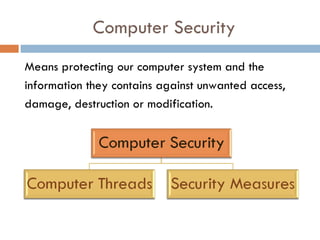
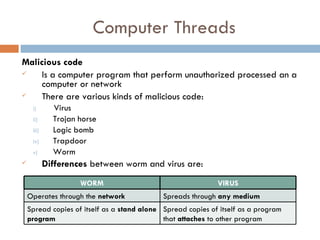
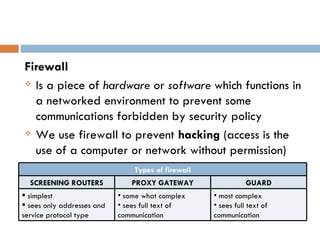
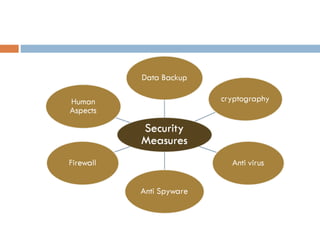
This document discusses various aspects of computer security and information protection. It describes threats like malicious code, hacking, natural disasters, and theft. It then outlines security measures used to protect systems and information, including antivirus software, firewalls, backups, cryptography, and addressing human aspects of security. The overall purpose is to explain how computer security works to protect systems and data from various internal and external threats.