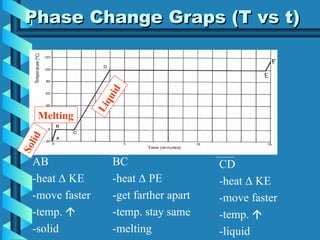
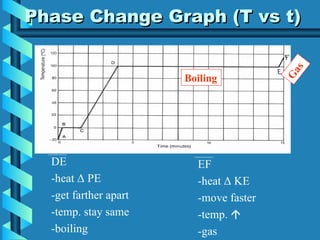
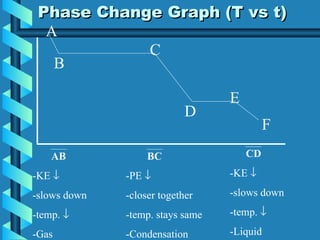
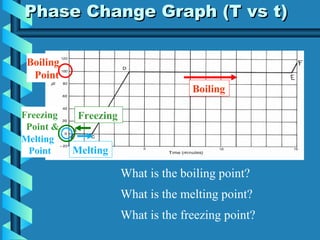
The document discusses phase changes in matter. It defines phase changes as changes of state that occur when energy is added to or removed from a substance, causing its temperature to remain constant. There are six types of phase changes: melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. Phase changes can be visualized through temperature vs. time graphs where the temperature plateaus during a change of state. Phase changes can also be classified as endothermic or exothermic depending on whether energy is absorbed or released during the change.