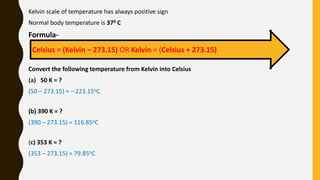
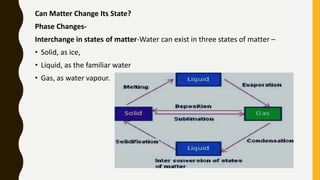
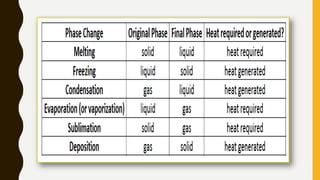
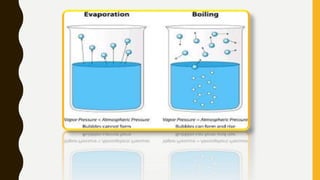
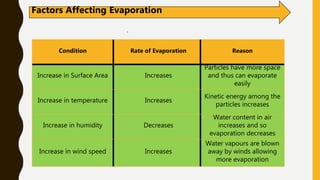
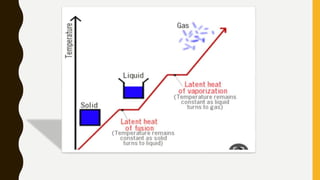
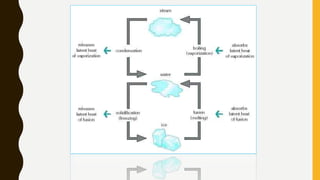
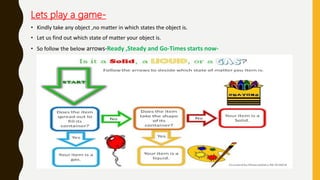
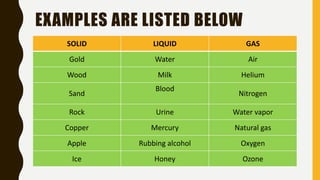
The document covers the states of matter, their properties, and phase changes such as melting, boiling, evaporation, and condensation. It explains temperature scales and provides formulas for temperature conversion between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Additionally, it discusses the factors affecting evaporation and thermal properties like latent heat of fusion and vaporization.






![TEMPERATURE SCALES
Celsius[°C] Fahrenheit[°F] Kelvin[K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-200514071011/85/MATTER-IN-OUR-SURROUNDING-10-320.jpg)