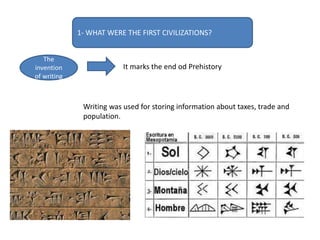
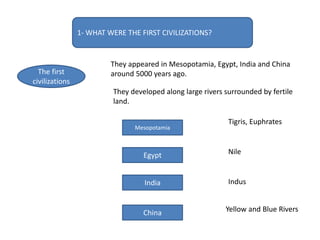
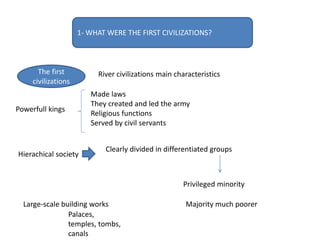
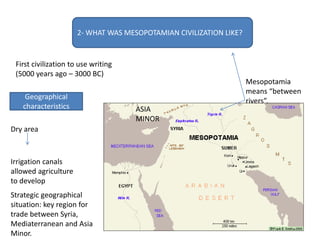
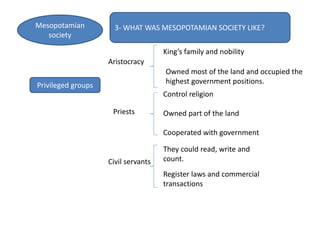
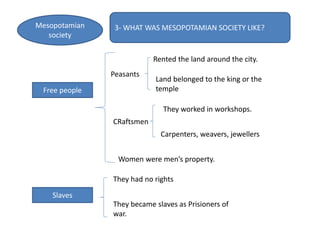
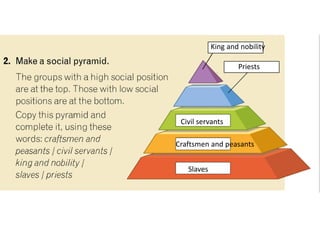
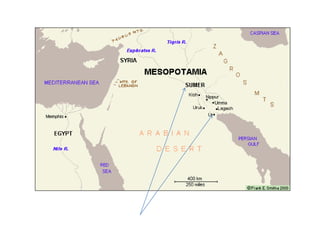
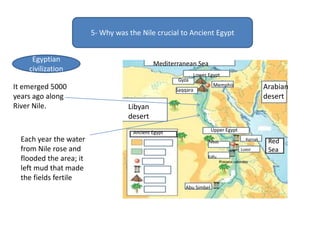
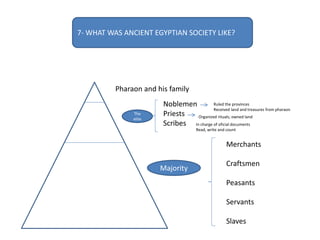
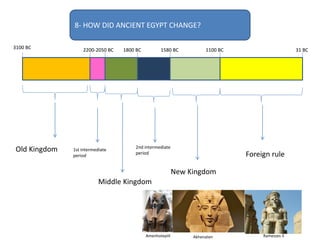
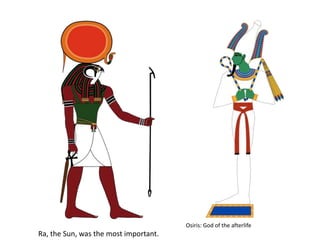
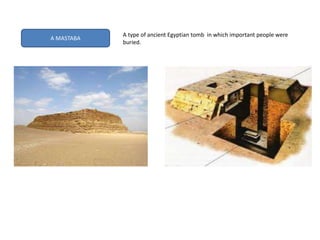
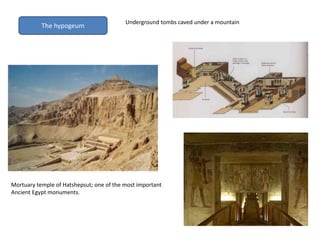
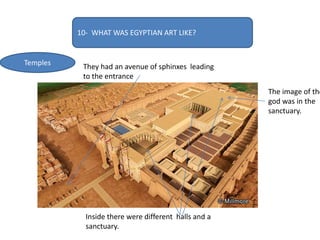
This document provides an overview of early civilizations and Mesopotamian and Egyptian civilization. It discusses the first civilizations emerging around 5000 years ago along major rivers like the Tigris, Euphrates, Nile, Yellow River, and Indus River. Mesopotamian civilization was the first to develop writing in around 3000 BC, with cuneiform writing on clay tablets. Egyptian civilization emerged along the Nile River, with the annual flooding providing fertile land. Powerful pharaoh kings ruled ancient Egypt, and religion was important for ensuring order. Both civilizations had hierarchical societies divided between elites and commoners. Mesopotamian and Egyptian art served religious and political functions through temples, statues