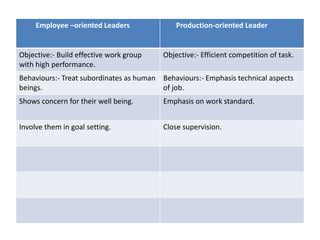
Unit-7 Leadership discusses different theories of leadership. The trait approach from the 1940s proposed that leaders are born with certain qualities like drive, integrity and confidence. However, traits alone do not distinguish effective vs ineffective leaders. Behavioural theories from the late 1940s examined what effective leaders do, focusing on consideration for subordinates and initiating structure. The Ohio and Michigan studies identified dimensions like concern for production vs employees. Contingency theory proposes there is no best leadership style and the situation affects which approach is most effective, like a task-focused leader in a routine situation. Fiedler's contingency theory matches leader and situational factors for effectiveness.