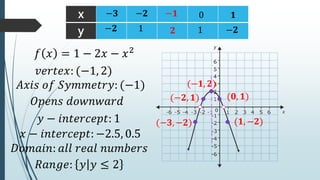
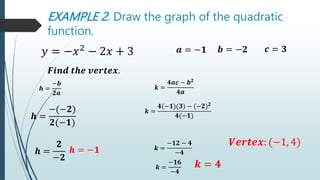
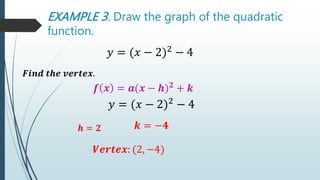
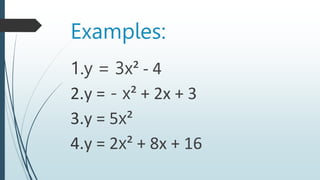This document discusses quadratic functions and their graphs. It defines key features of quadratic graphs including the vertex, axis of symmetry, and effect of coefficients on the opening of the parabola. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to identify these features from the equation, generate tables of values, and graph the quadratic function. Learning targets are outlined to draw and analyze quadratic graphs and the effect of changing coefficients on the graph.