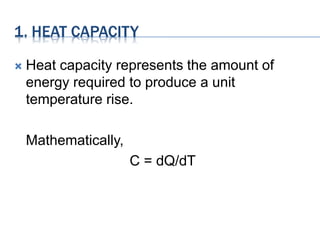
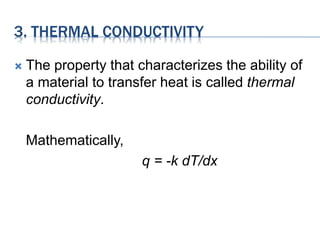
This document discusses several key thermal properties of materials: heat capacity, thermal expansion, thermal conductivity, and thermal stress. Heat capacity represents the amount of energy required to produce a temperature change in a material. Thermal expansion describes how the dimensions of a material change with increasing temperature. Thermal conductivity characterizes a material's ability to transfer heat. Thermal stress refers to stresses induced in a material due to changes in temperature. Each property is defined and its relationship to heat transfer is explained mathematically.