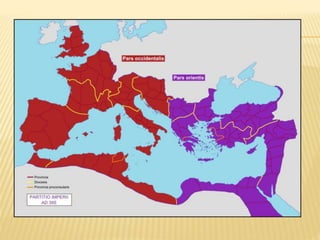
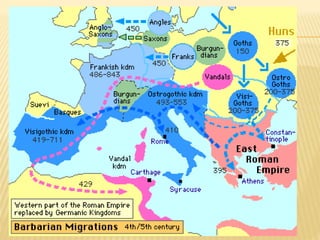
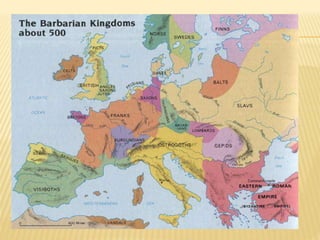
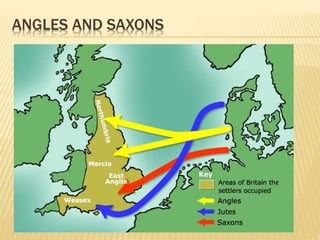
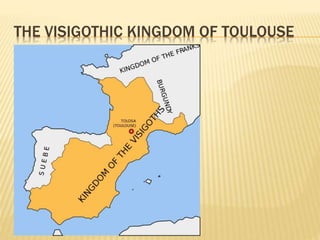
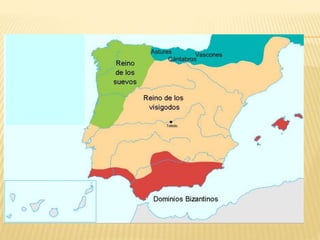
The document provides an overview of the early Middle Ages, focusing on the decline of the Roman Empire, the migrations of Germanic tribes, and the establishment of kingdoms such as the Visigoths in Toledo. It details the invasions of various tribes, the internal crises faced by the Roman Empire, and the eventual rise and fall of the Visigothic kingdom. Key cultural, economic, and societal changes during this period are also discussed, highlighting the transition from Roman rule to fragmented Germanic kingdoms.