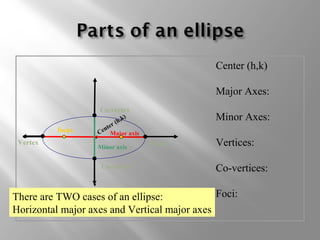
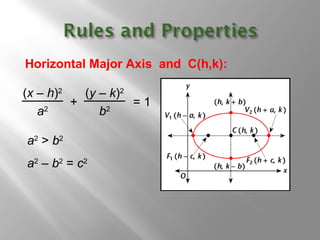
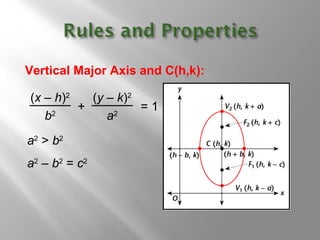
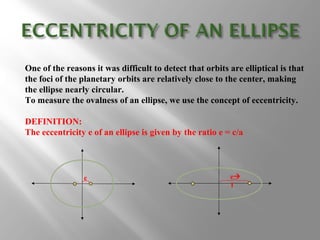
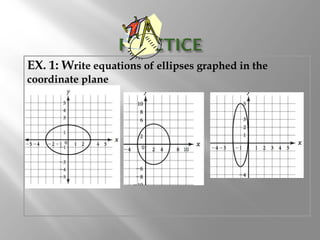
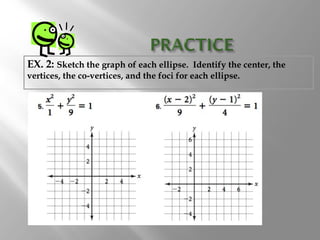
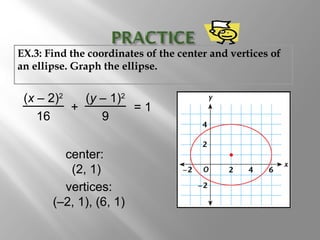
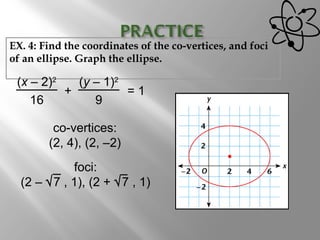
An ellipse is a curve where the sum of the distances from two fixed points (foci) is a constant. It is defined by the equation (x-h)2/a2 + (y-k)2/b2 = 1, where a and b are the lengths of the semi-major and semi-minor axes. The eccentricity e = c/a measures how oval the ellipse is, with a circle being e = 0 and e approaching 1 being very oval. Examples show how to graph ellipses from equations in standard form and identify features like foci, vertices, and co-vertices.