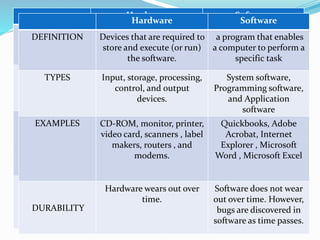
The document discusses the definitions and distinctions between software and hardware, highlighting various types of educational software and their applications. It categorizes software into system software, application software, and programming software, and details specific educational examples such as courseware and classroom management software. Guidelines for evaluating computer-based instructional materials are also provided, emphasizing the importance of instructional worth and pedagogical principles.