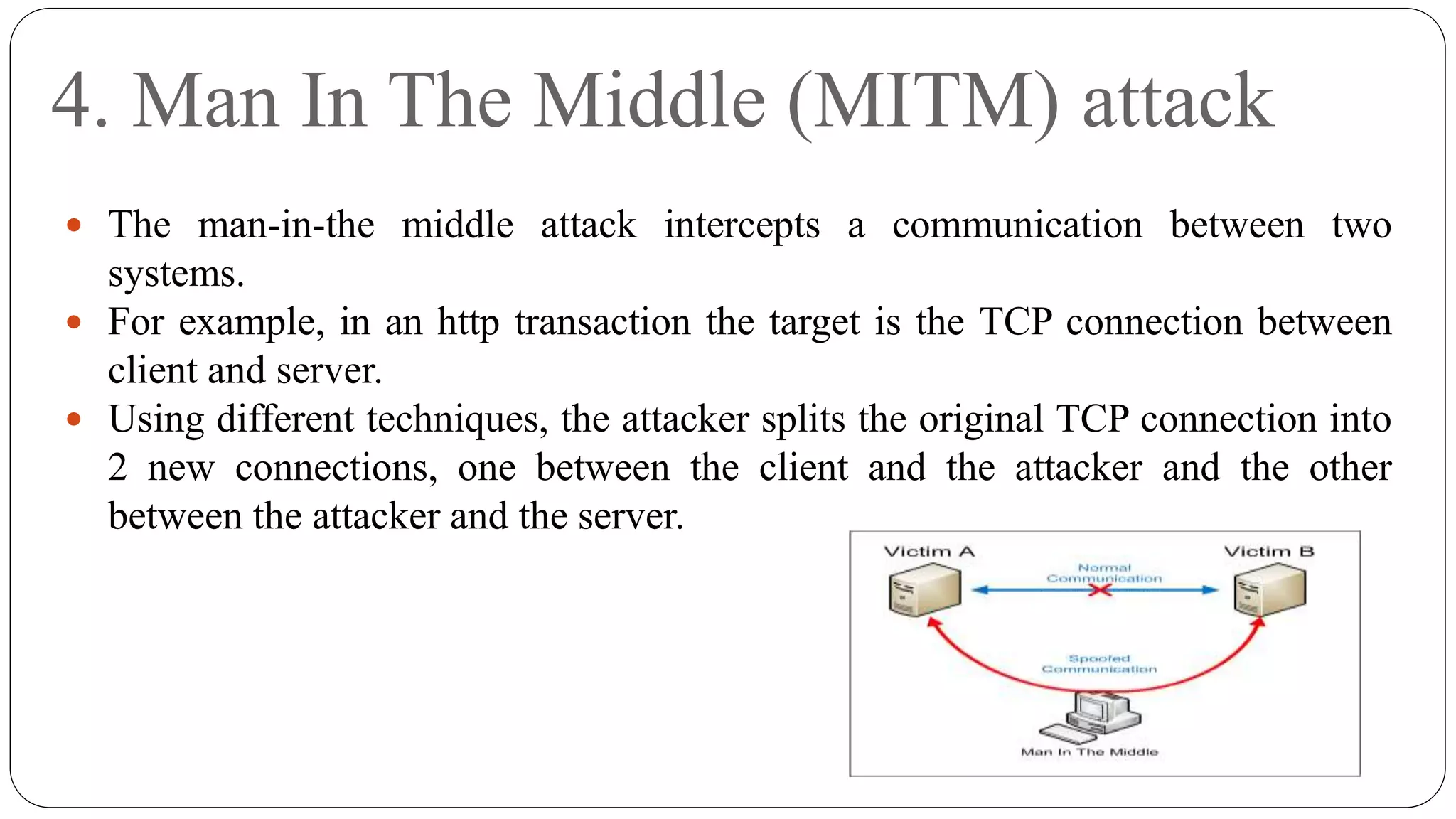
This document provides an overview of computer security concepts. It discusses threats like viruses, worms, bots and rootkits that can compromise security. It defines key terms like assets, attacks, intruders and vulnerabilities. The CIA triad of confidentiality, integrity and availability is explained as the standard for information security. Common attacks are also outlined, such as password cracking, man-in-the-middle, spoofing and social engineering. Malware is defined and the characteristics of viruses, worms and trojans are described.