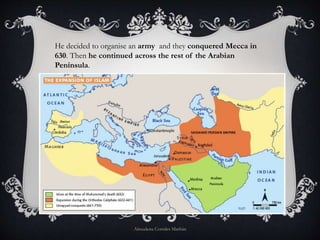
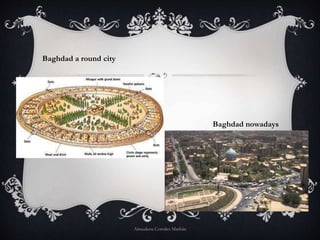
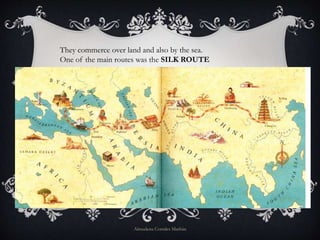
The document provides information on the origin and expansion of Islam. It began in the 7th century AD in the Arabian Peninsula under the prophet Muhammad. Muhammad and his followers fled from Mecca to Medina in 622 AD due to attacks, in an event known as the Hegira. After Muhammad's death, his successors continued conquering new territories across North Africa and the Middle East. One of the most significant Islamic empires was the Umayyad Caliphate, which established its capital in Damascus and expanded across the Iberian Peninsula to establish al-Andalus. The document also briefly outlines Islamic society, politics, economy, and urban layout during this period.