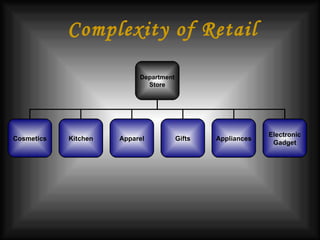
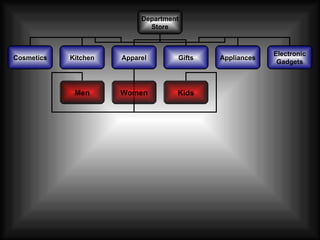
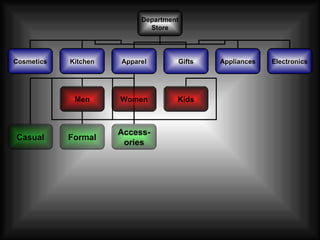
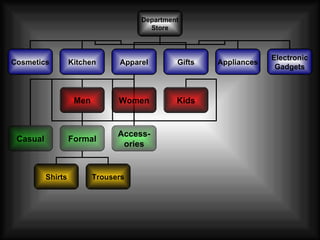
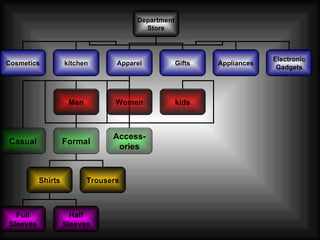
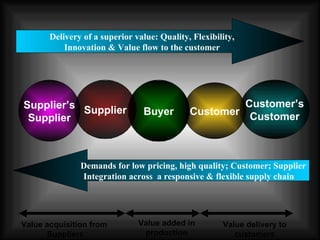
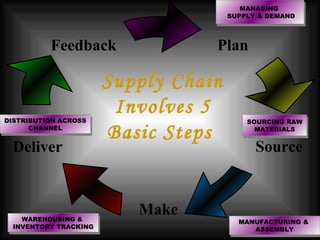
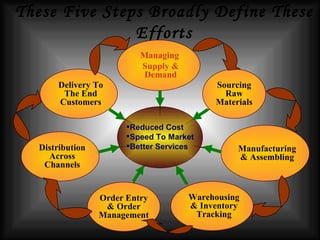
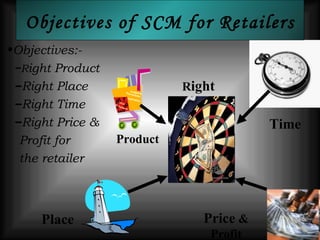
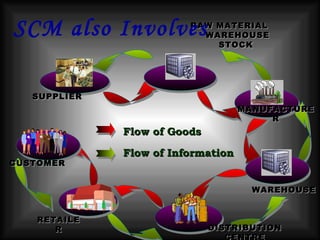
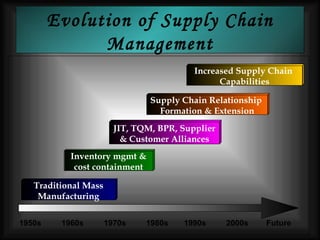
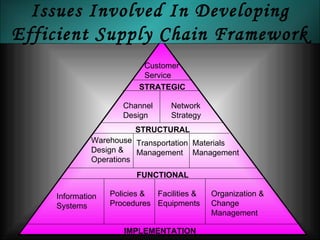
The document discusses supply chain management in the retail industry. It provides an overview of supply chain management concepts, including the key steps of sourcing, manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, and delivery to customers. It also outlines the need for supply chain management due to increasing complexity, costs, and competition in retailing. Finally, it briefly discusses the evolution of supply chain management approaches over time and some of the issues involved in developing an efficient supply chain framework.