Embed presentation
Downloaded 107 times
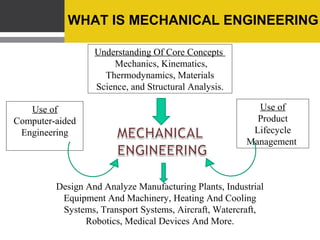







Mechanical engineering involves understanding core concepts in mechanics, kinematics, thermodynamics, and materials science to design and analyze machines, systems, and tools. Mechanical engineers work in diverse fields like manufacturing, aerospace, robotics, biomechanics and more. Some examples of mechanical engineering include bicycles, CD players, snowmobiles, and video game consoles. Emerging areas include micro electromechanical systems, nanotechnology, composite materials, and robotics. With a degree in mechanical engineering, one can pursue career paths in automobile, manufacturing, aerospace, energy and other industries.









