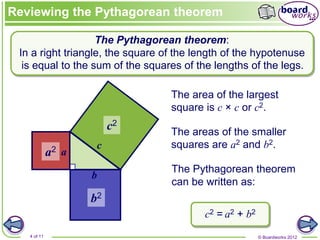
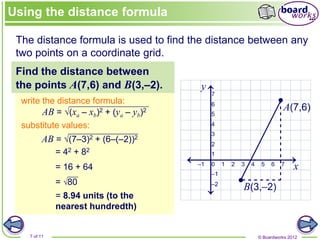
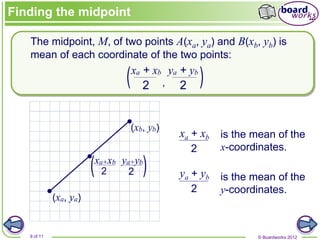
The document discusses the Cartesian coordinate system and formulas for distance, midpoint, and solving for unknown points given other point information. It provides examples of using the distance formula to calculate the distance between two points, finding the midpoint of a line segment using the average of the x- and y-coordinates, and solving for the coordinates of an unknown point if given the midpoint and one other point.