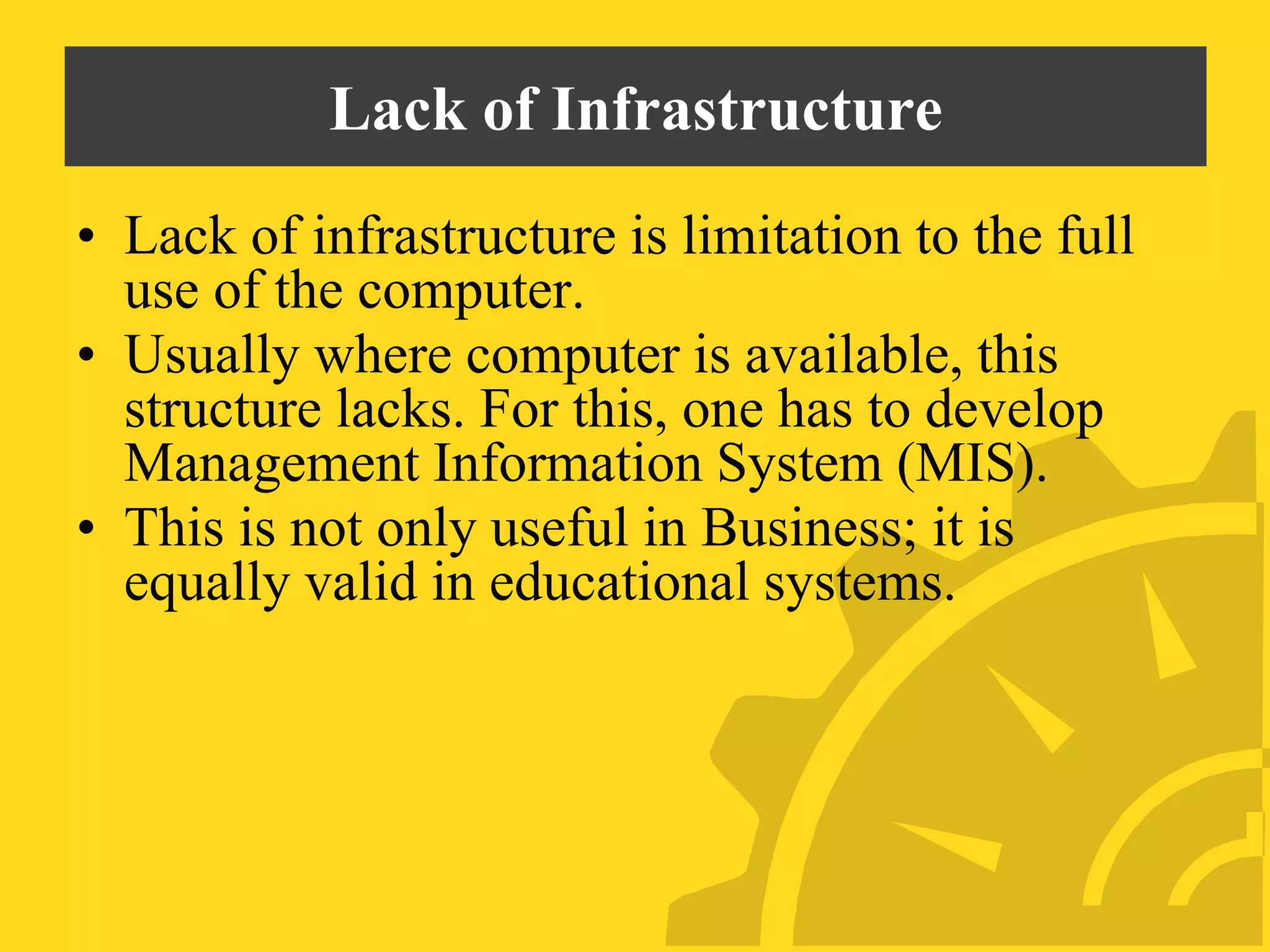
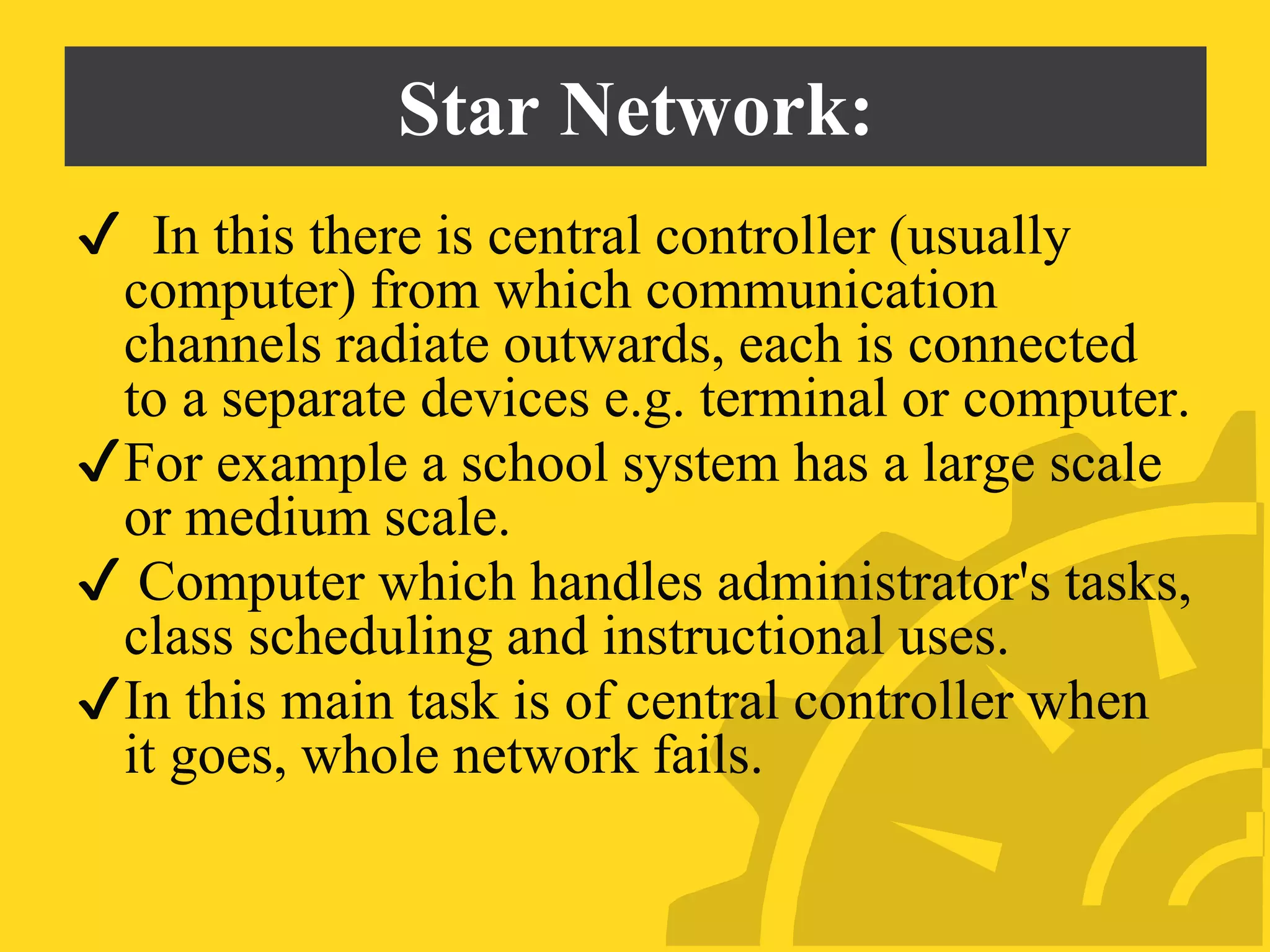
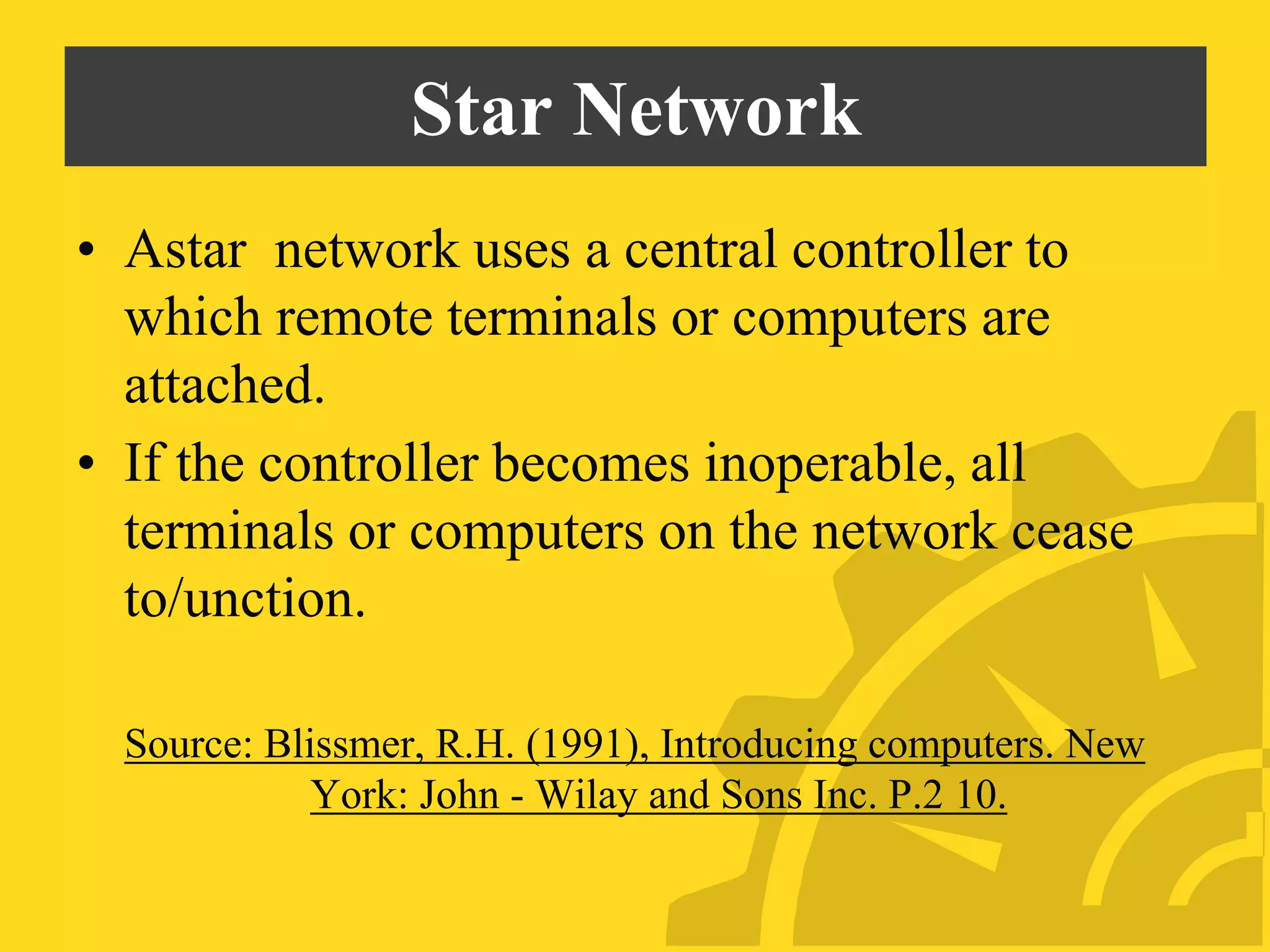
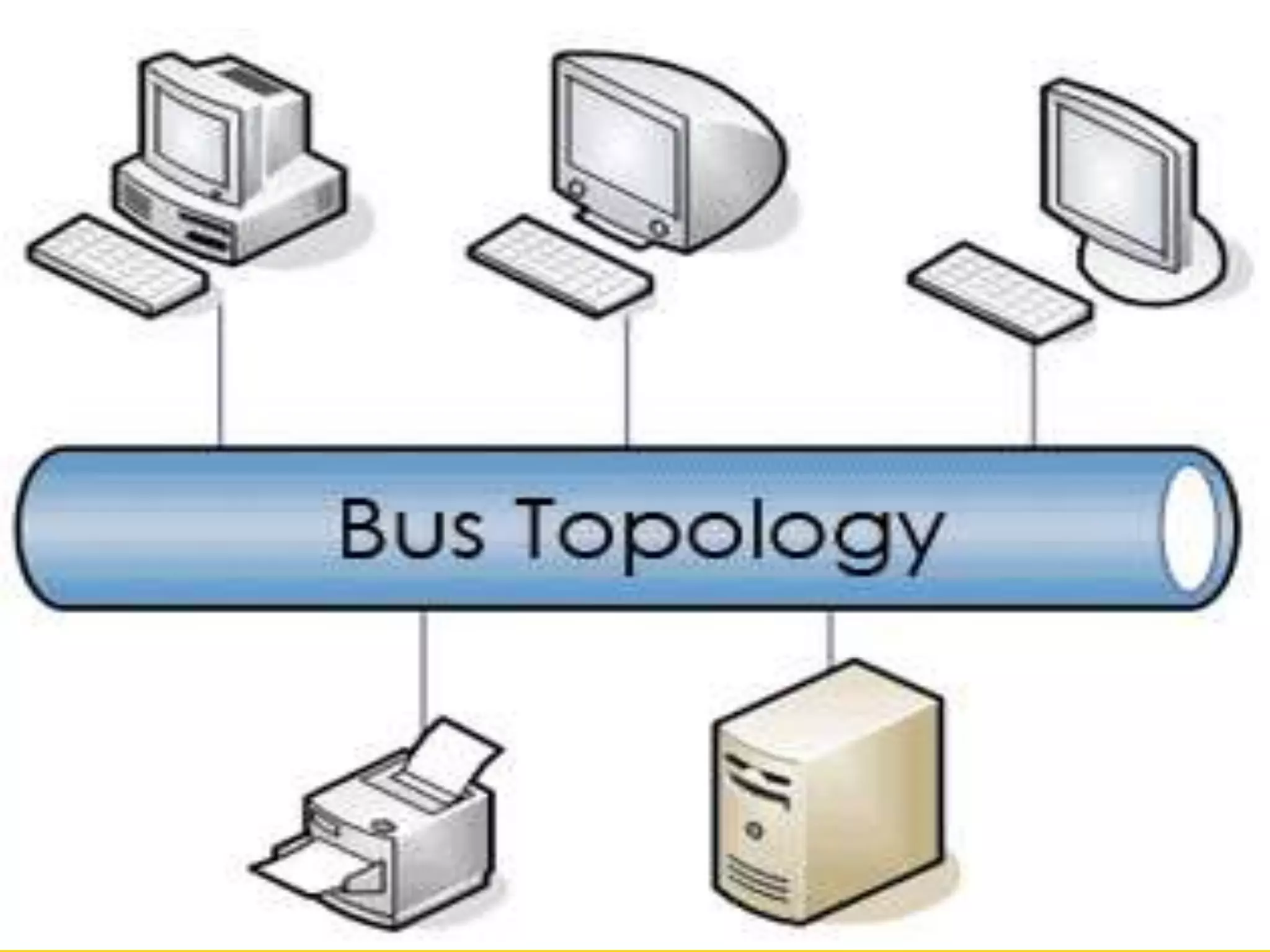
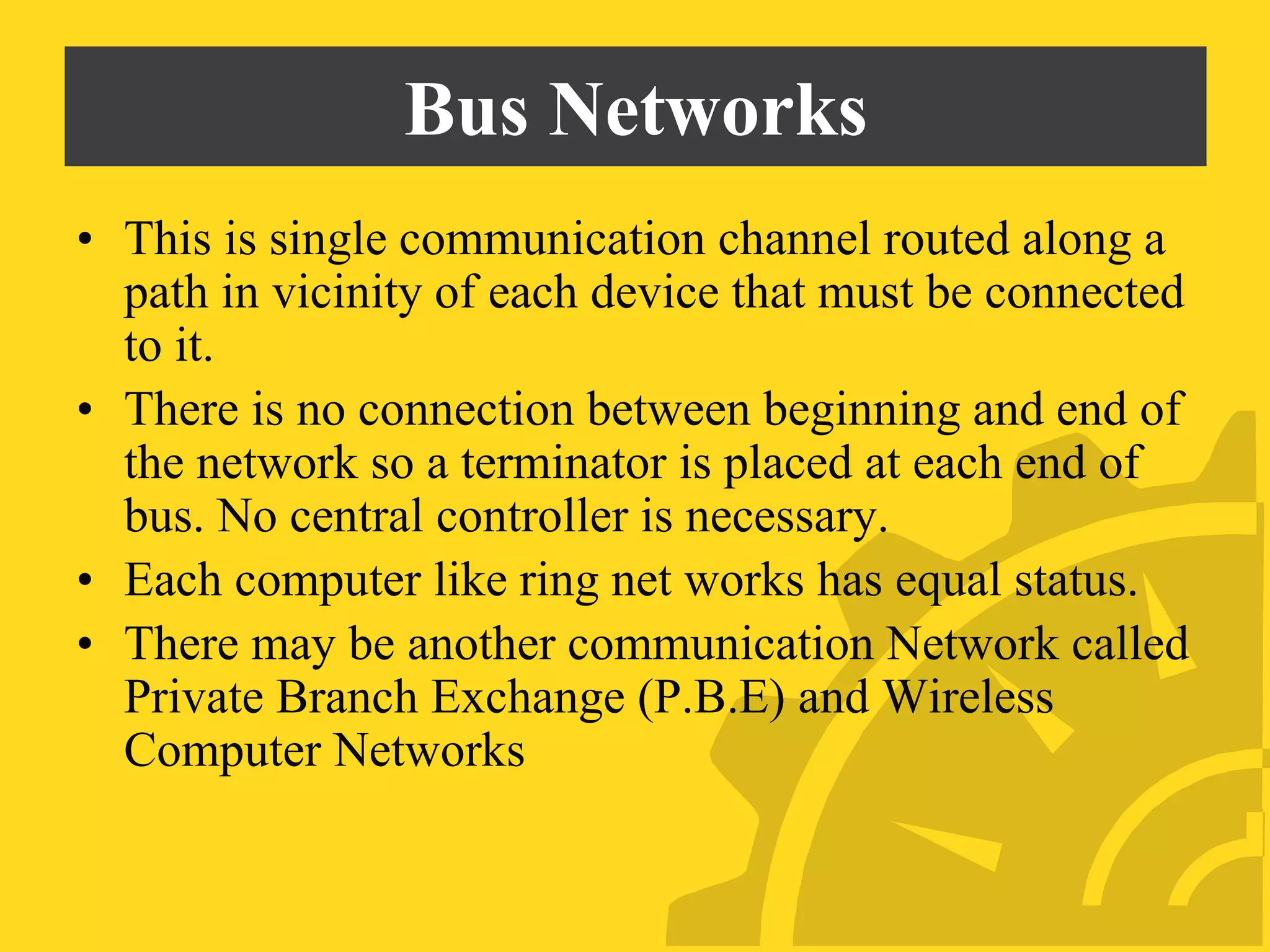
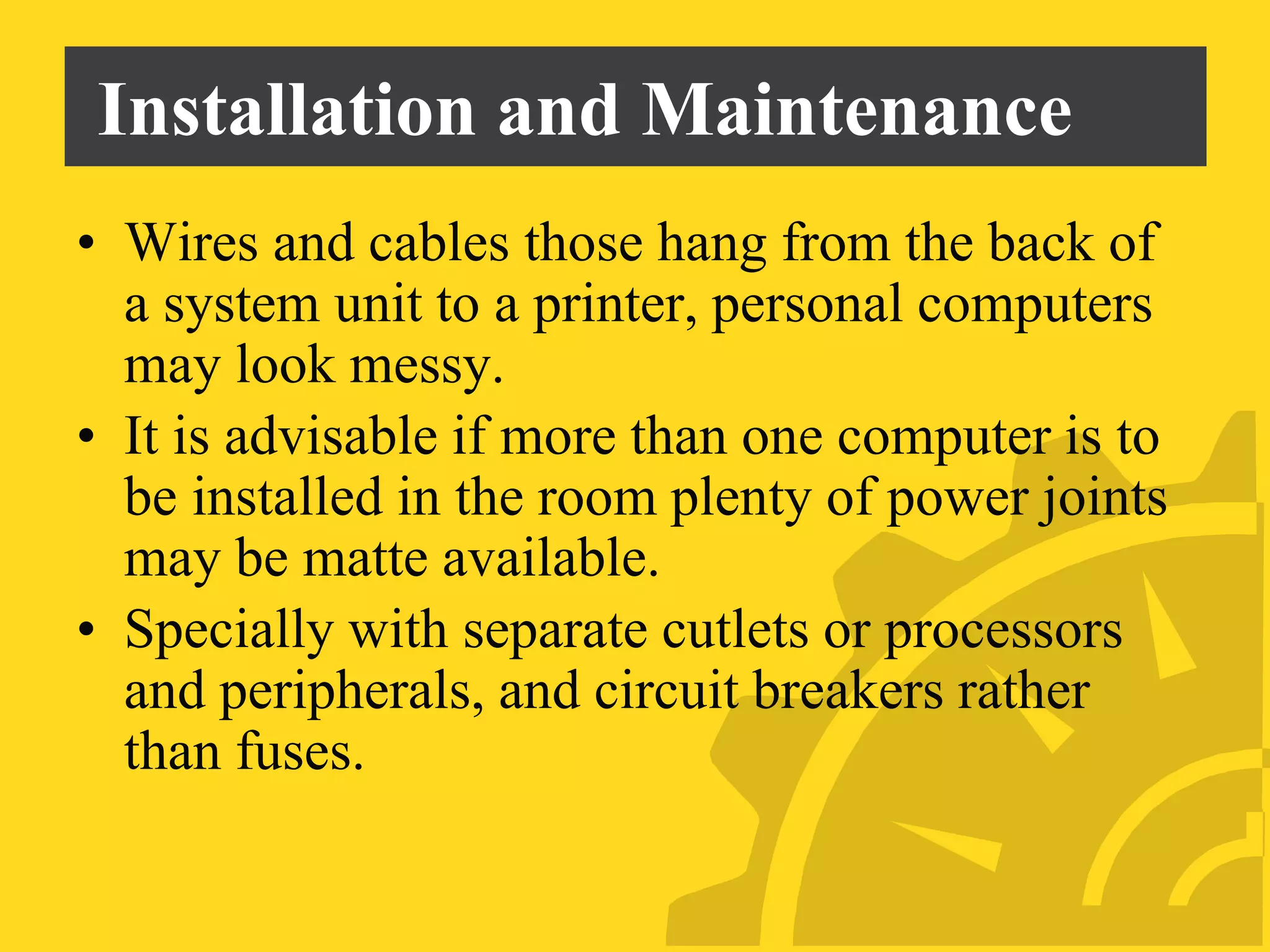
This document discusses several problems with using computers for education, including economic factors, lack of infrastructure, educational software, attitudes towards computers, and issues with installation, maintenance, planning, and teacher professional development. Some key challenges are the high costs of computers and software, lack of networking capabilities, scarcity of appropriate educational programs, and teachers' reluctance to adopt new technologies in the classroom. Effective implementation requires careful planning, training, and evaluation to maximize the educational benefits of computer use.