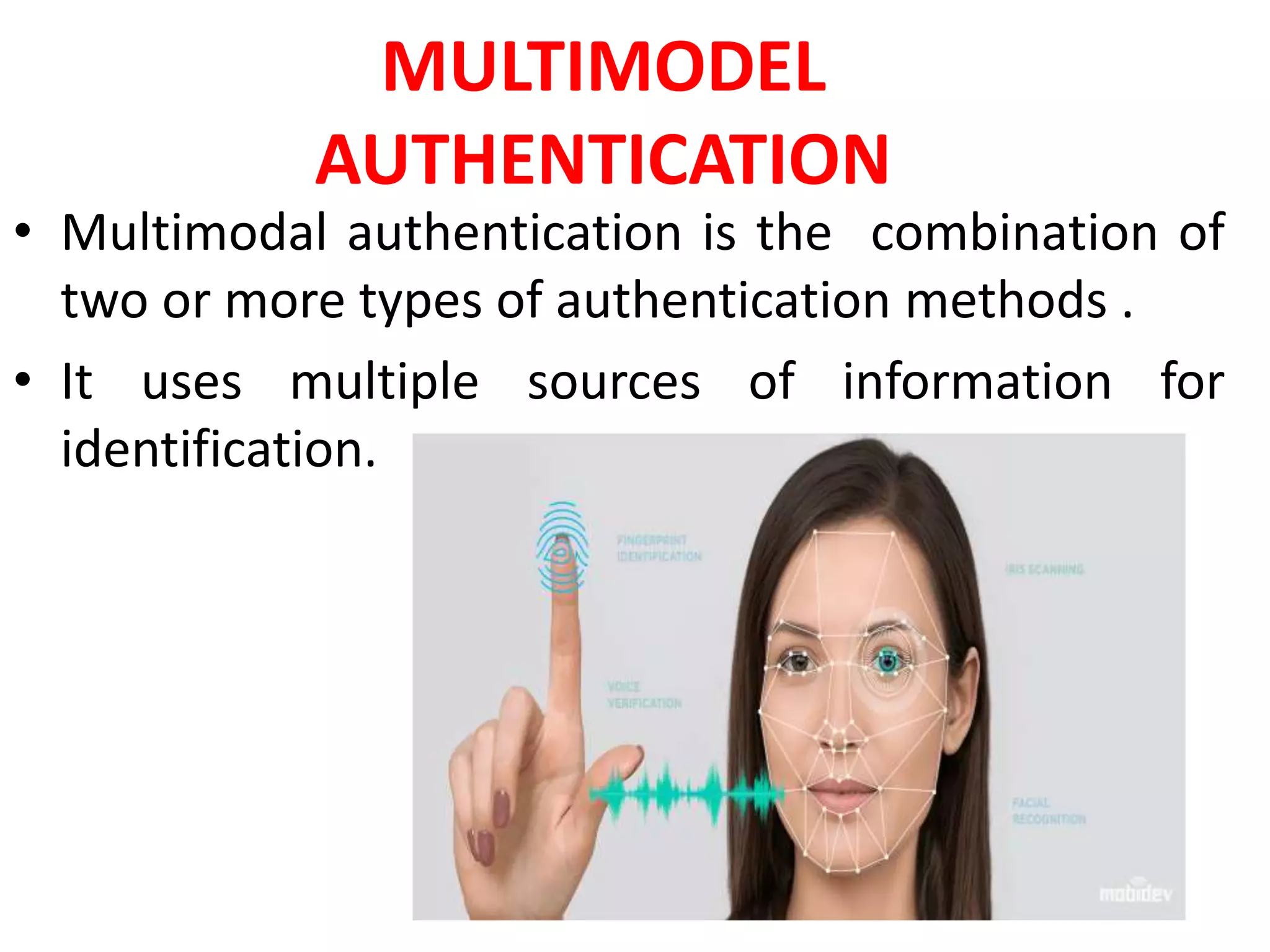
The document discusses various topics related to computer security and ethics. It defines computer security as protecting hardware, software and stored information from threats. It describes common cybercrimes like hacking, cracking and malware. Malware types discussed include viruses, worms, spyware and adware. Authentication methods for identifying users are also summarized, such as usernames/passwords, PINs, access cards and biometrics. The importance of antivirus software, updates and ethical computer use are highlighted.