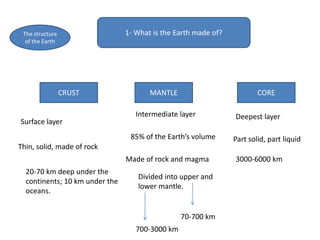
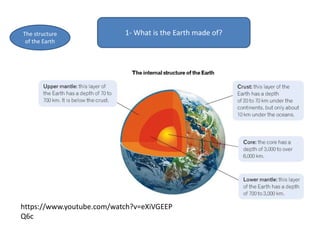
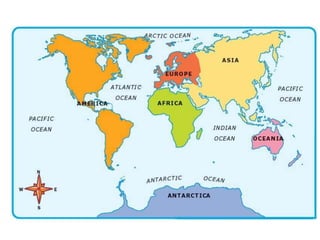
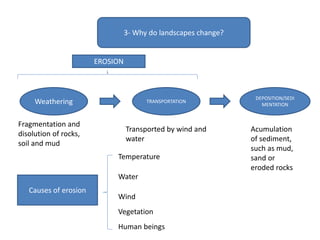
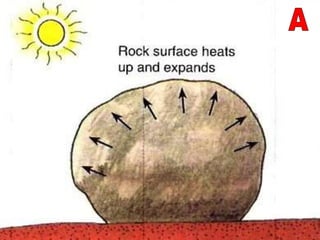
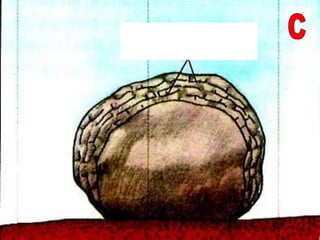
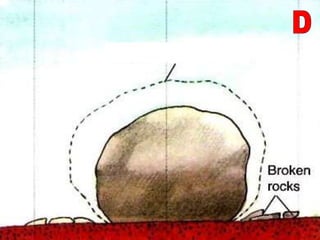
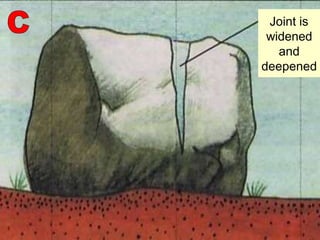
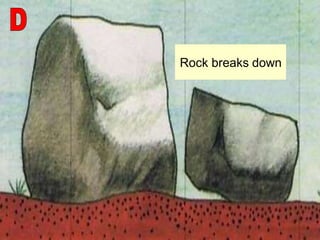
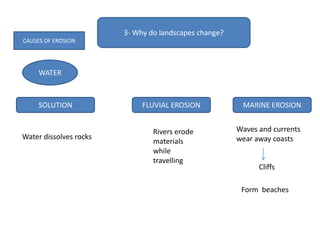
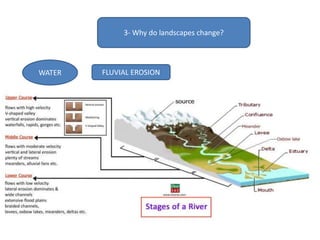
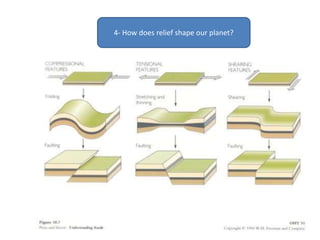
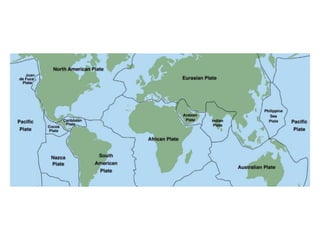
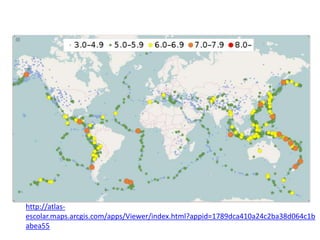
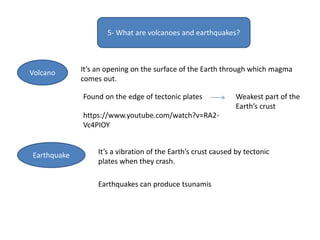
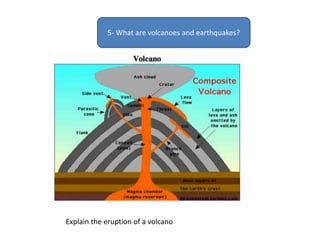
The document summarizes key concepts about Earth's physical geography and relief. It describes the three main layers that make up the Earth's structure - crust, mantle and core. It then explains how landscapes change over time due to various erosion processes like weathering, transportation and deposition by forces such as water, wind and glacial activity. Finally, it discusses major relief features on Earth's surface like volcanoes and mountains, and how they are formed by the movement of tectonic plates.