The document provides an overview of developments during the Renaissance period, including:
- The Renaissance saw developments in science, art, architecture, painting, and sculpture as humanism flourished and scholars looked to antiquity for inspiration. Figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo were influential in multiple disciplines.
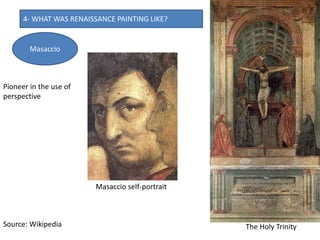
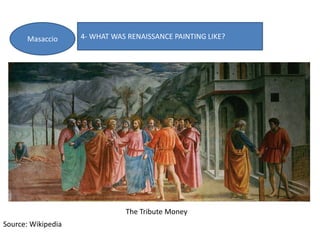
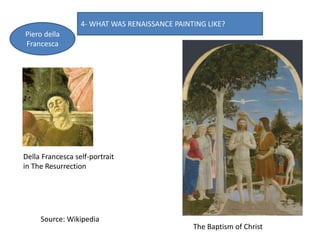
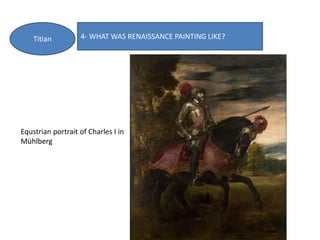
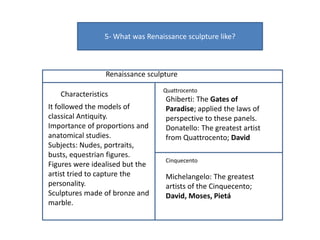
- Architecture revived classical elements and emphasized harmony and proportion. Brunelleschi and Alberti were pioneers. Painting developed techniques like perspective and idealized figures. Key painters included Masaccio, Botticelli, da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael, and Titian. Sculpture also emulated antiquity through proportions and anatomy, with masters including Ghiberti,